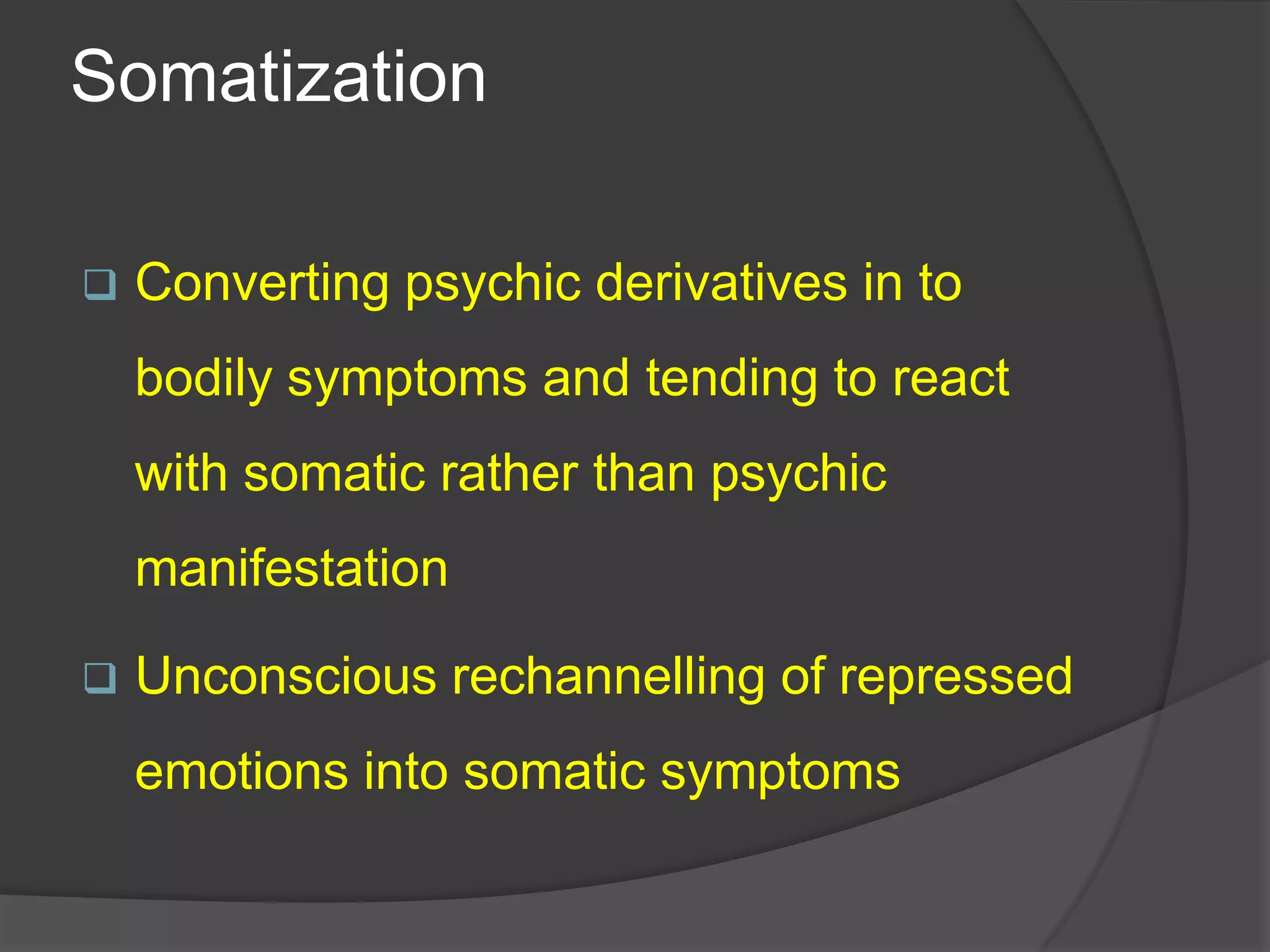
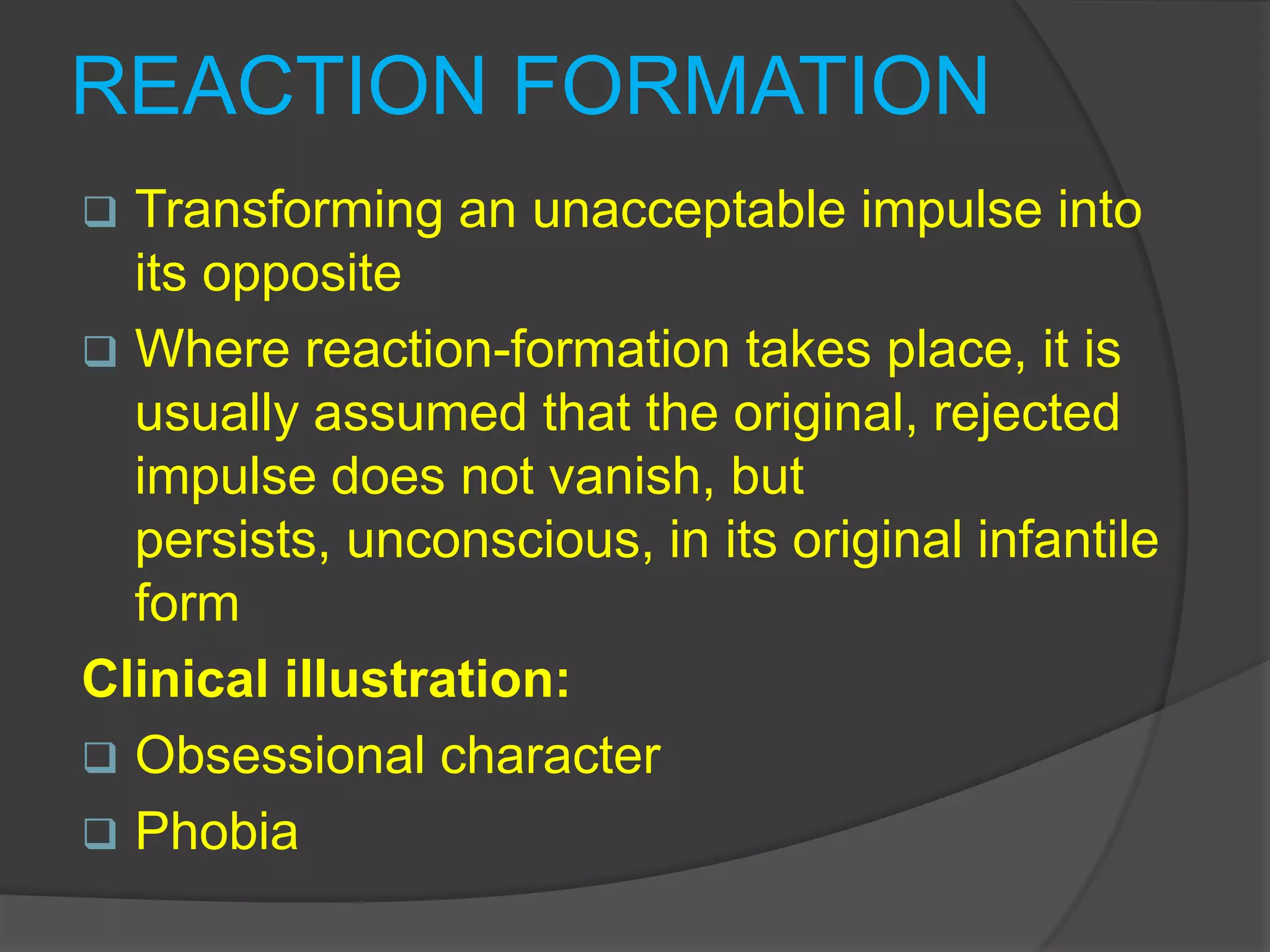
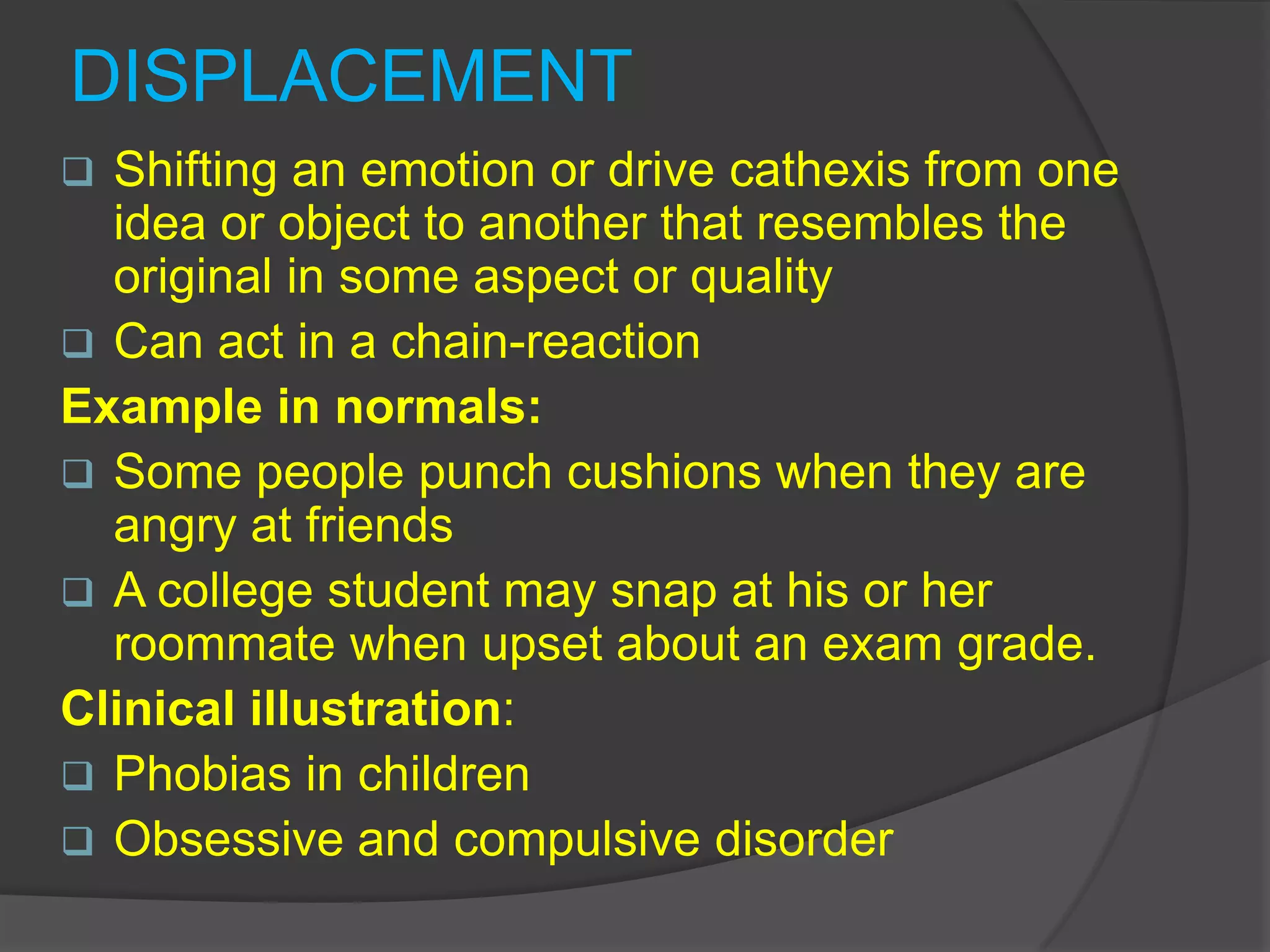
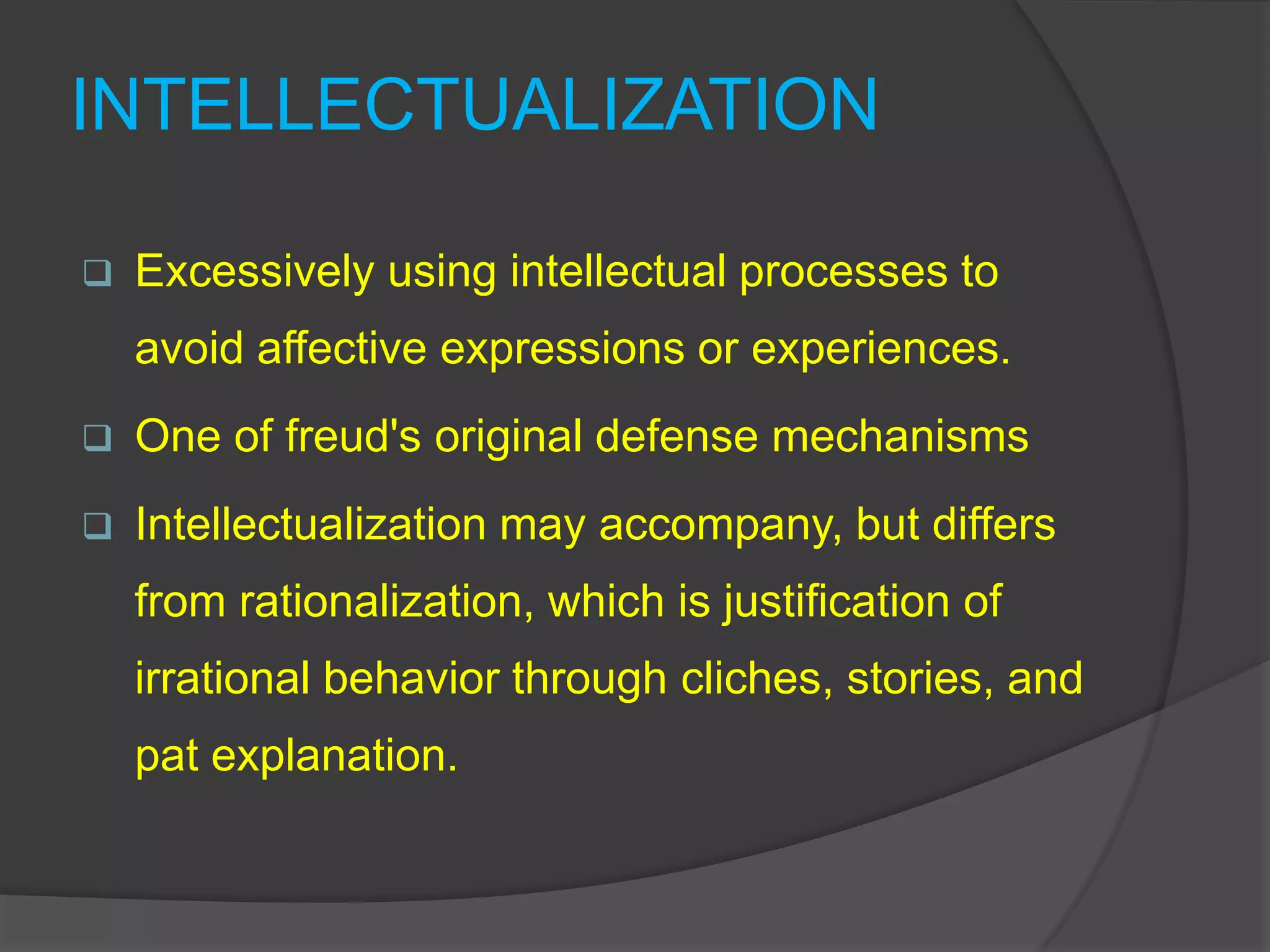
This document defines and classifies various ego defense mechanisms including: denial, distortion, projection, regression, acting out, hypochondriasis, introjection, passive aggression, rationalization, intellectualization, reaction formation, repression, displacement, dissociation, inhibition, isolation, compensation, splitting, sublimation, anticipation, and altruism. It provides examples of how these defenses are used unconsciously to protect the ego from anxiety and manage internal or external conflicts and stressors.