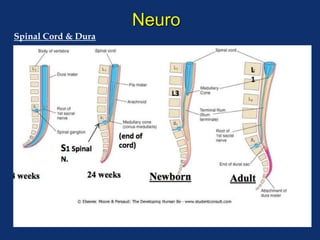
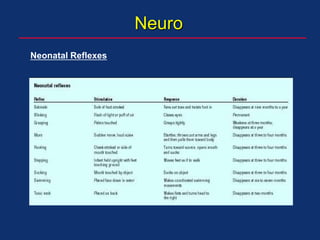
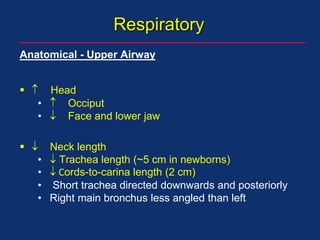
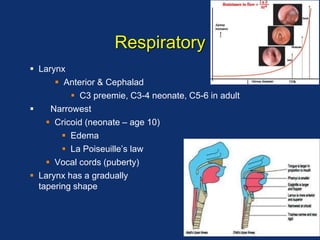
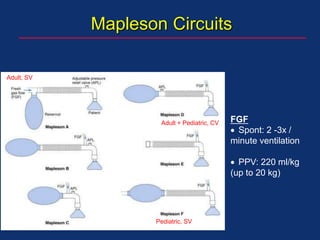
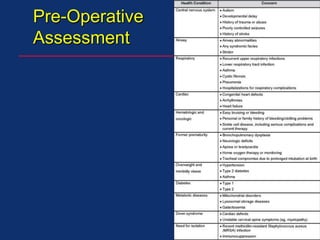
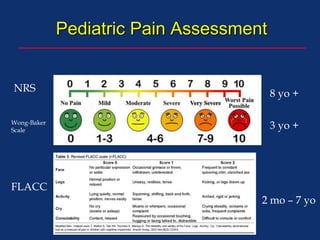
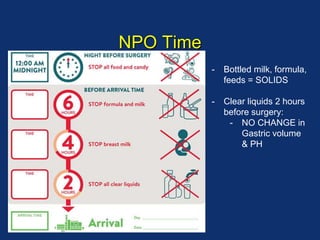
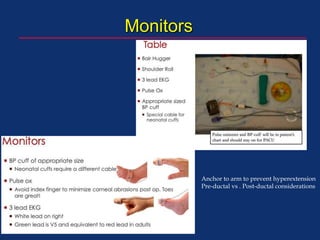
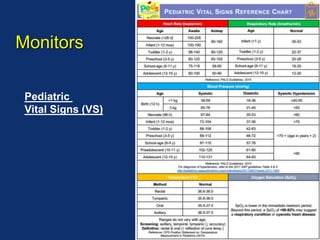
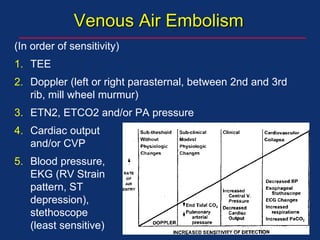
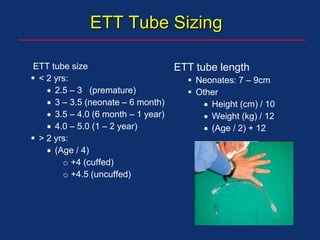
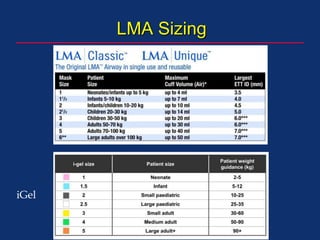
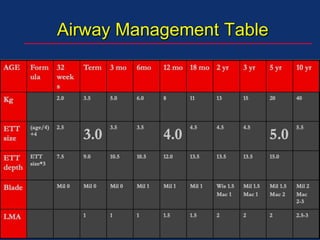
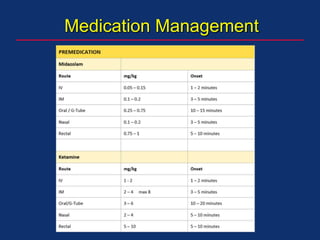
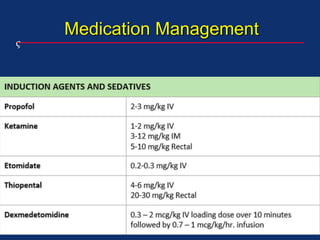
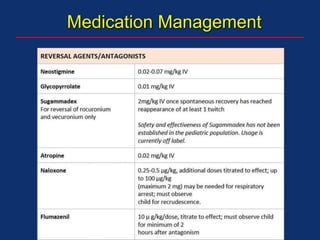
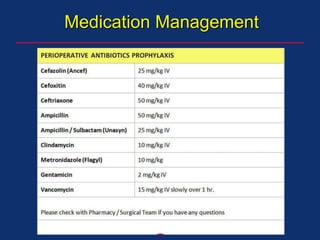
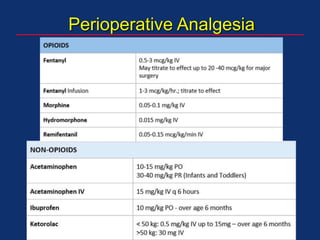
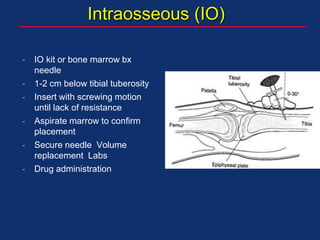
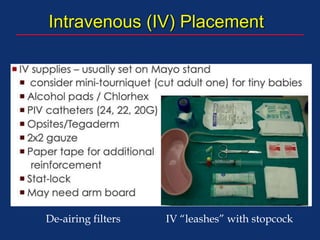
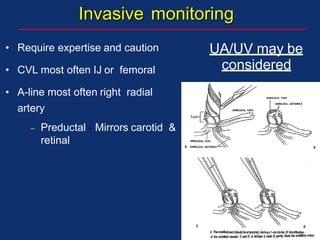
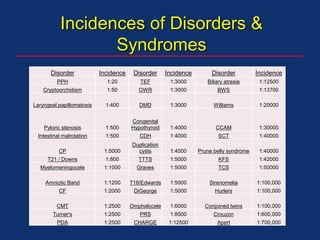
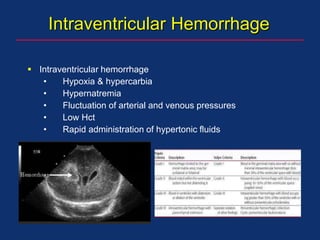
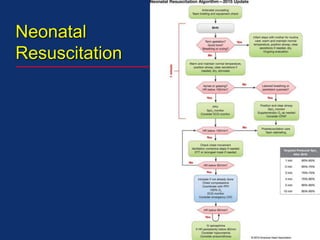
