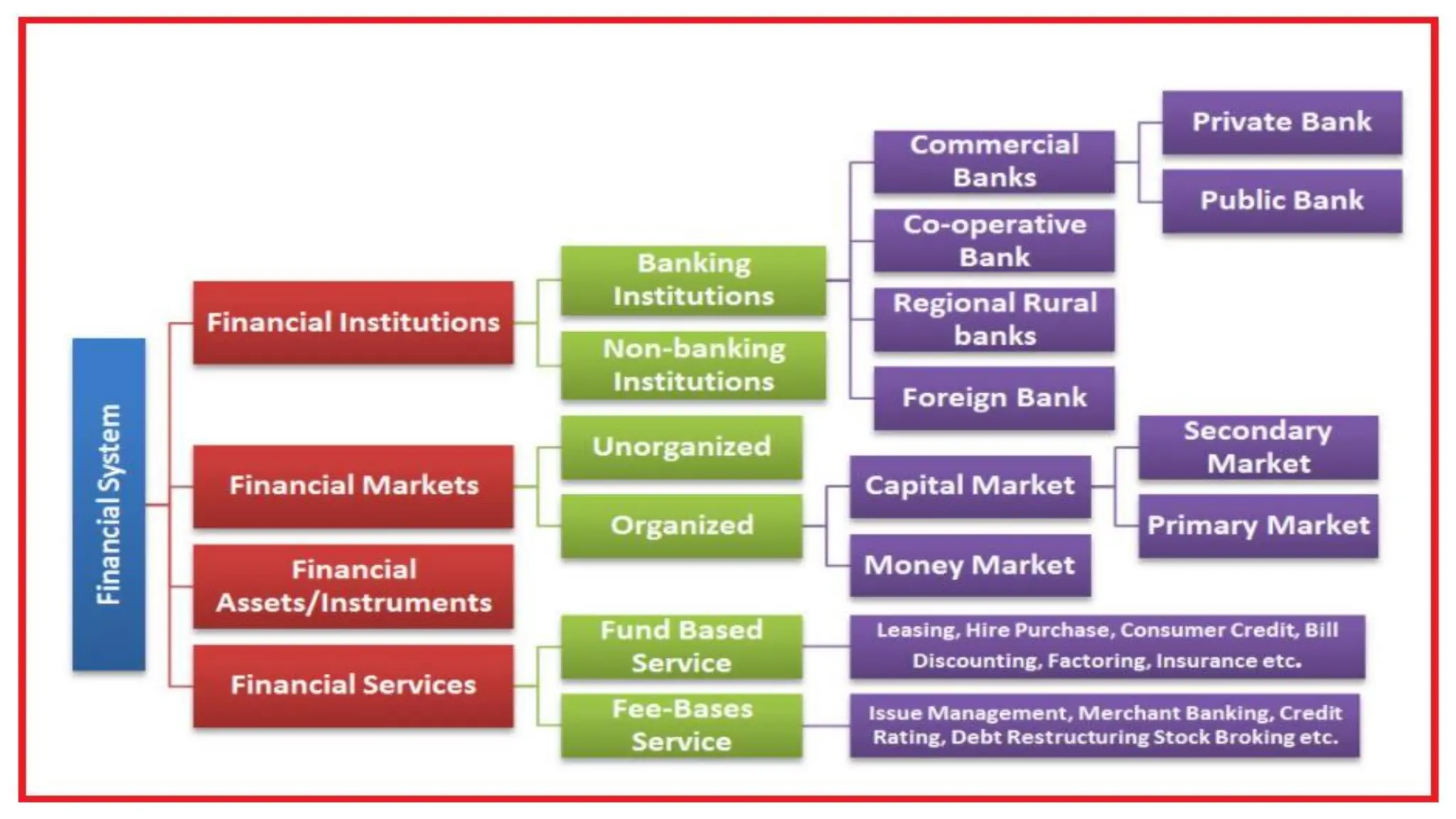
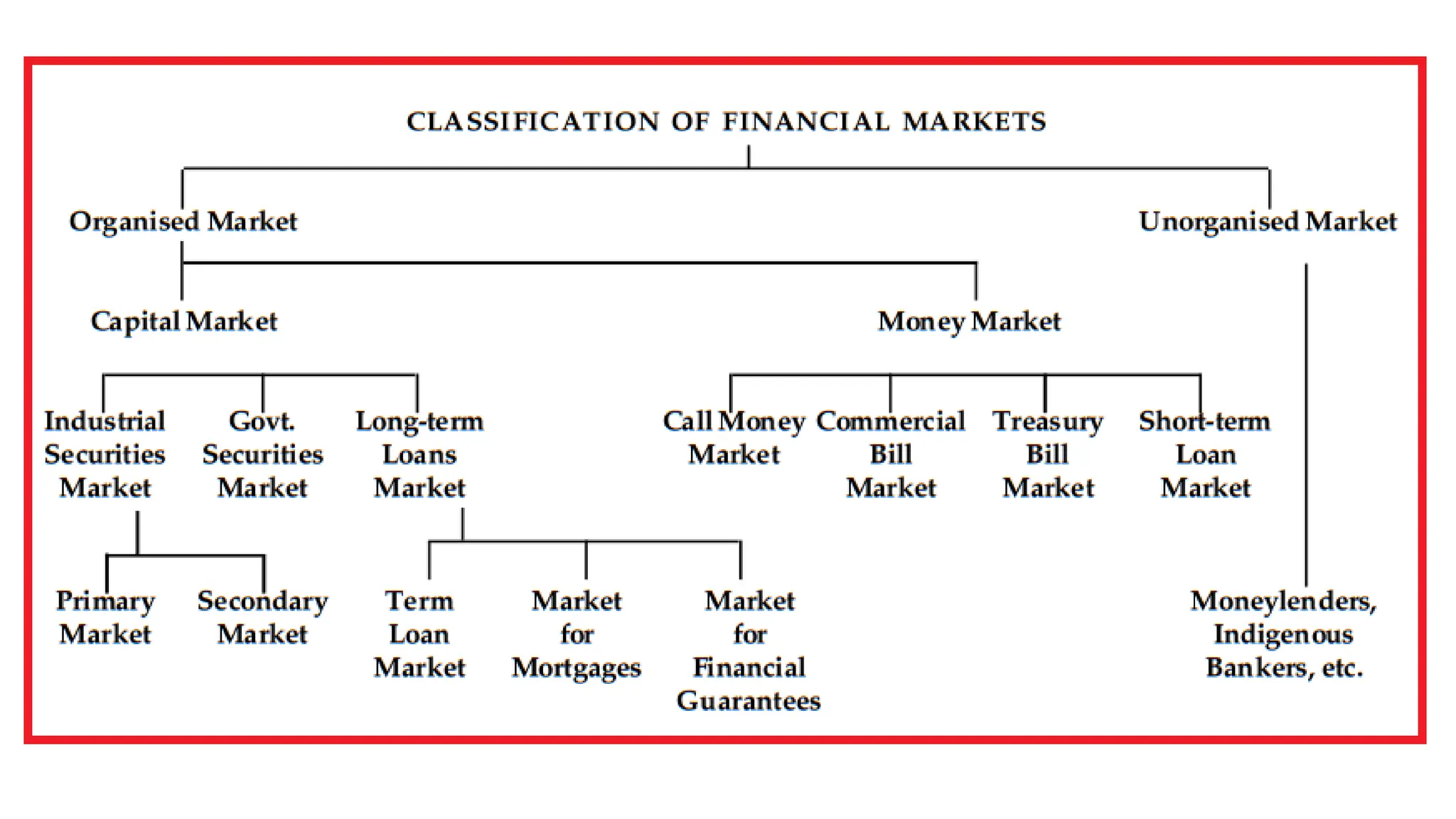
The document provides an overview of the Indian financial system, its structure and functions. It discusses key topics like financial markets, instruments, regulatory bodies like RBI and SEBI, and their roles. It also briefly introduces global financial markets and their importance. The key functions of the Indian financial system discussed are provision of liquidity, mobilization of savings, size and risk transformation. Regulatory bodies RBI and SEBI work to protect investors, develop and regulate financial markets and institutions.