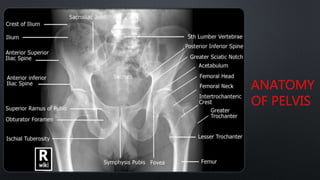
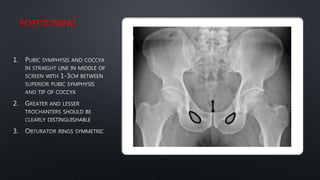
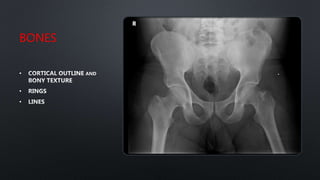
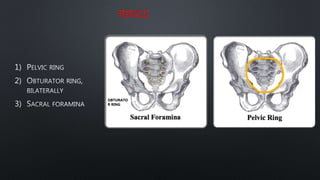
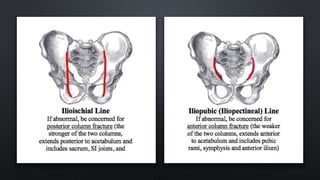
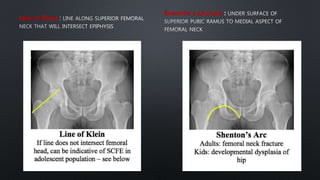
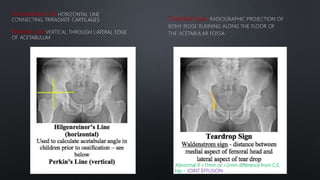
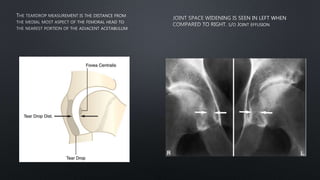
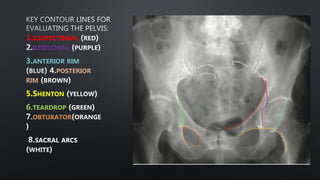
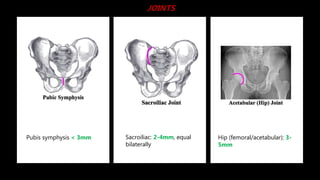
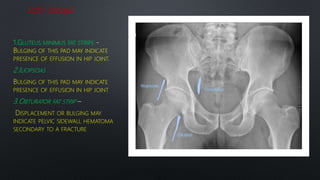
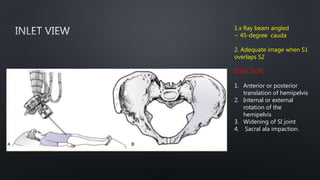
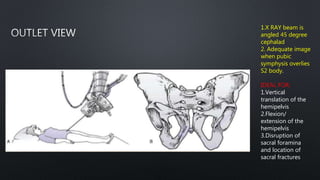
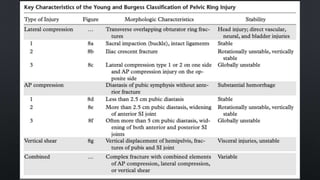
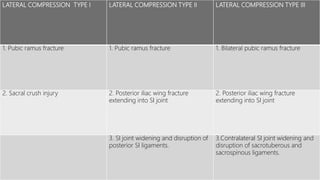
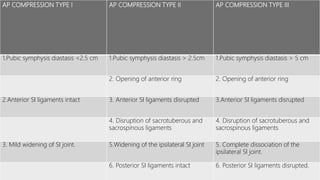
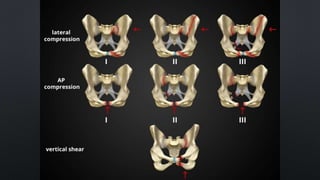
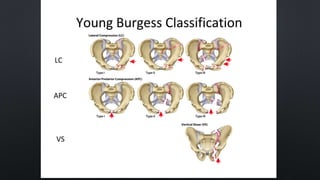
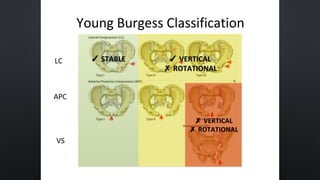
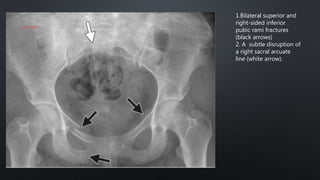
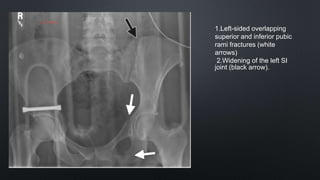
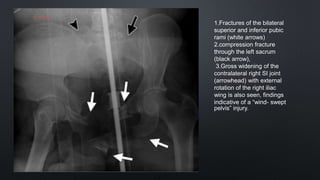
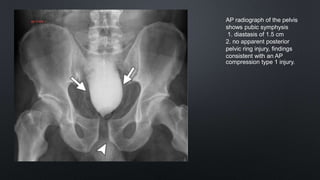
