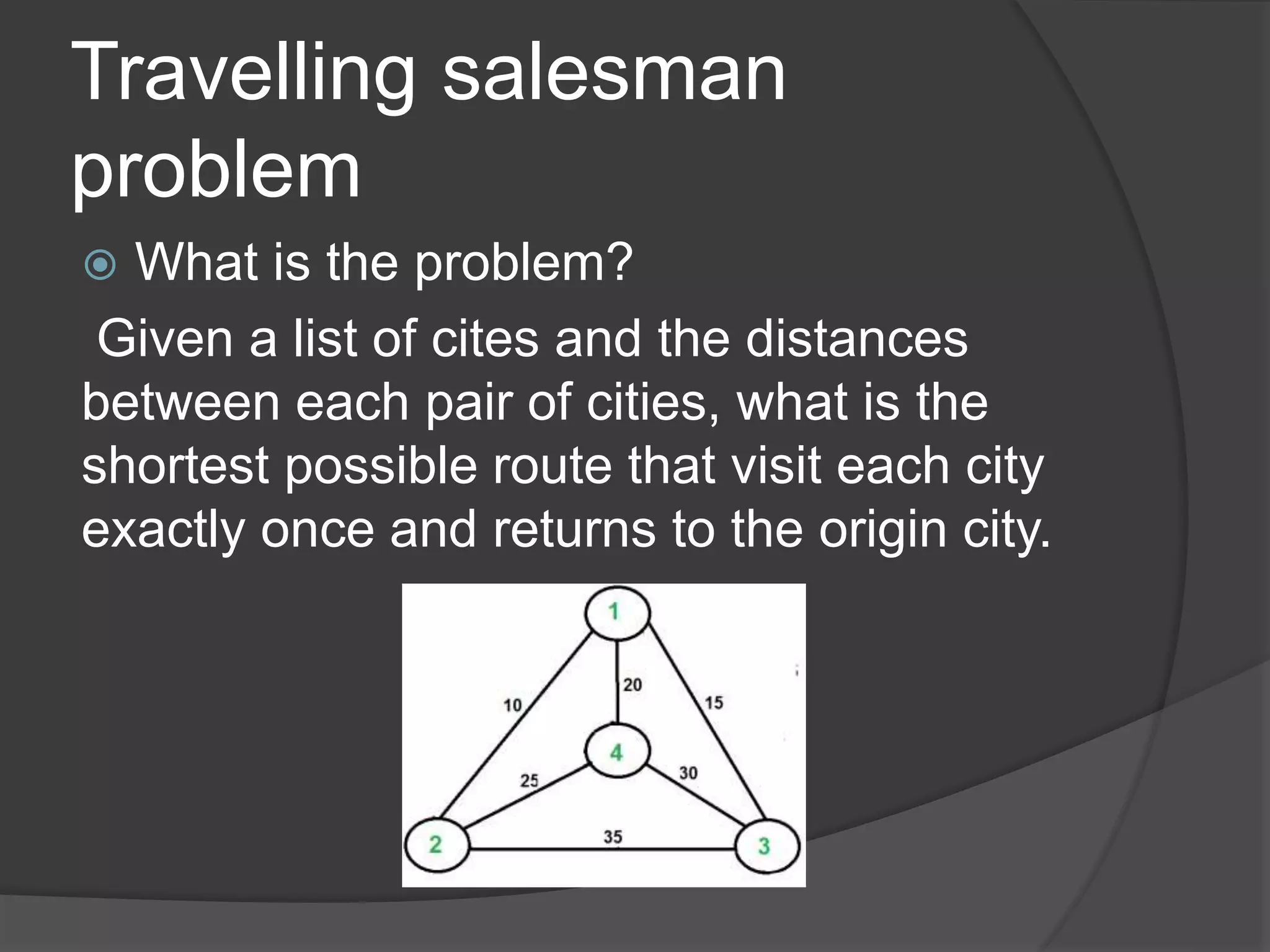
This document discusses methods for solving the travelling salesman problem, specifically focusing on the Hungarian method. It provides an overview of the travelling salesman problem and describes several algorithms to solve it, including genetic algorithms, branch and bound, and dynamic programming. It then explains the Hungarian method in more detail, outlining the algorithm's steps to find an optimal assignment with minimum cost by drawing lines through rows and columns to cover zero entries in the cost matrix. The advantages of the Hungarian method for solving travelling salesman problems are highlighted, along with its time complexity of O(n^3).