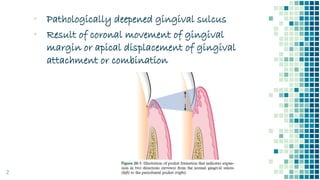
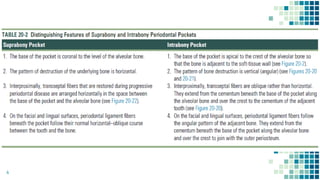
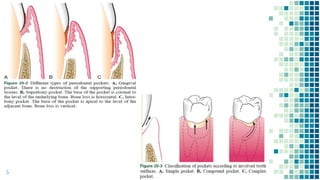
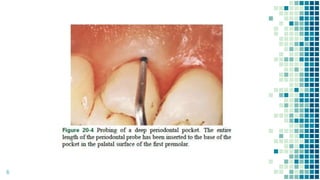
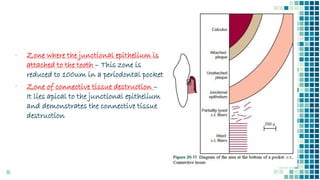
The document discusses periodontal pockets, which are pathologically deepened gingival sulci resulting from the displacement of the gingival margin or attachment. It outlines the types, formation mechanisms, clinical features, and implications for periodontal health, emphasizing the role of bacteria, inflammation, and tissue destruction. Additionally, it highlights the significance of understanding the etiopathogenesis of periodontal pockets for effective diagnosis and treatment planning.