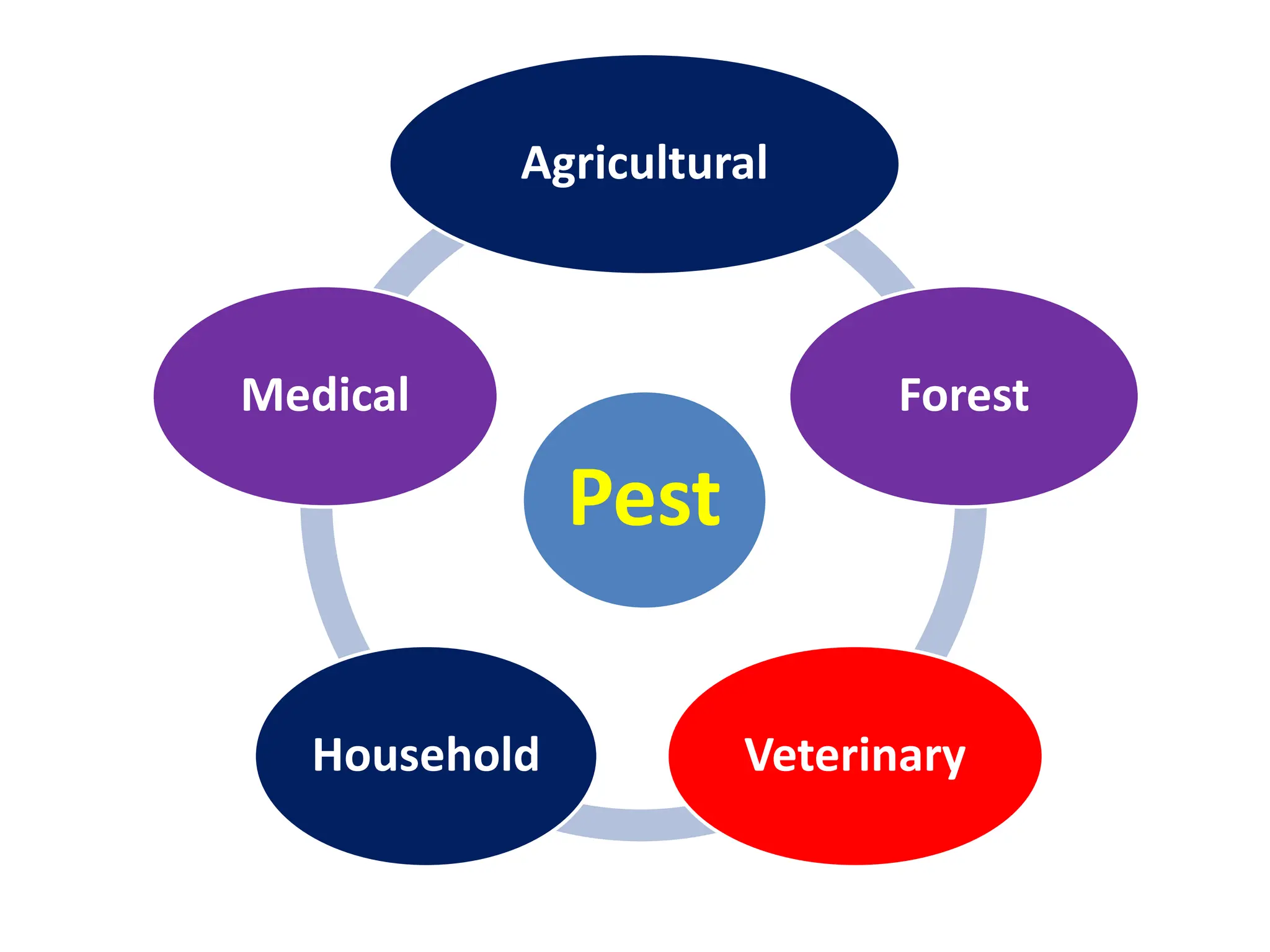
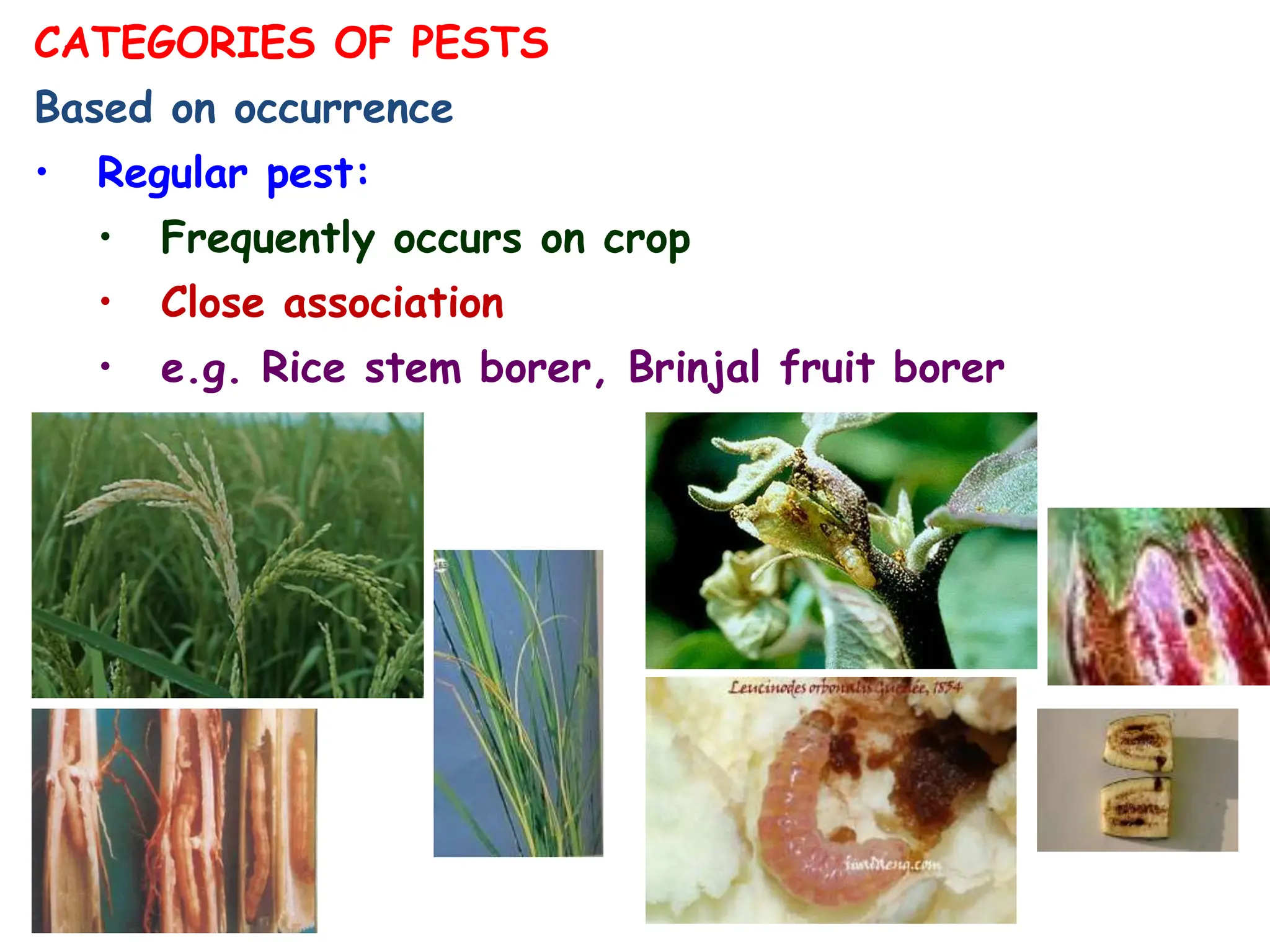
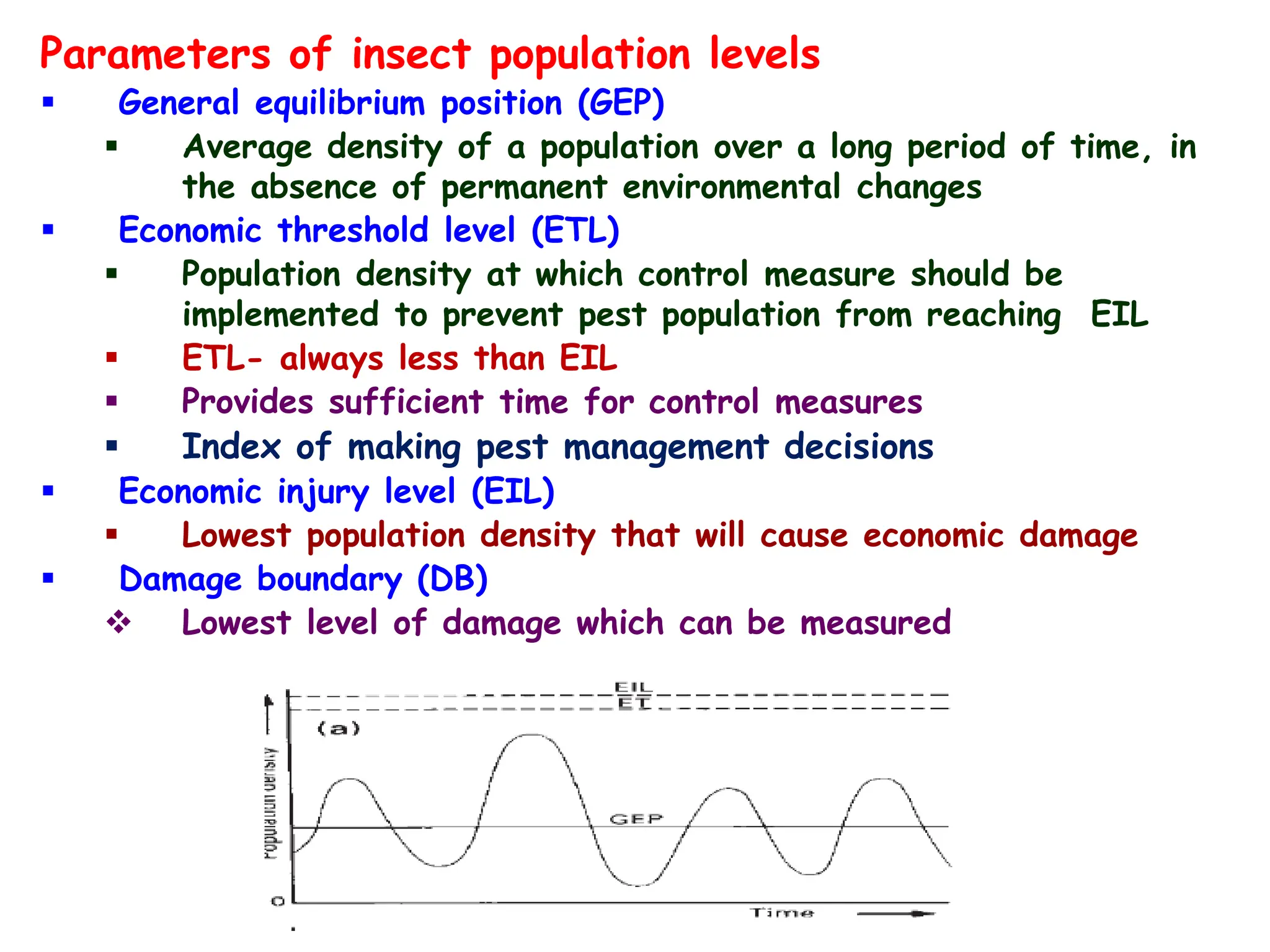
