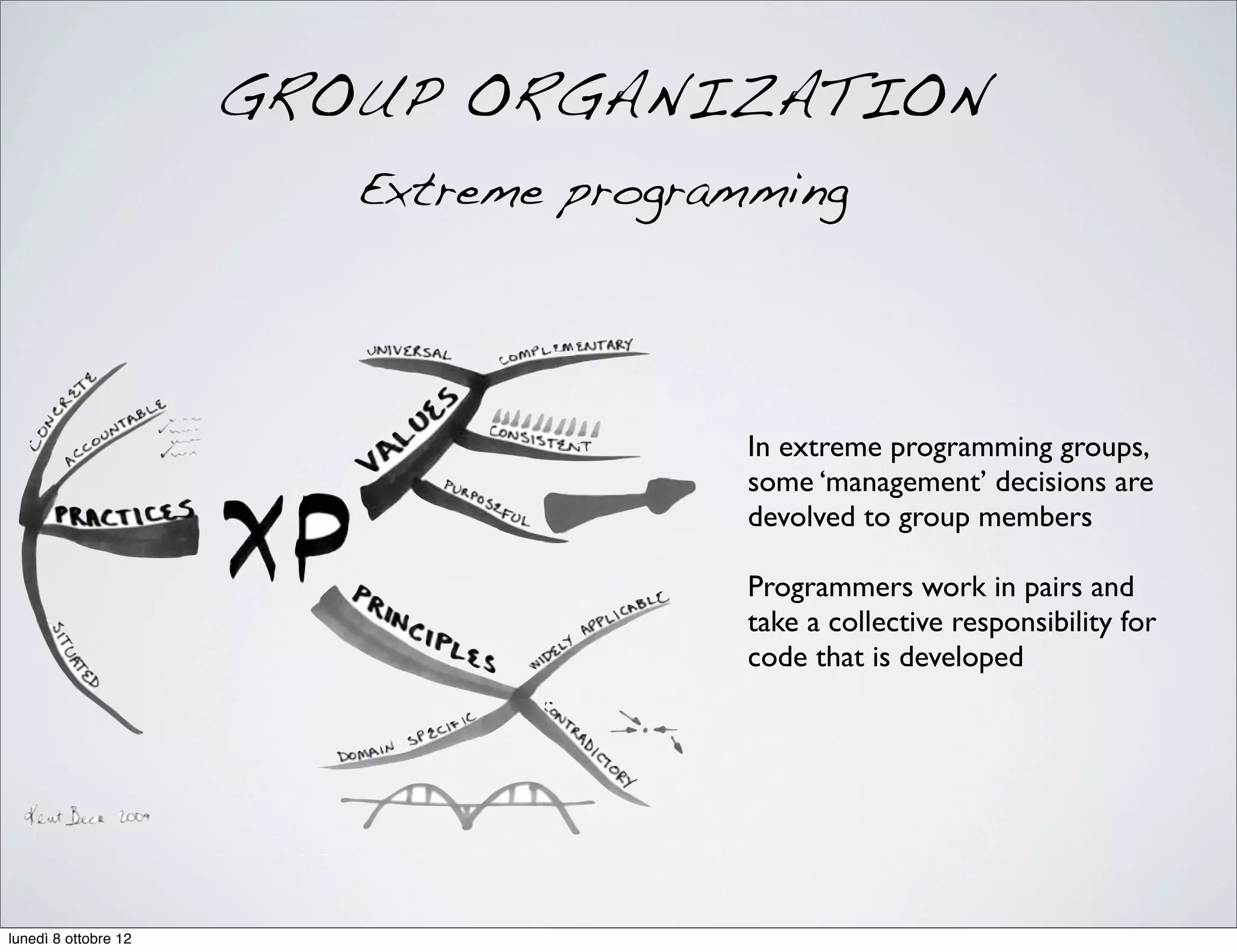
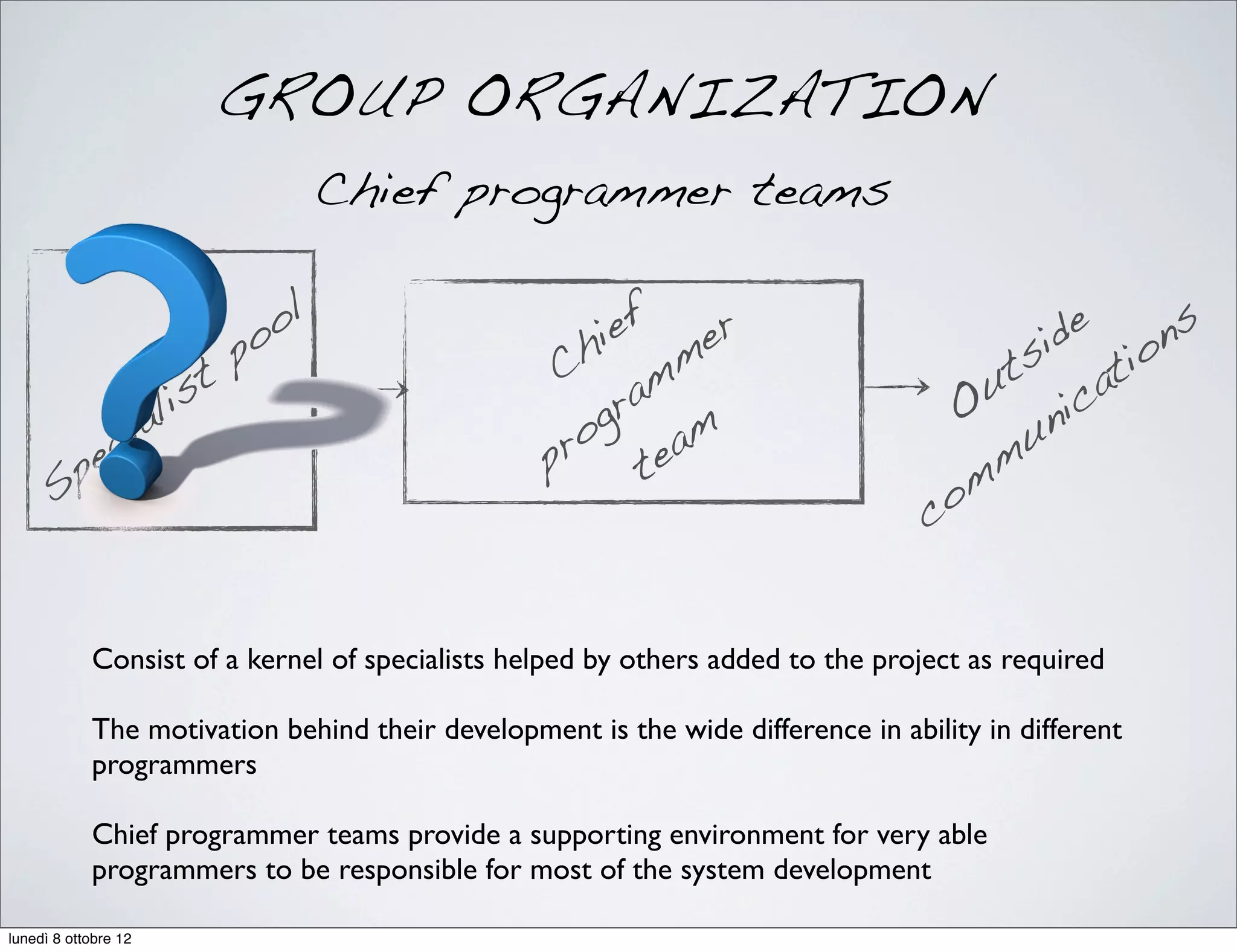
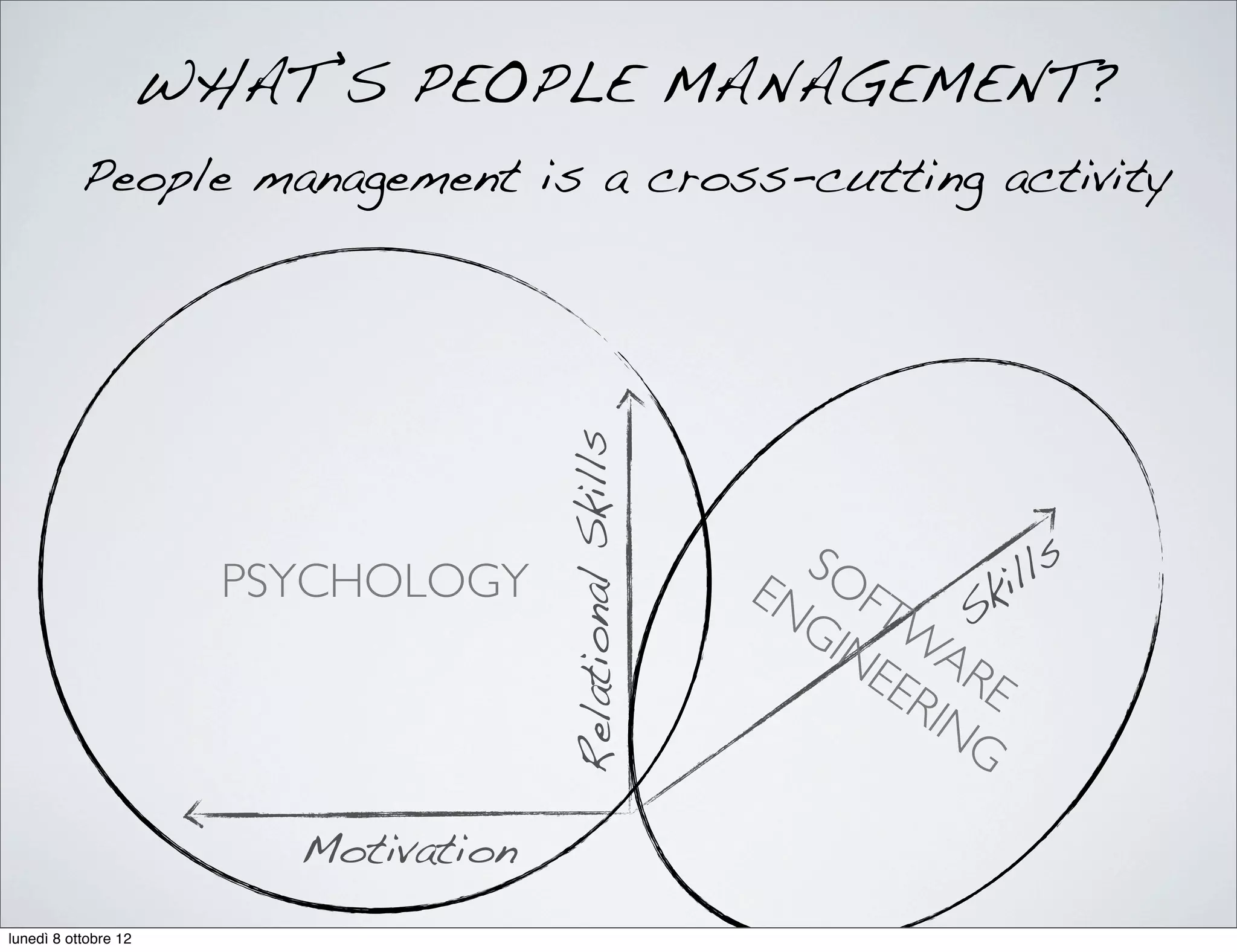
