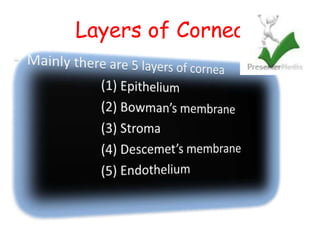
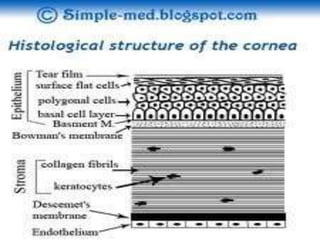
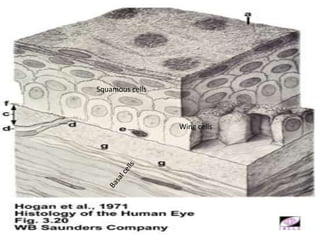
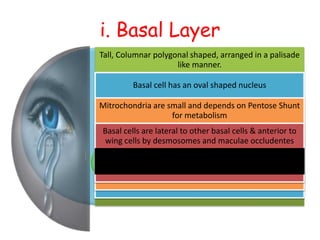
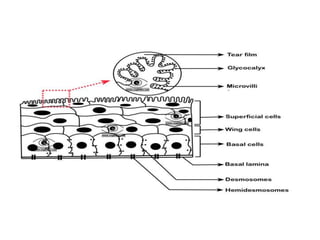
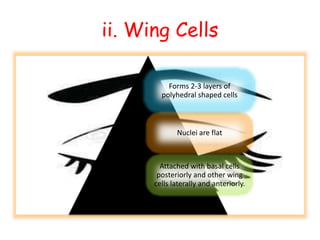
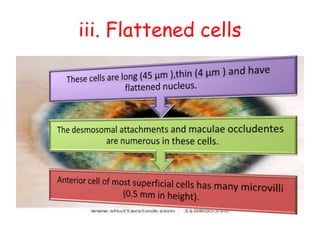
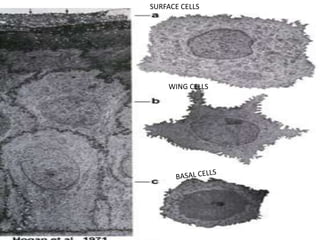
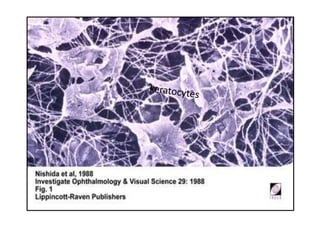
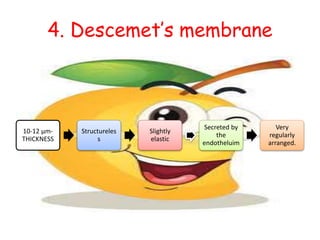
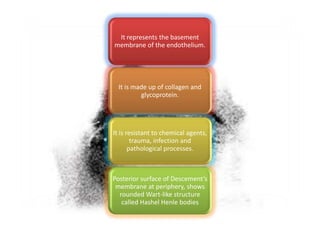
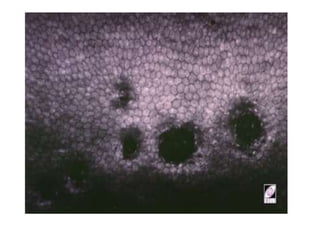
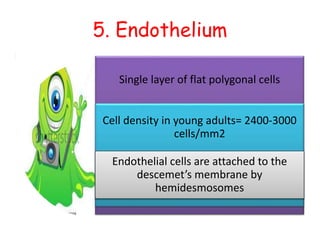
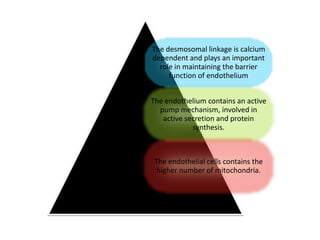
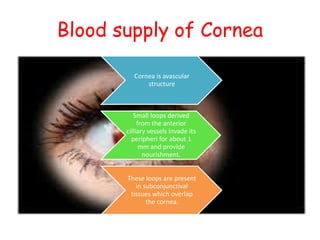
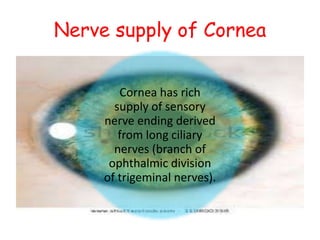
The cornea is the transparent outer coat of the eye. It has 5 layers - epithelium, Bowman's membrane, stroma, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The stroma makes up around 90% of the corneal thickness and contains collagen fibrils and keratocytes. The cornea is avascular but receives nutrients from blood vessels in the surrounding tissues. It has sensory innervation from the trigeminal nerve but lacks blood vessels in its central region to maintain transparency.