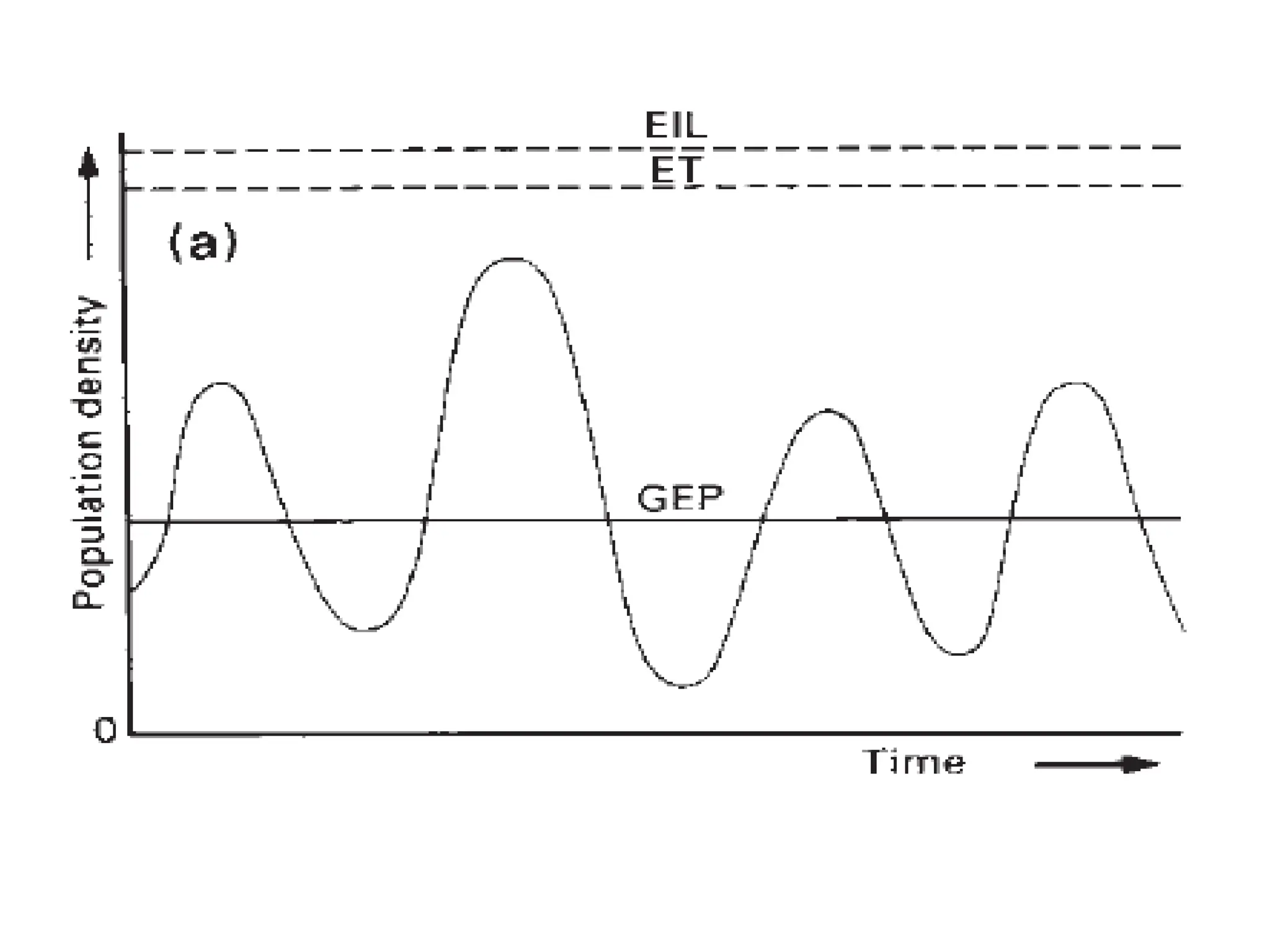
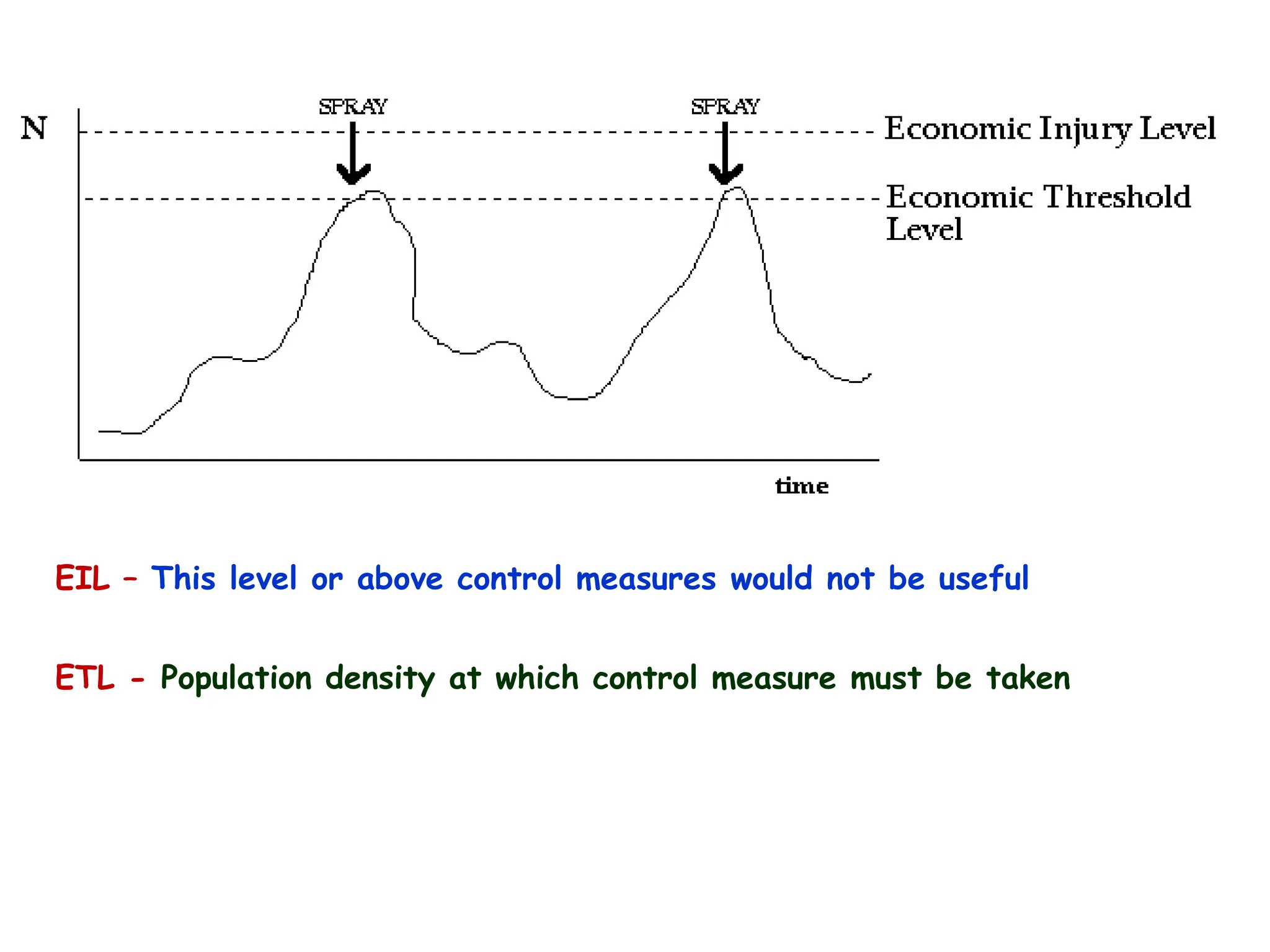
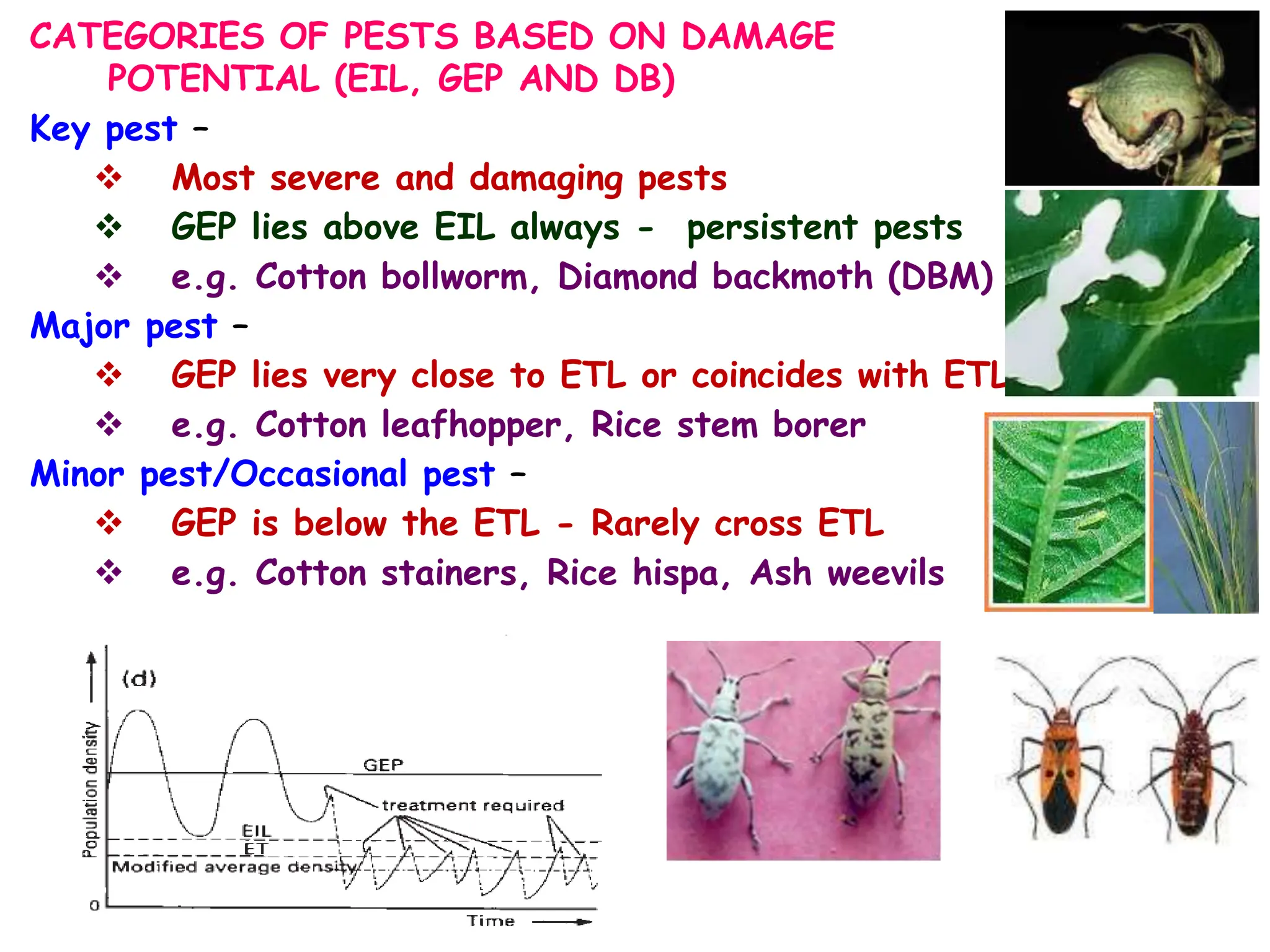