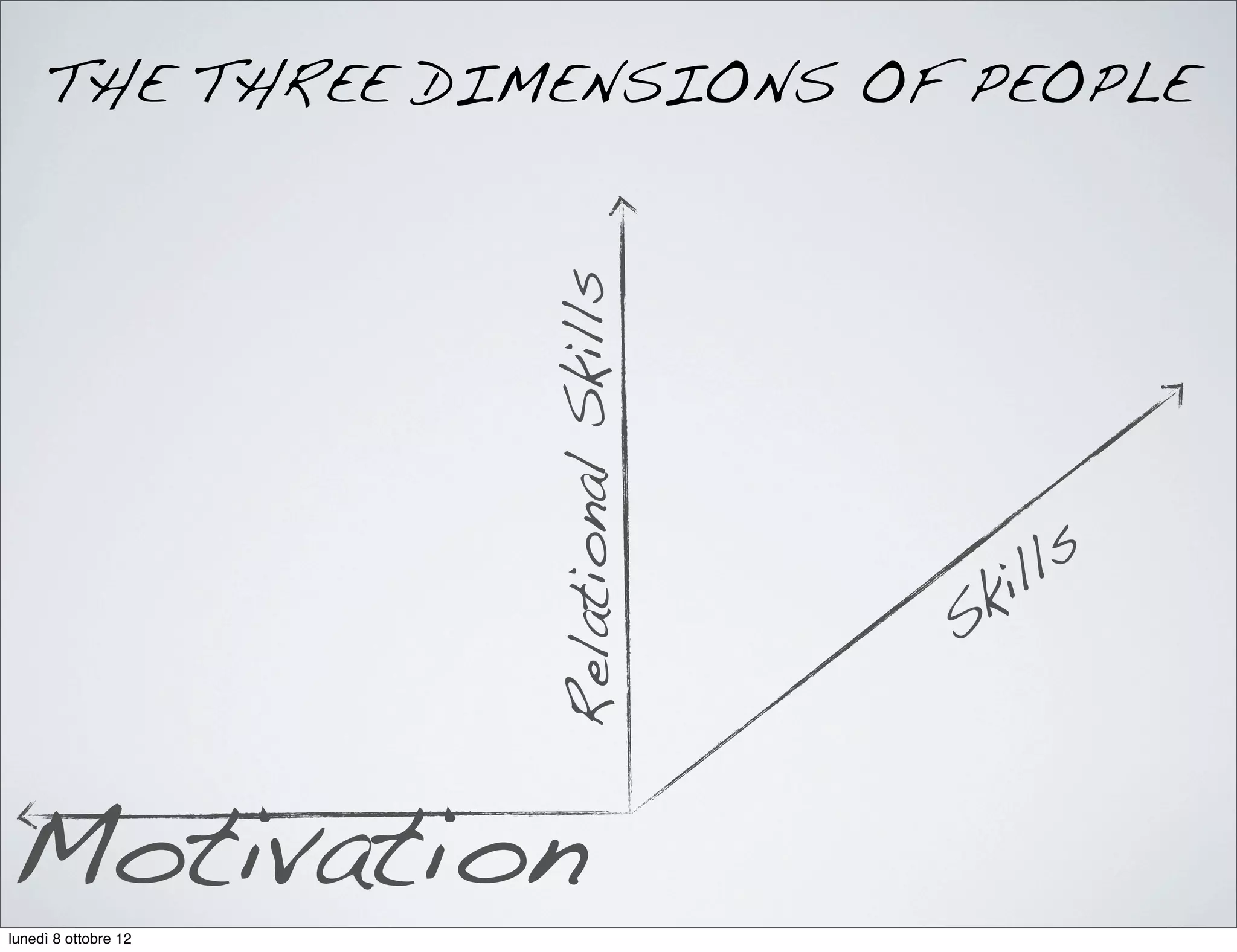
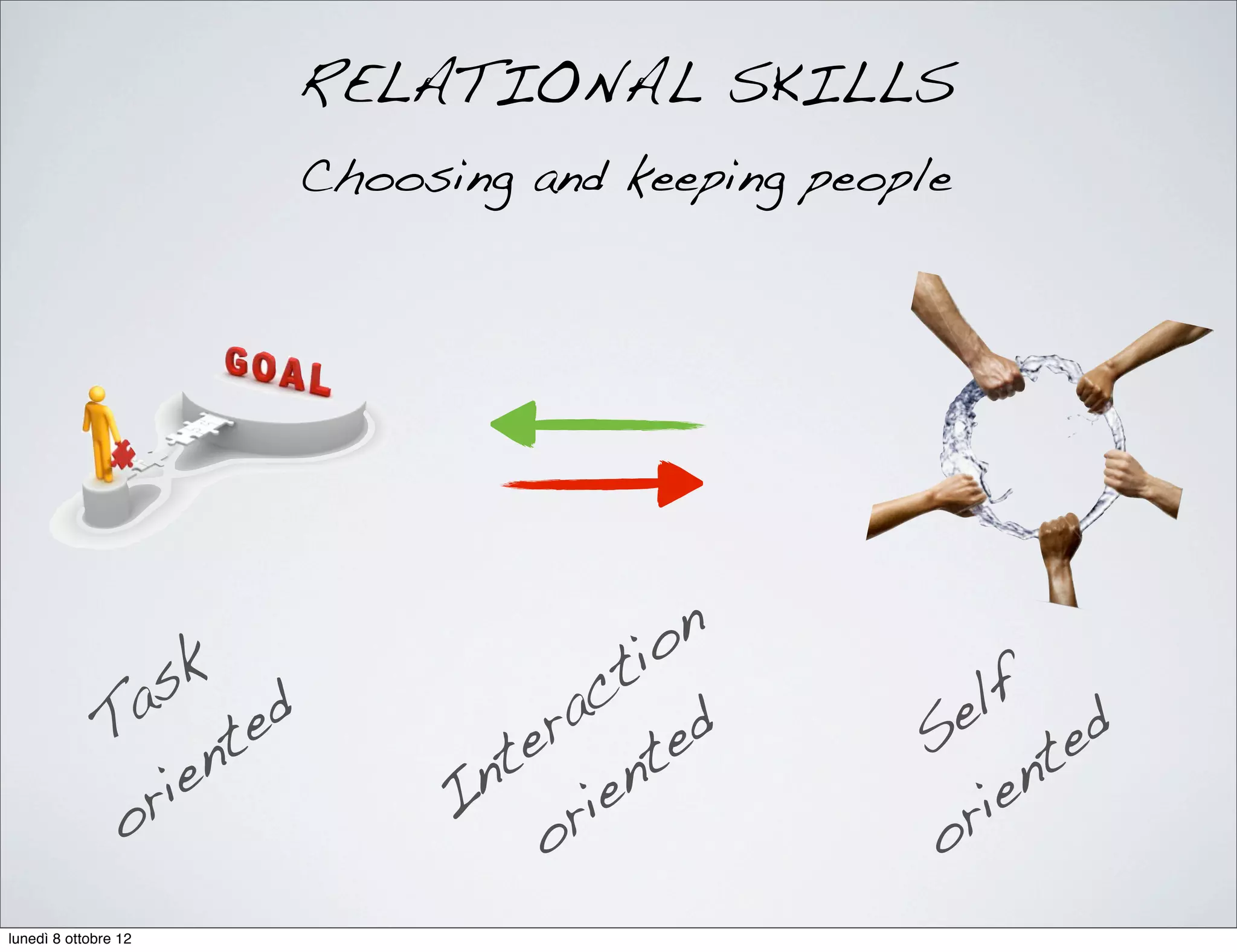
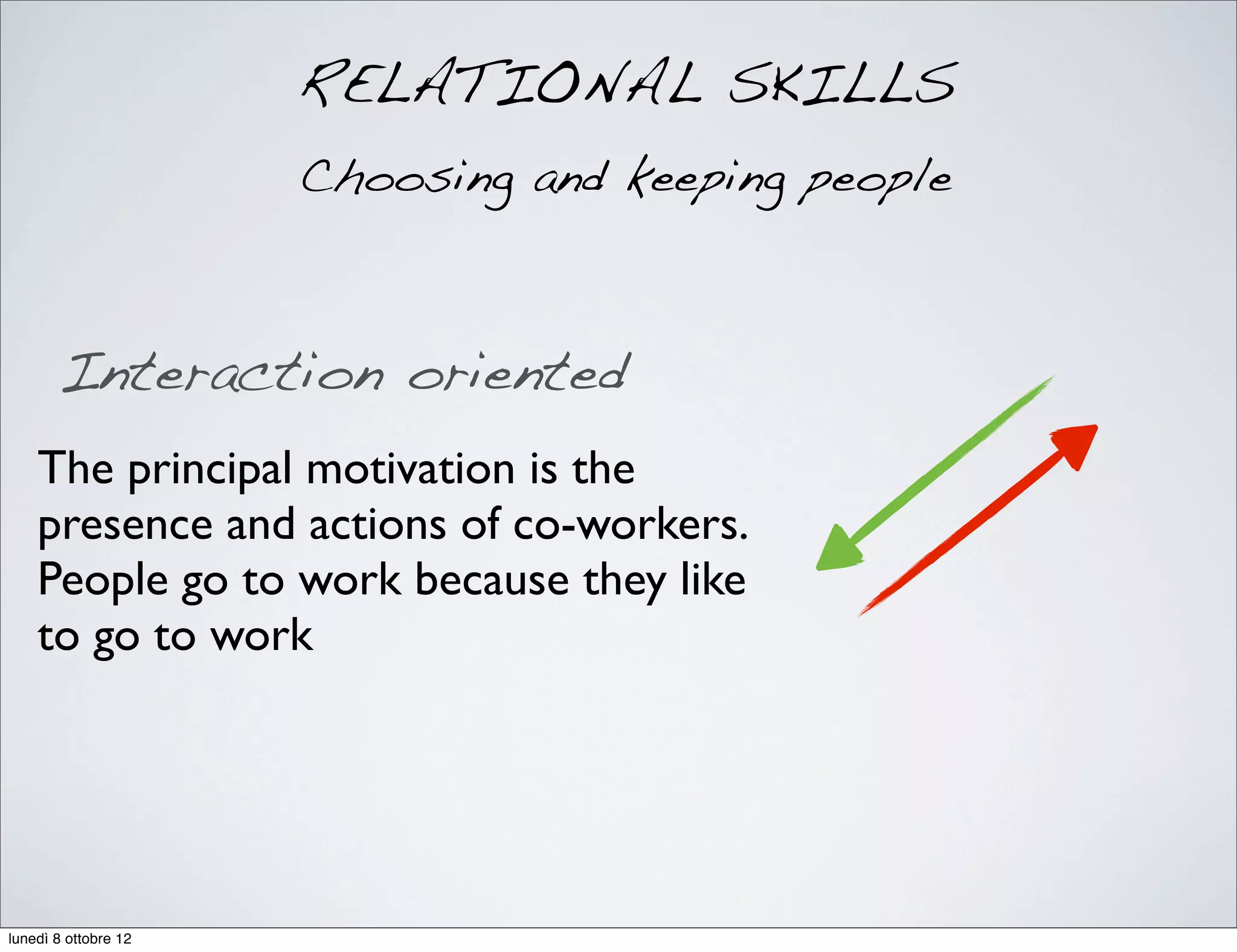
The document discusses the importance of people management, highlighting that motivation is a critical component for organizational success. It outlines the various dimensions of motivation and relational skills necessary for effective leadership and group organization. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for a balance between task-oriented, interaction-oriented, and self-oriented motivations within teams to enhance productivity and cohesion.





![Impact of People Management Practices on Business
Performance [Patterson et al.]
