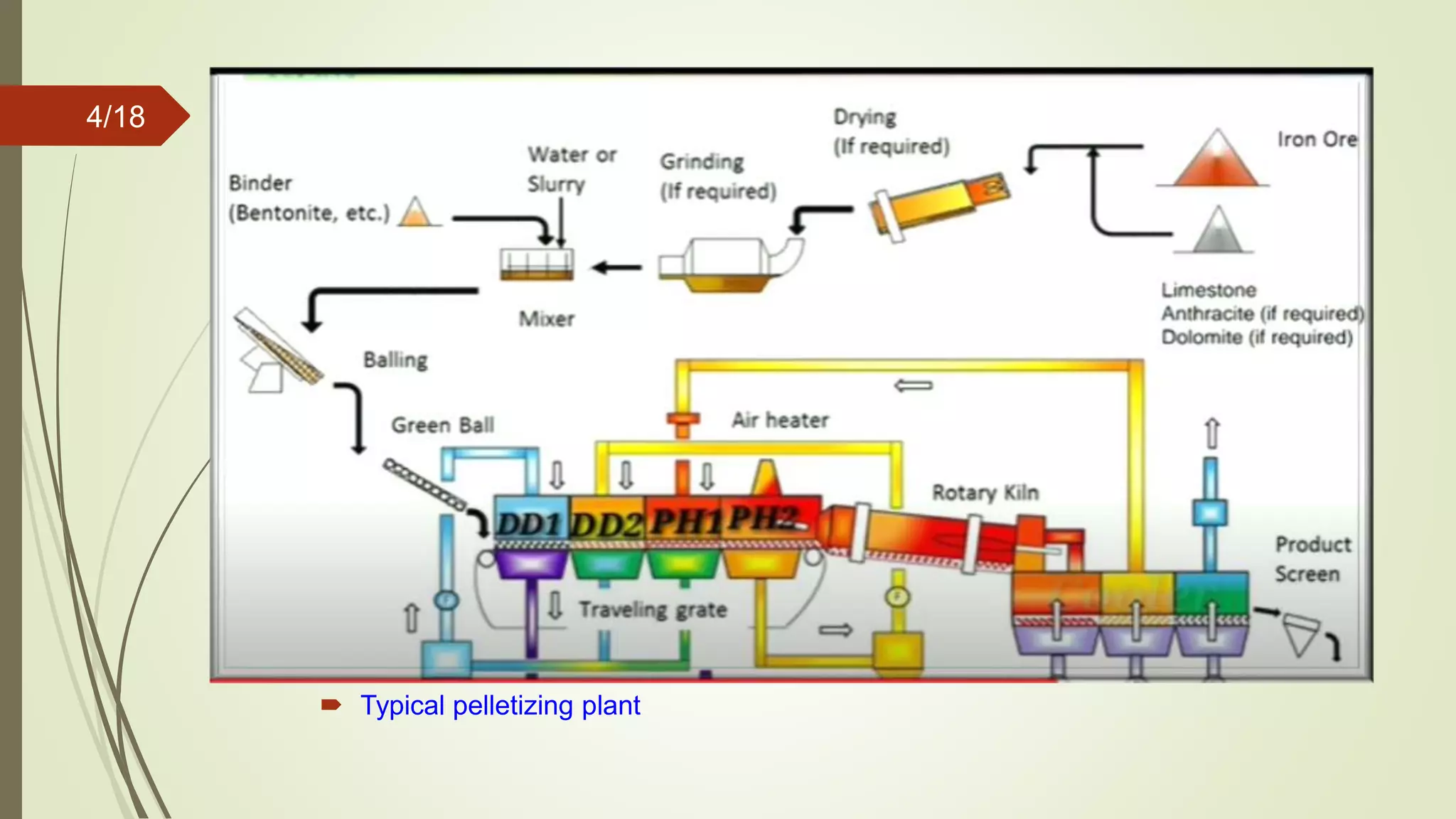
The document summarizes the key steps in the iron ore pelletization process. It describes how iron ore fines and binders are mixed and formed into green balls either using a disc pelletizer or drum pelletizer. The green balls are then indurated through drying, preheating, and firing to develop bonds between fine ore particles at high temperatures. This process produces hardened iron ore pellets that offer advantages for blast furnace operations over using iron ore fines alone.