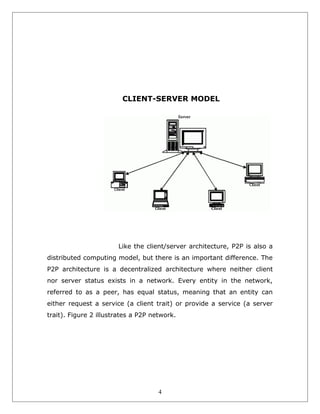
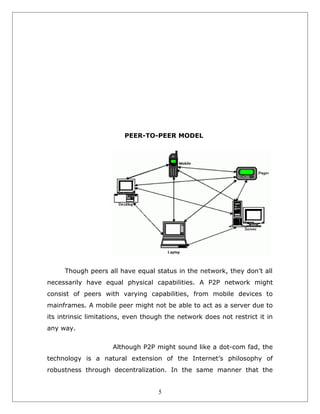
This document describes a peer-to-peer messaging system built using the JXTA platform. The system allows instant messages to be sent between peers in a decentralized JXTA network. JXTA defines protocols for peer-to-peer communication, where all peers have equal status and can request or provide services. The system includes a JXTA relay that receives commands from J2ME clients, performs actions on their behalf, and represents the clients on the JXTA network by discovering peers and routing messages. The goal of the project is to enable instant messaging between peers in a peer-to-peer manner without a centralized server.