The impact of strategical human resource management on
Organizational Performance [Caliskan]
There’s an huge impact of
people management on
the success of a project
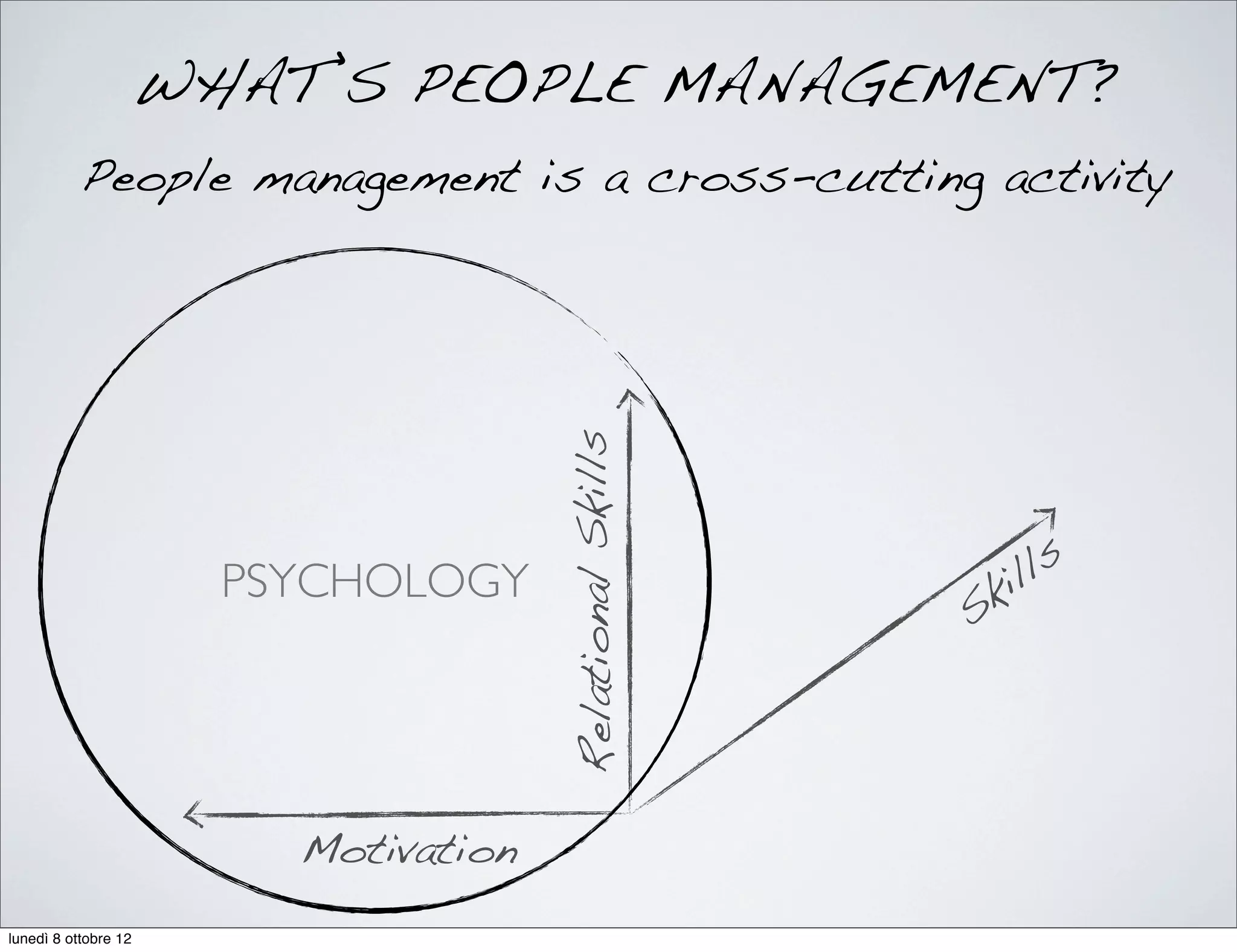
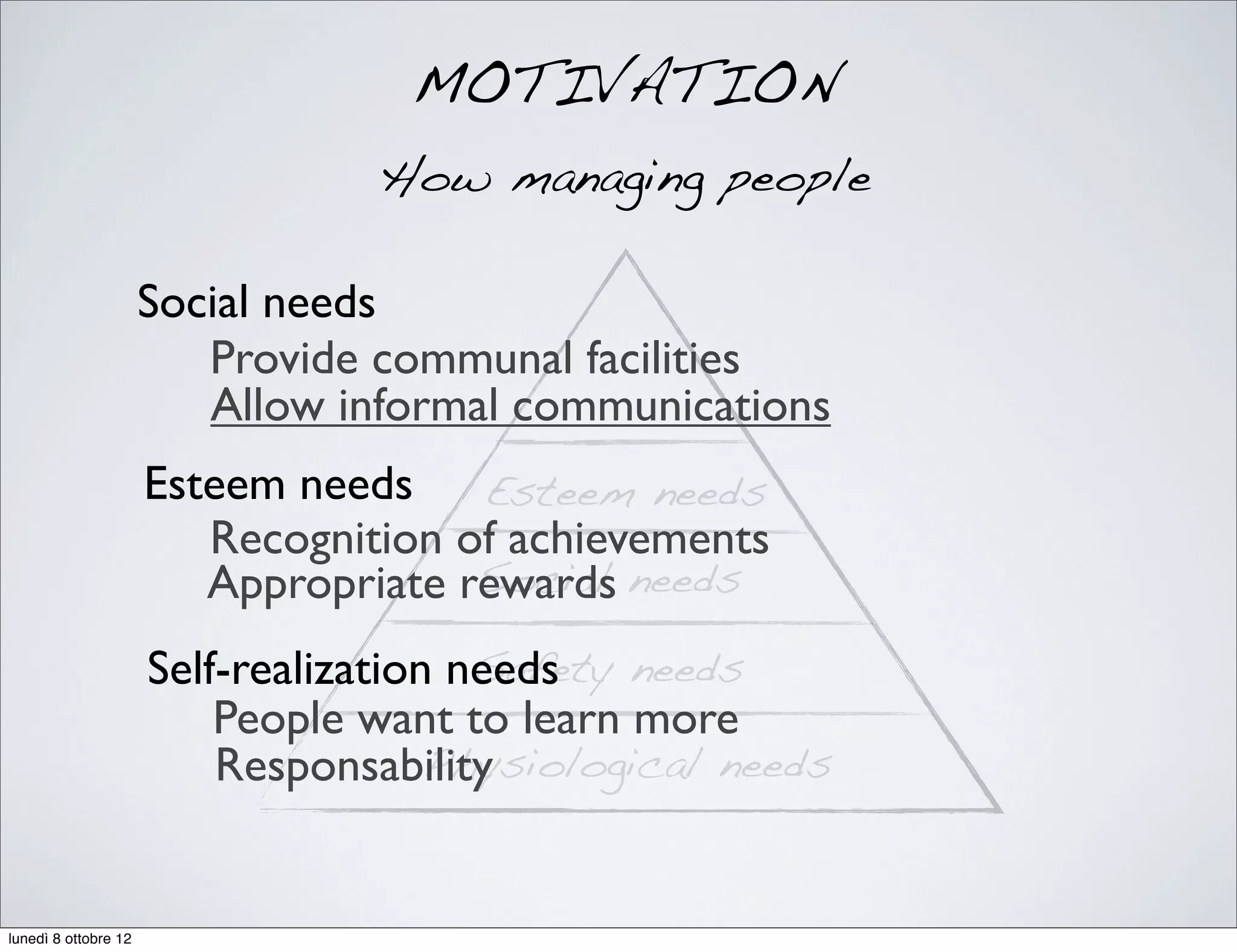
MOTIVATION
How managing people
lunedì 8 ottobre 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peoplemanagement-130928124446-phpapp02/75/People-management-10-2048.jpg)









![Sex composition and Leadership in Small Groups
[Eskilson et al.]
GROUP LEADERSHIP
How to choose a good leader?
Group
leadership
W
oman
leadership
lunedì 8 ottobre 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peoplemanagement-130928124446-phpapp02/75/People-management-23-2048.jpg)