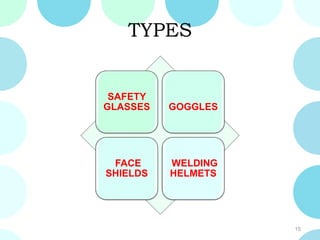
This document discusses personal protective equipment (PPE) and focuses on eye and face protection. It notes that nearly 2 million people receive disabling work injuries each year, with over a quarter involving the head, eyes, hands or feet. PPE is designed to protect workers from hazards like chemicals, radiation, impacts and more. The document outlines OSHA standards for employers to assess hazards, provide necessary PPE and training. It details types of eye and face protection like safety glasses, goggles, face shields and welding helmets and notes criteria for selecting the right protection for specific hazards.