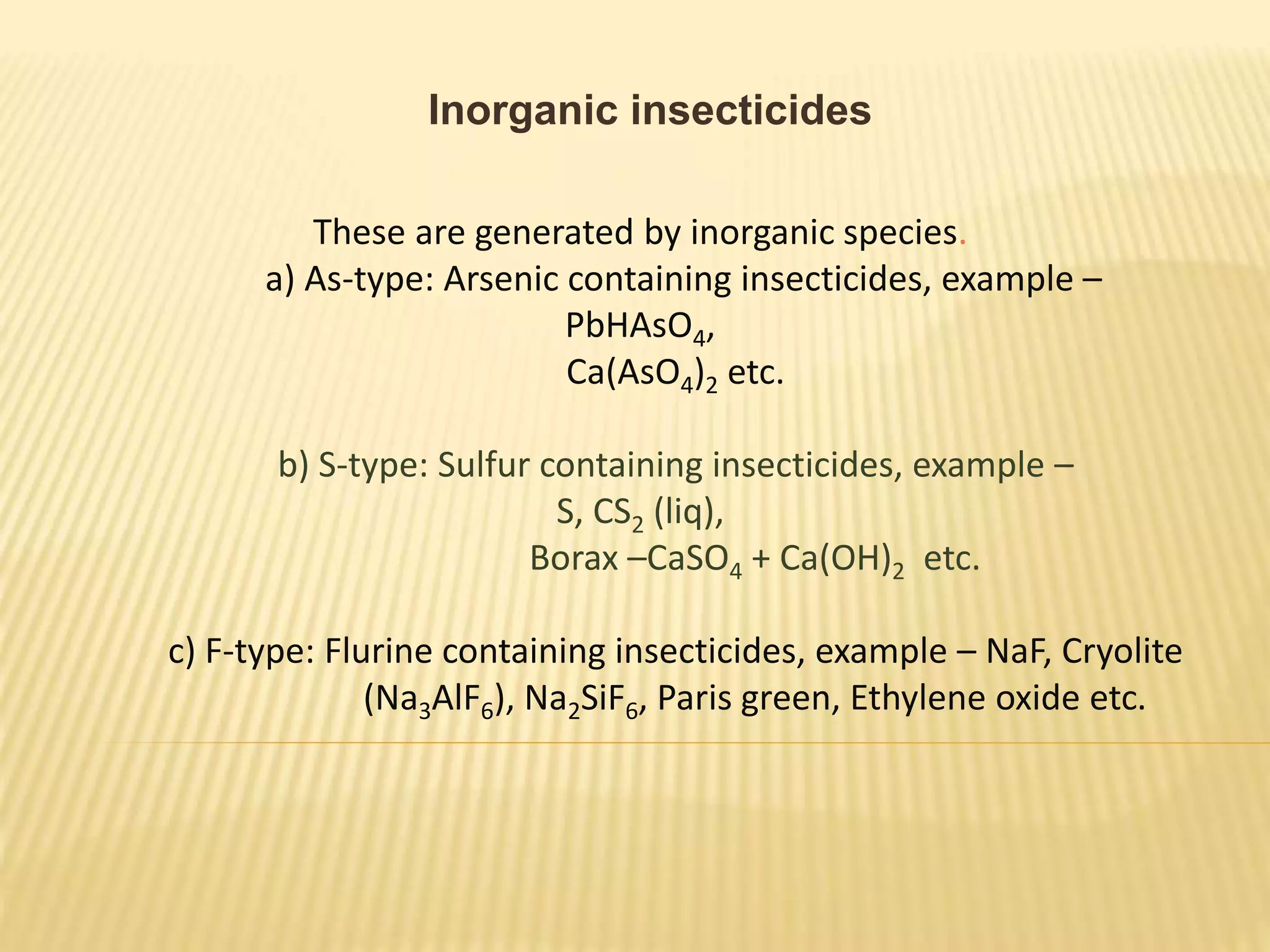
This presentation discusses agrochemicals and pesticides. It defines agrochemicals as chemical products used in agriculture, and pesticides as substances used to eradicate pests. Pesticides are classified according to their mode of action and chemicals. Insecticides are substances used to kill insects, and are classified as systemic or contact based on activity, and inorganic or organic based on chemical nature. The presentation notes the first use of synthetic pesticides in 1940 and their environmental impacts like air, water, and soil pollution.