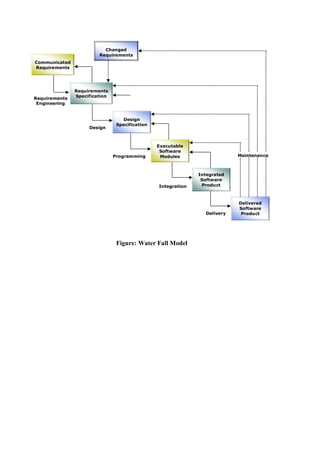
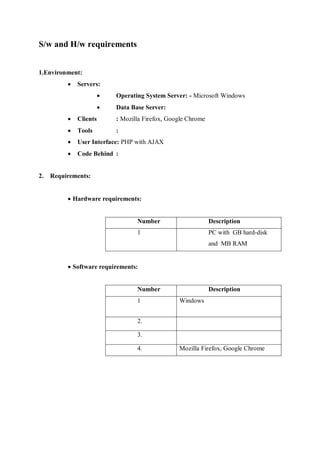
The document is an internship report detailing the development of the N-Grade university management system aimed at automating the management of student, faculty, and course information. It highlights the shortcomings of the existing manual system and proposes an efficient intranet-based solution that allows for real-time data access and management. Key features include user roles for administrators and students, a web-based interface, and a waterfall model approach to software development.