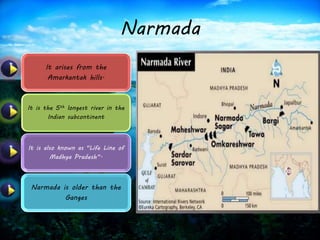
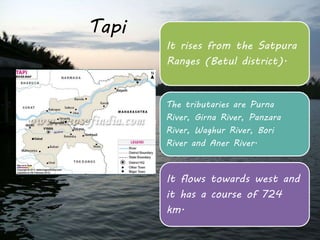
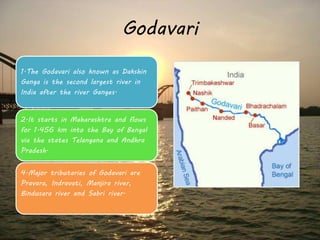
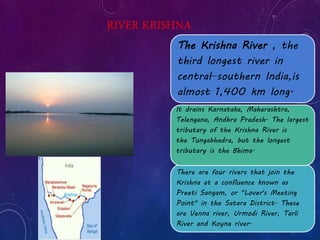
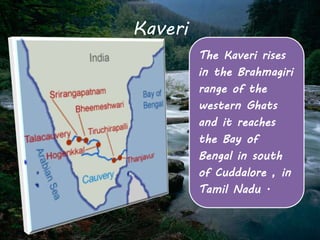
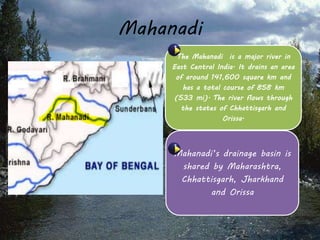
This document provides information on six major rivers in peninsular India: Narmada, Tapi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, and Mahanadi. It details the source and course of each river, as well as notable tributaries and areas drained. The Narmada rises in Madhya Pradesh and is known as the "Life Line of Madhya Pradesh". The Godavari is the second largest Indian river after the Ganges. The Krishna drains parts of four states before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.