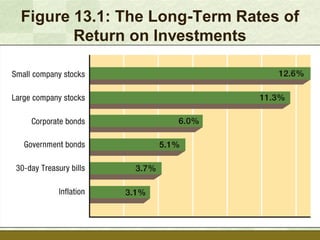
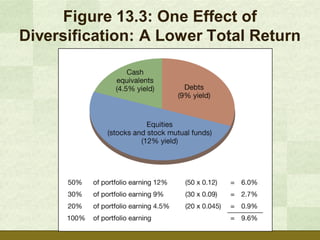
The document discusses various ways that people invest, including putting money into stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. It outlines reasons for investing such as financial goals, income, wealth, and retirement. Key aspects of investing covered include having a budget and savings plan, establishing investment goals, understanding returns, risks, and diversification. The document provides strategies for long-term investing like asset allocation, dollar cost averaging, and following golden rules of fundamentals.