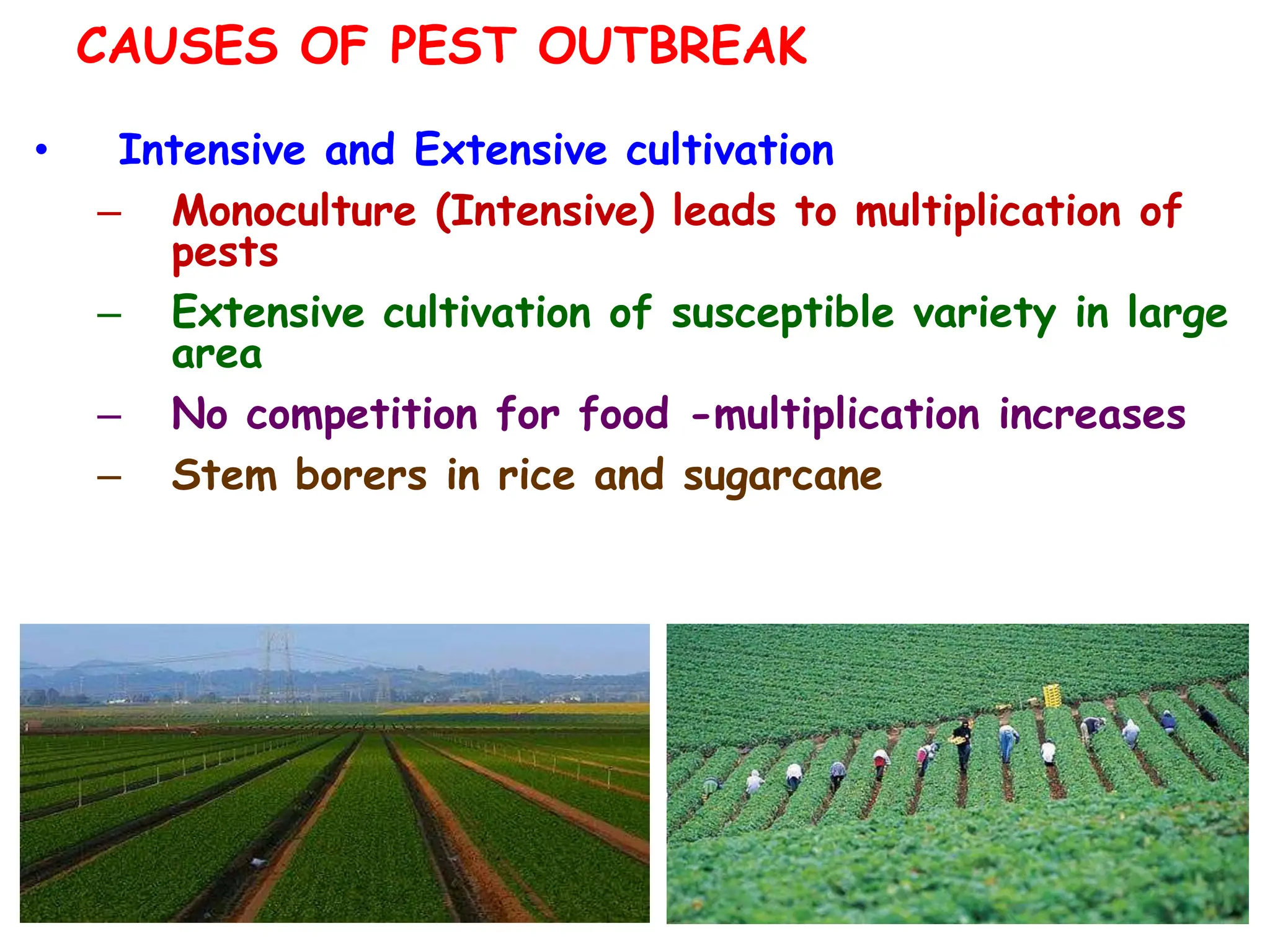
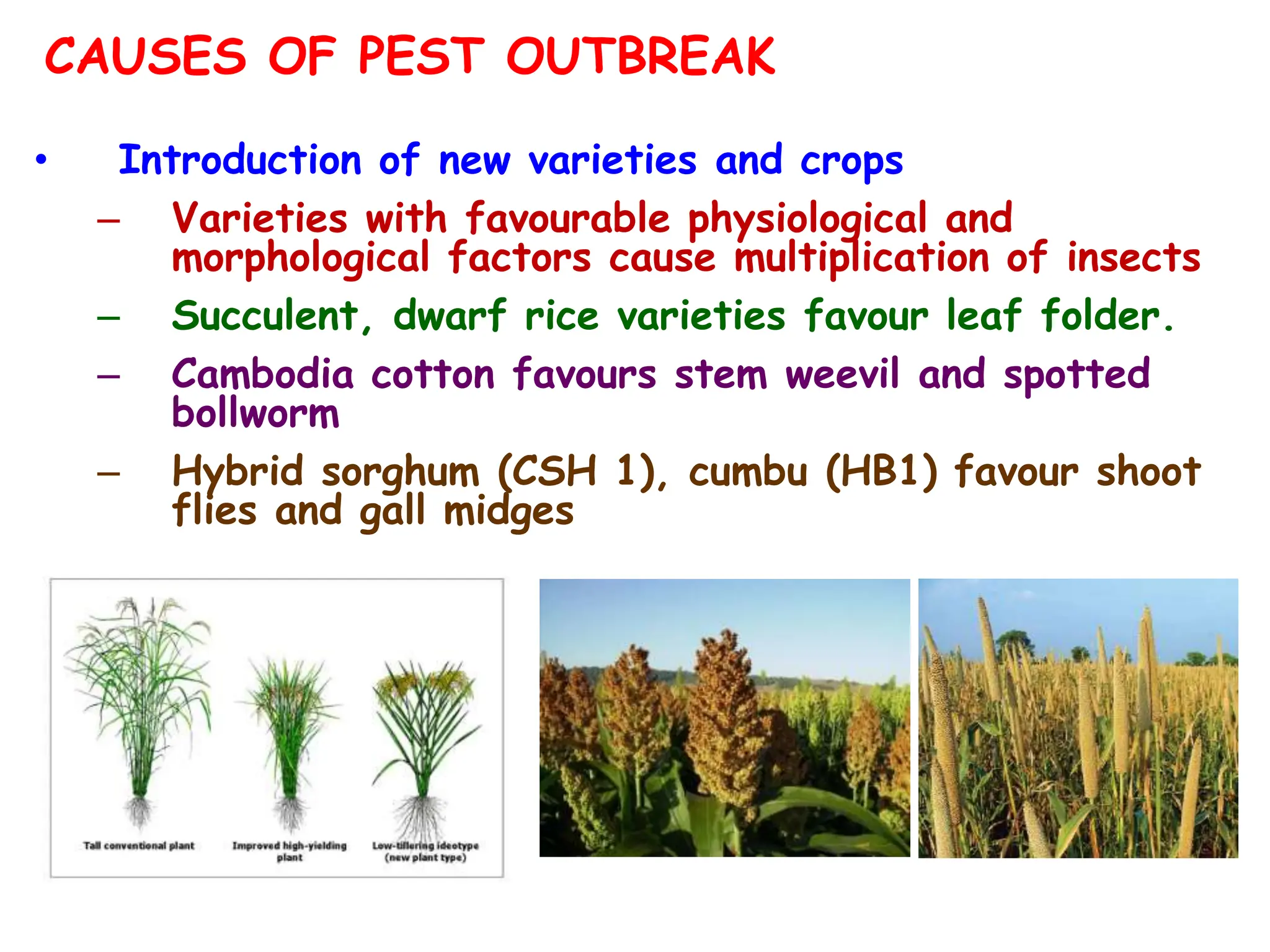
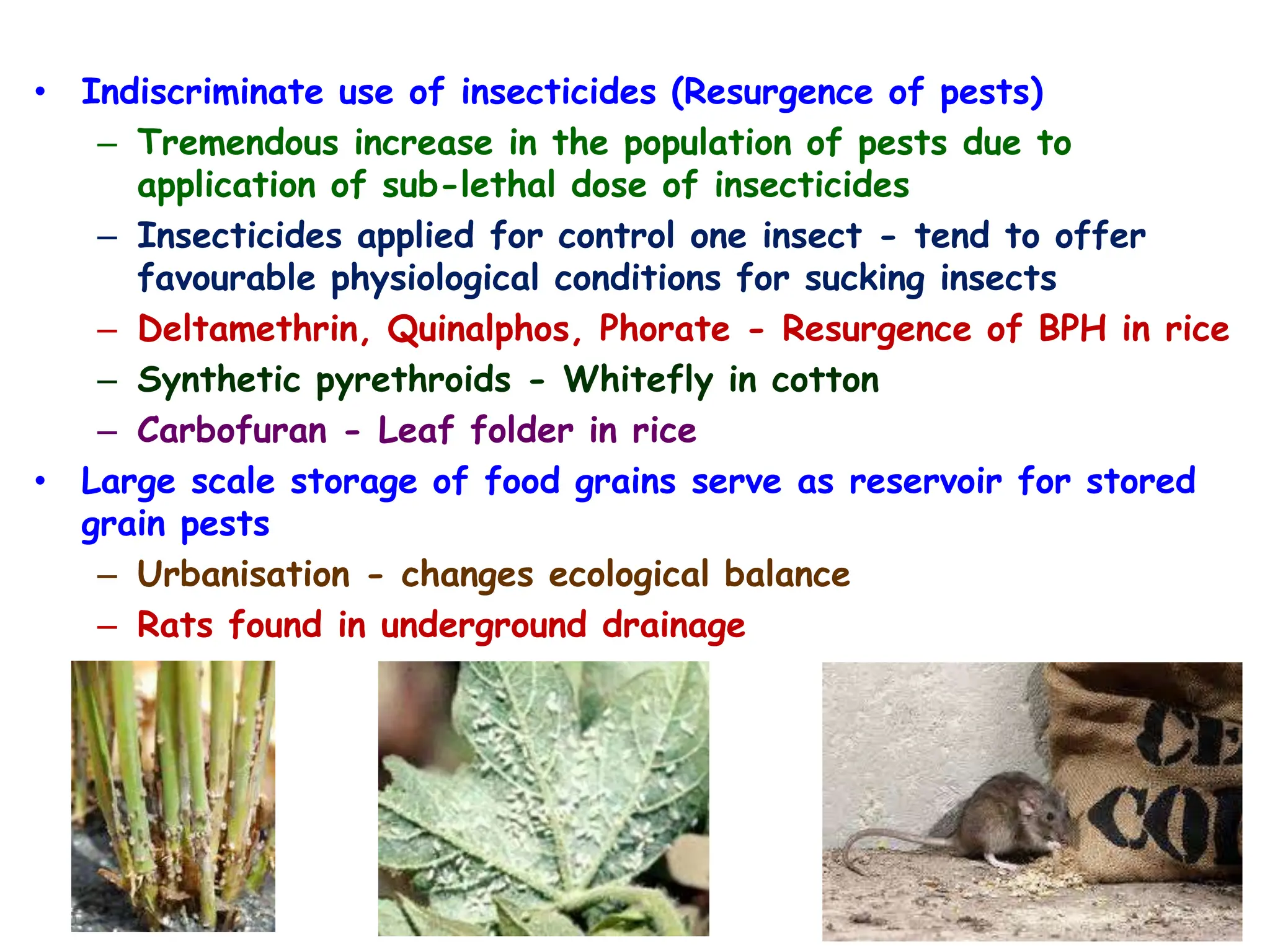
