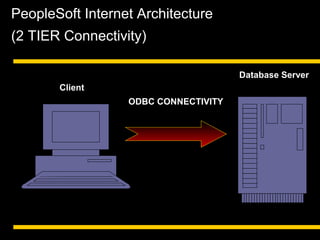
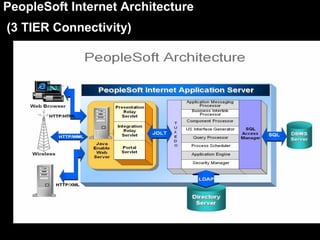
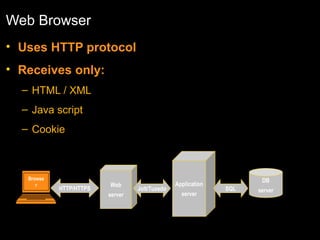
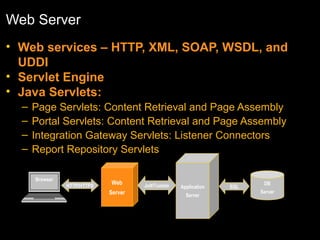
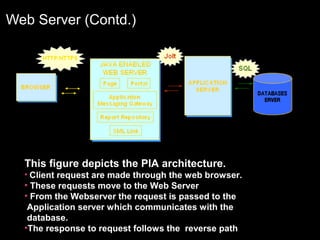
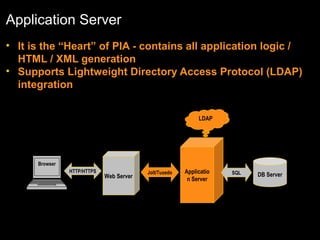
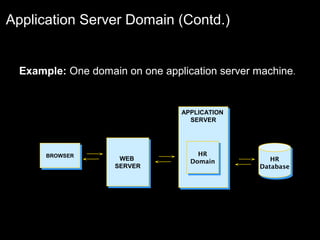
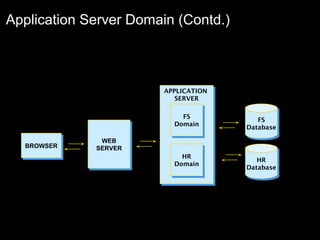
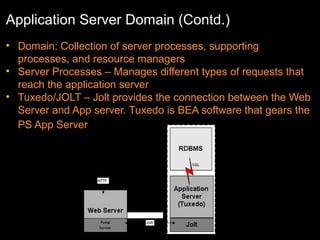
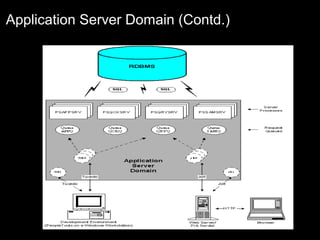
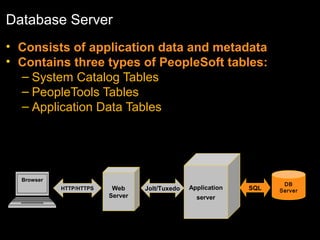
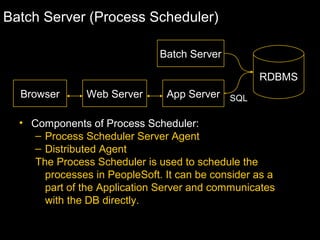
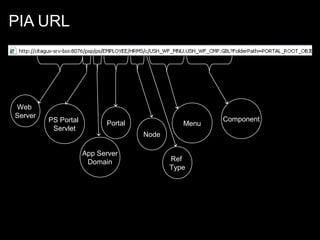
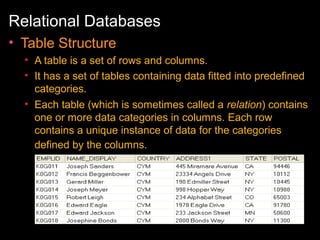
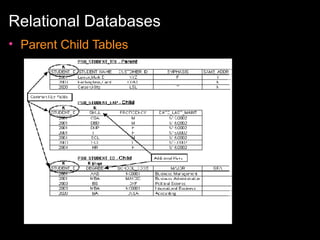
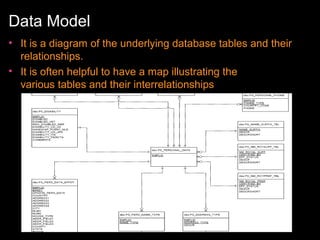
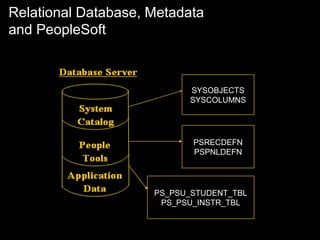
The document discusses relational databases and how they organize data into tables that can be accessed and reassembled in different ways without reorganizing the tables, it also covers how PeopleSoft uses a 3-tier architecture called PeopleSoft Internet Architecture (PIA) consisting of a web browser, web server, application server and database server to deliver pure internet applications to users. PIA provides advantages over traditional client/server architectures like thin clients, improved performance, and the ability to scale more easily to meet increasing user demands.








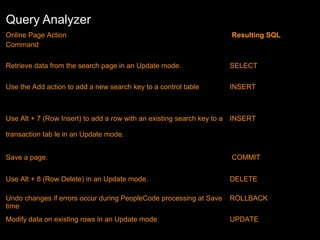
![Query Analyzer
•
SQL “SELECT” Syntax
•
SELECT [COLUMNS] FROM [TABLE_NAME]
•
SELECT [COLUMNS] FROM [TABLE_NAME] WHERE [COLUMN1] =
[CONDITION]
•
SELECT [COLUMNS] FROM [TABLE_NAME] WHERE [COLUMN1] =
[CONDITION] ORDER BY [COLUMNS] [DESC/ASC]
•
•
SELECT [COLUMNS],GROUP FUNCTIONS FROM
[TABLE_NAME] WHERE [COLUMN1] = [CONDITION] GROUP BY
[COLUMNS]
Group Functions – Max/Min/Count/Sum
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peoplesoftbasics-131206003140-phpapp02/85/People-soft-basics-13-320.jpg)
![Query Analyzer
• SQL INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE Syntax
• INSERT INTO [TABLE_NAME] [COLUMNS]
VALUES[VALUE1,VALUE2…]
• UPDATE [TABLE_NAME] SET [COLUMN] = [VALUE]
WHERE [COLUMN1] = [CONDITION]
• DELETE FROM [TABLE_NAME] WHERE [COLUMN1] =
[CONDITION]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peoplesoftbasics-131206003140-phpapp02/85/People-soft-basics-14-320.jpg)