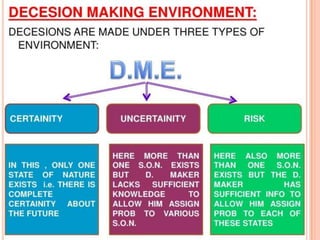
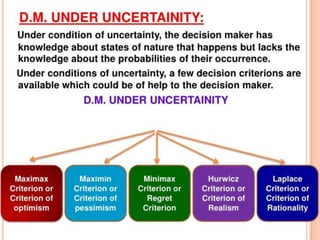
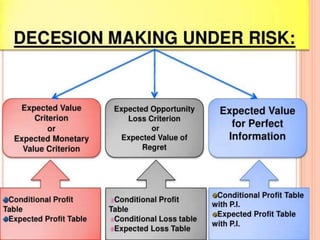
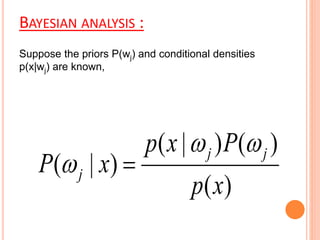
This document discusses decision making environments and techniques. It describes three types of decision making environments: decision making under certainty, uncertainty, and risk. It also discusses decision trees, Bayesian analysis, and utility theory as tools for decision making under uncertainty and risk. The key techniques covered are expected value analysis, maximax/maximin criteria, and expected opportunity loss criterion for decision making under risk.