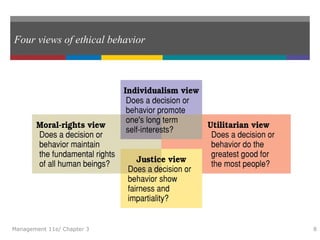
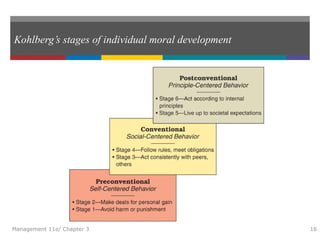
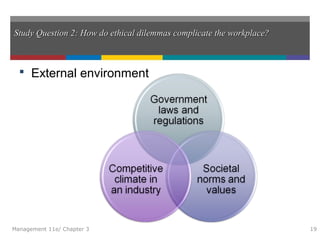
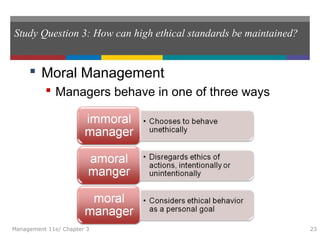
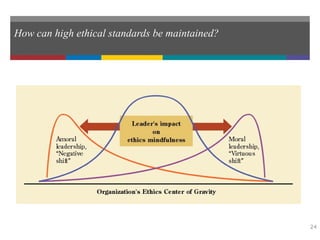
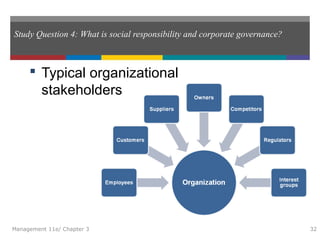
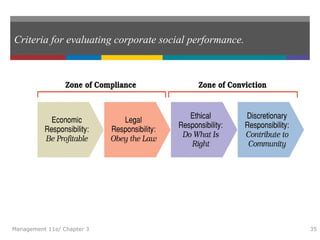
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 3 of the textbook "Introduction to Management 11e" by John Schermerhorn. It addresses four study questions: 1) What is ethical behavior? 2) How do ethical dilemmas complicate the workplace? 3) How can high ethical standards be maintained? 4) What is social responsibility and corporate governance? The summary defines ethics and ethical behavior, explores sources of ethical dilemmas in organizations, and discusses approaches like ethics training and codes of conduct that can help maintain high standards of ethical conduct. It also defines social responsibility, stakeholder management, and corporate governance.