This document provides an overview of the Government Securities Market (GSM) in India. It discusses:
- What government securities are and how they are issued by the government to fund its activities.
- The key types of government securities including treasury bills, cash management bills, treasury notes, bonds, and zero coupon bonds.
- The major holders of government securities like commercial banks, insurance companies, and the Reserve Bank of India.
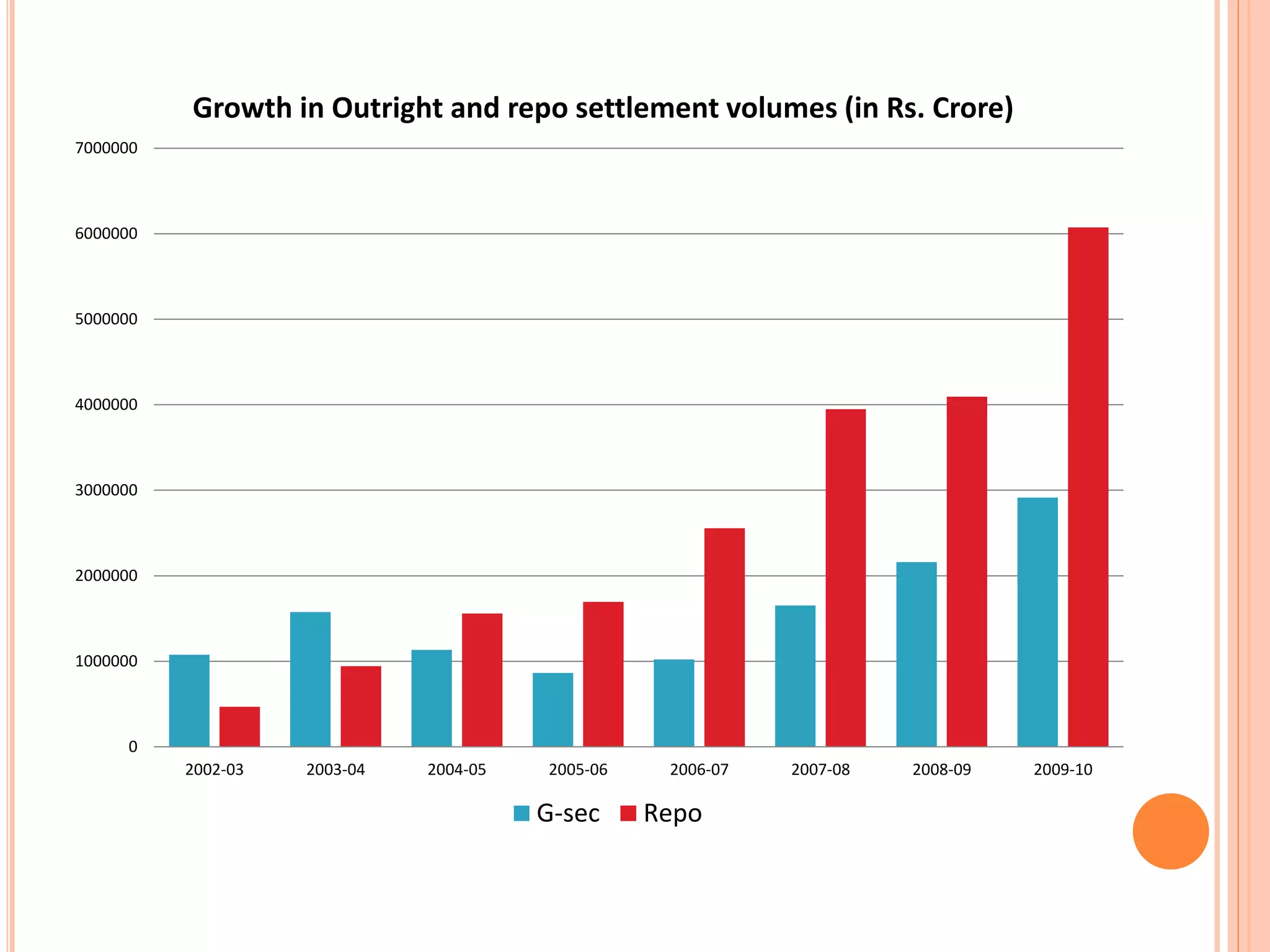
- The strengths of the GSM like its large size, well-regulated primary dealers, and sound depository system.
- Some weaknesses like potential for fiscal dominance outpacing demand and a skewed investor base.