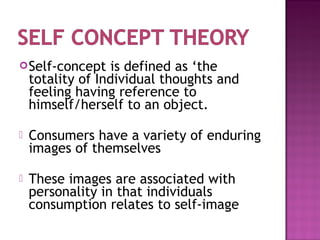
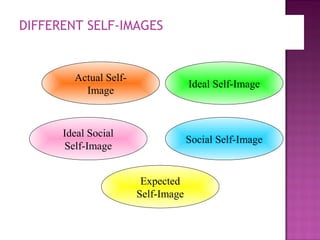
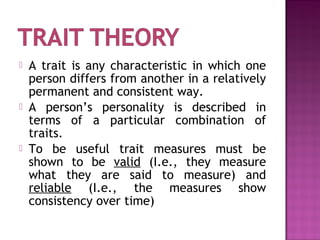
Personality refers to characteristics patterns of behavior and thinking that determine how a person adjusts to their environment. It includes internal and external traits that are relatively stable but can be both inherited and shaped. Personality theories include psychoanalytic theory, which views personality as consisting of the id, ego and superego; trait theory, which describes personality in terms of combinations of traits; and self-concept theory, which refers to a person's total thoughts and feelings about themselves. Marketers aim to appeal to consumers' self-images through advertising.