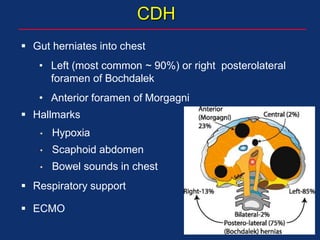
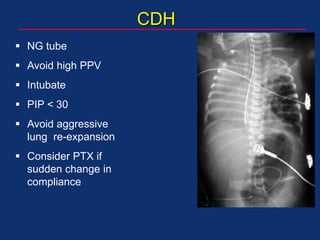
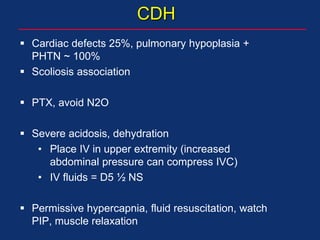
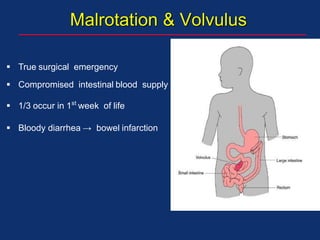
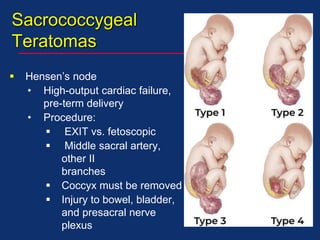
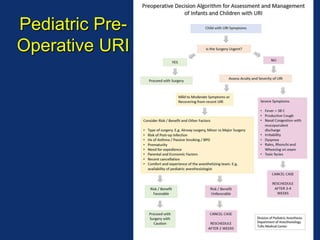
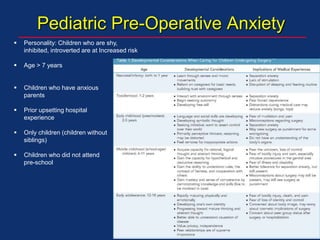
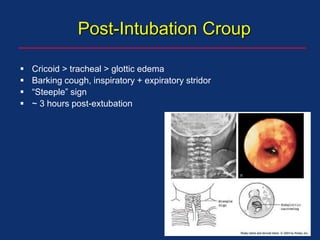
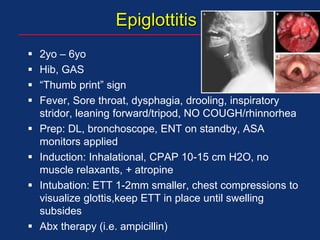
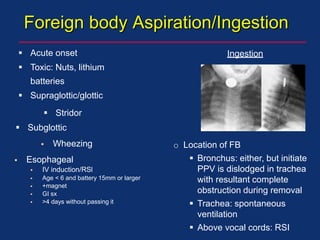
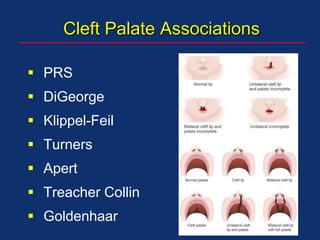
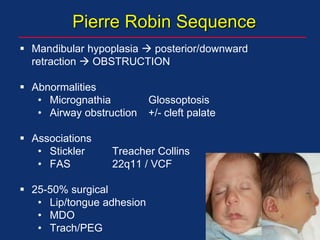
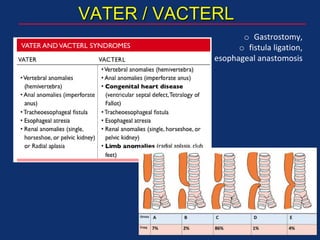
The document discusses pediatric anesthesia, covering essential topics such as anesthetic management for infants and children, pre-operative assessment, and physiological differences between neonates and adults. It includes specific guidelines related to airway management, drug dosing, fluid replacement, and post-operative care in children. Additionally, the document references various neonatal emergencies and conditions that require specialized care.