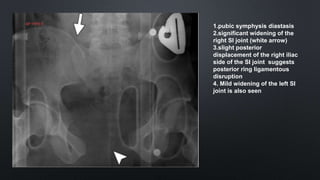
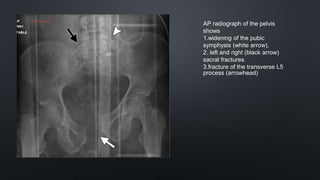
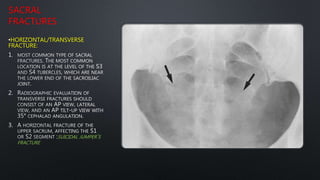
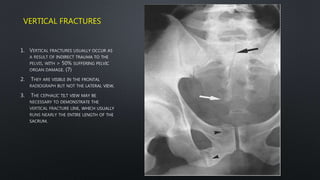
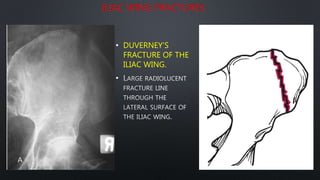
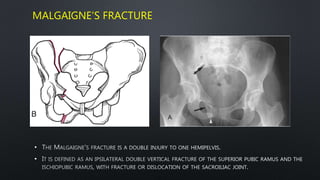
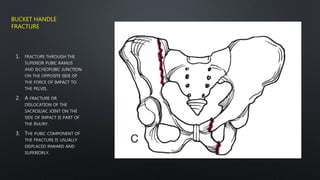
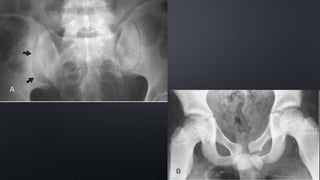
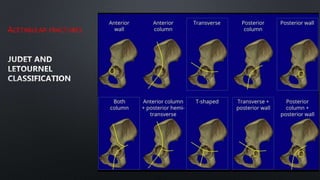
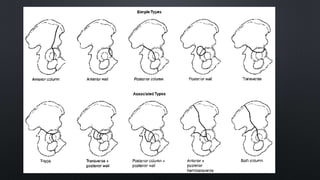
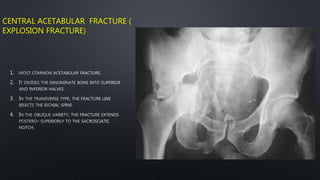
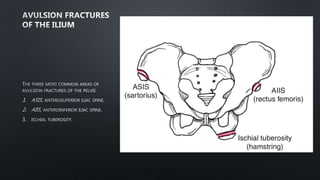
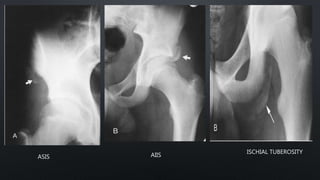
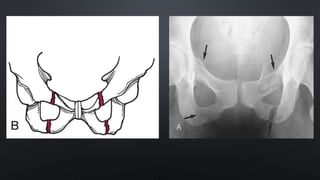
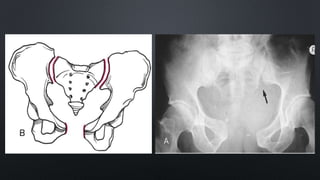
This document discusses the anatomy of the pelvis, including bones, joints, and soft tissues. It describes the positioning of pelvic radiographs and how to evaluate them. Common pelvic fractures are outlined, such as lateral compression, anteroposterior compression, and sacral fractures. Signs of instability and displacement are emphasized for diagnosis.