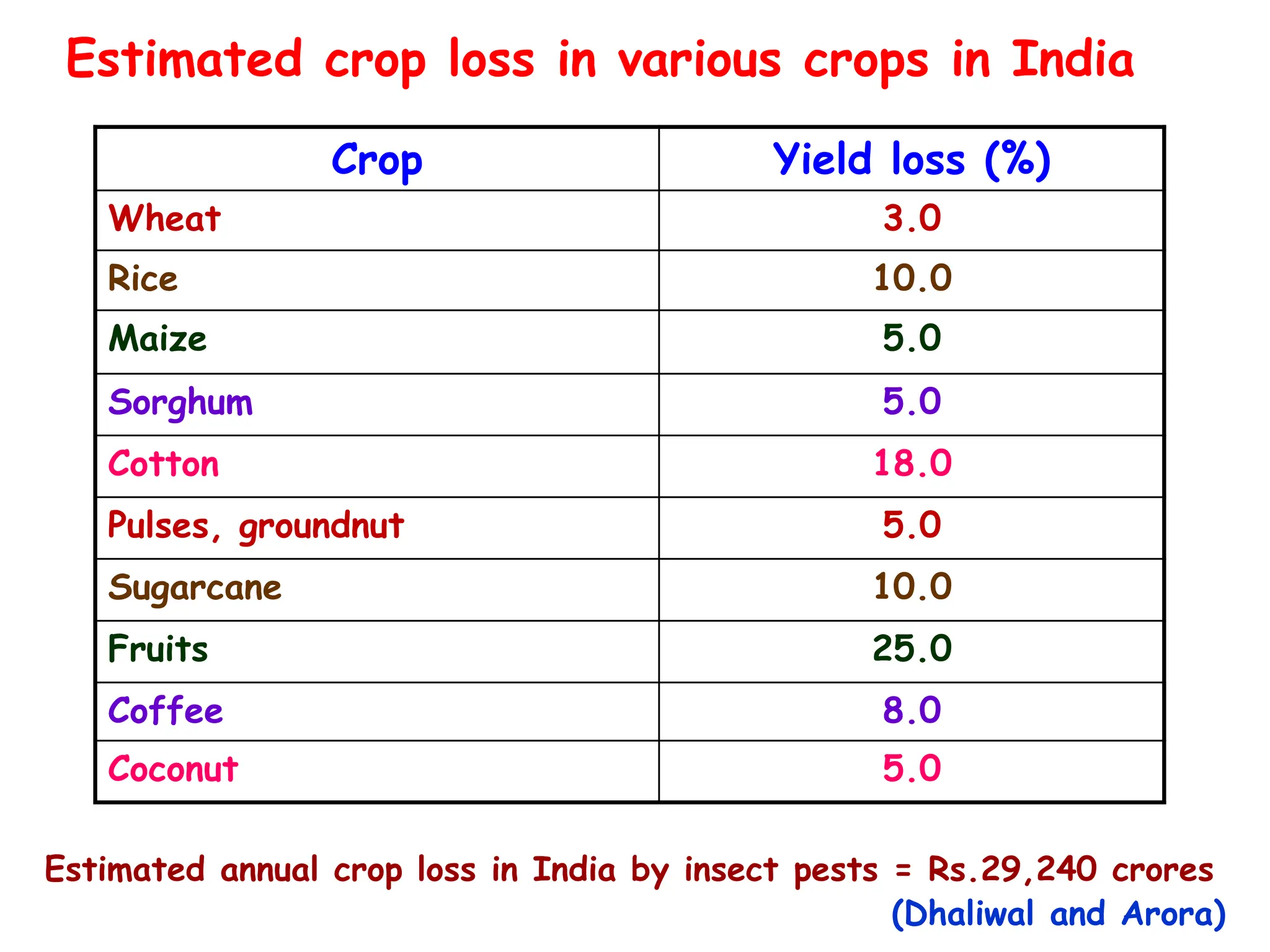
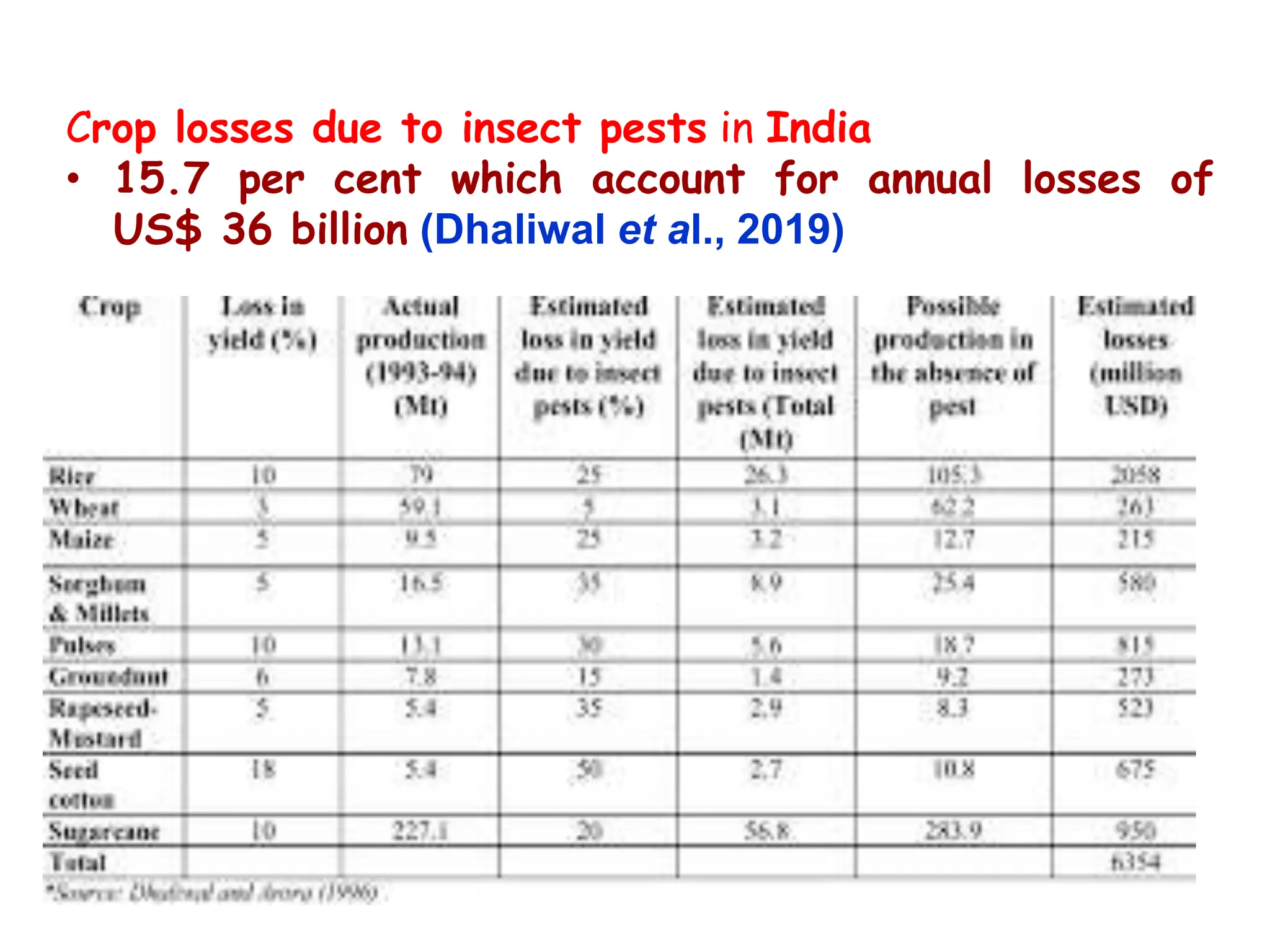
This document discusses definitions of pests and categories of pests. It defines pests as organisms that harm humans, agriculture, or property. Pests are categorized based on occurrence, level of infestation, host plants, and damage potential. Key causes of pest outbreaks are discussed as deforestation, destruction of natural enemies, monoculture practices, introduction of new crops/varieties, and indiscriminate pesticide use. The document estimates that insect pests cause annual crop losses of Rs. 29,240 crores in India, or 15.7% of total production.