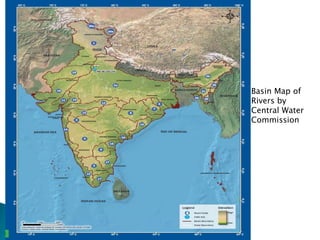
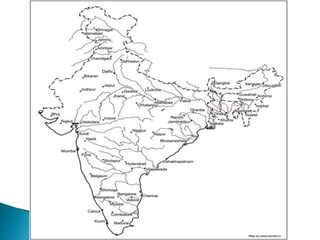
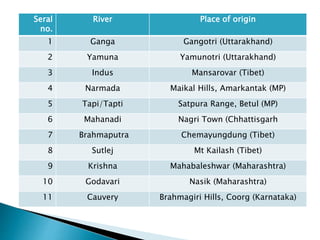
The document discusses the rivers of India, their classifications, and origins, emphasizing their ecological and economic significance to various stakeholders. It categorizes rivers into Himalayan and peninsular types and details seven major river systems, including the Ganga, Yamuna, Indus, and Brahmaputra, among others. Each river's unique characteristics, tributaries, and water flow patterns are described, highlighting their roles in the geography and culture of India.