Embed presentation
Download as ODP, PPTX
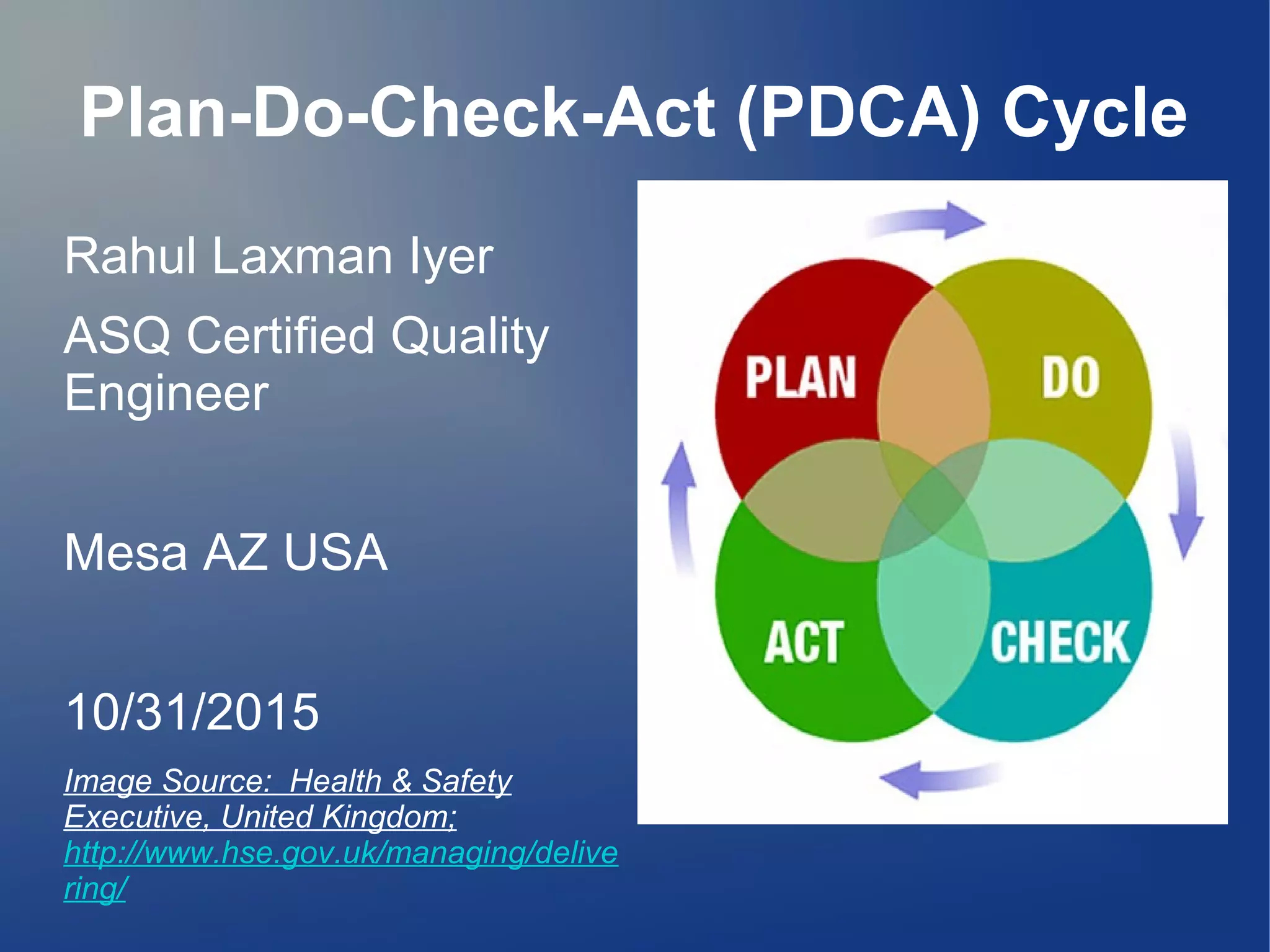


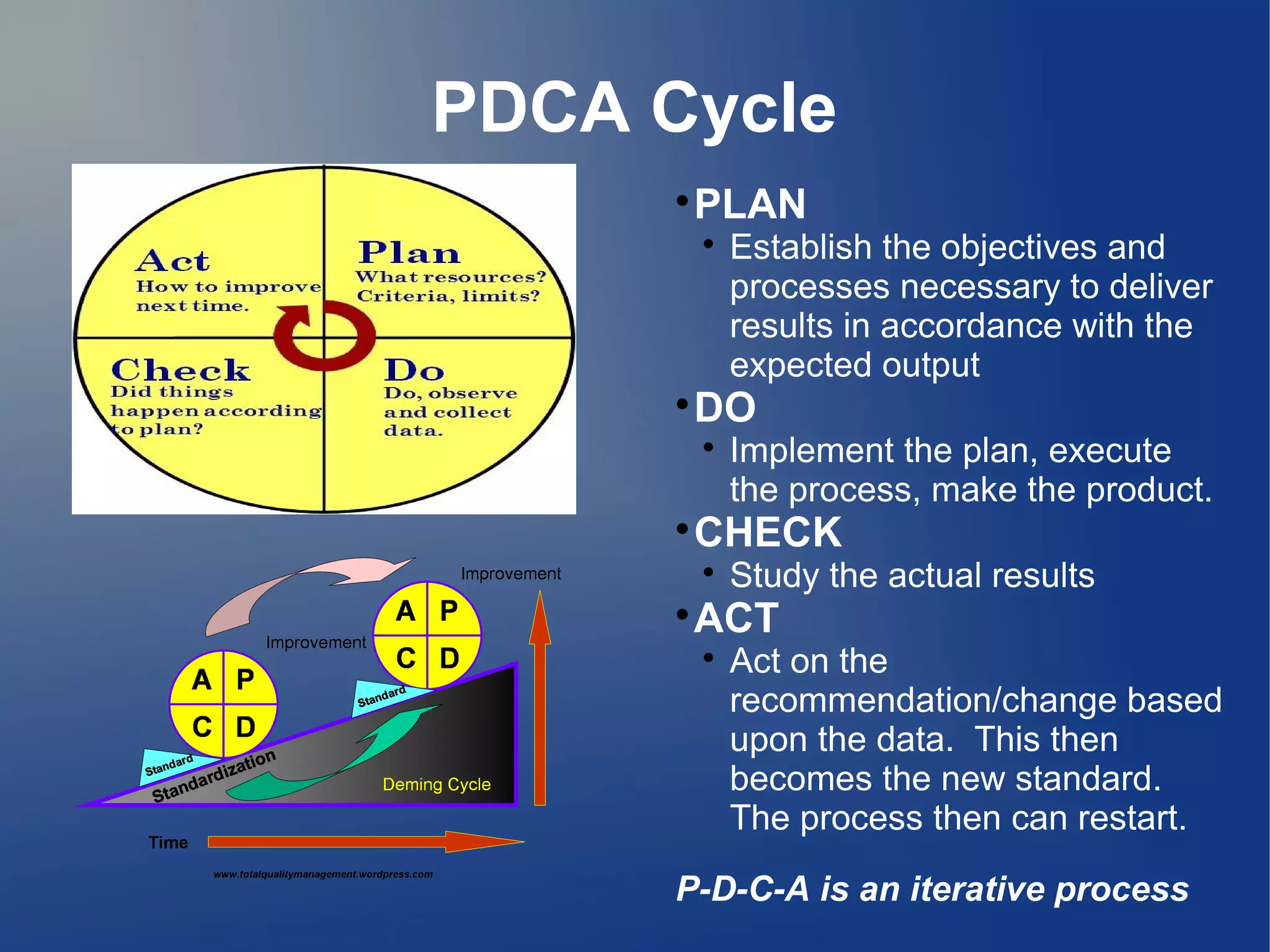






The PDCA cycle, also known as the Deming Circle, is a four-step iterative management method used for continuous improvement of processes and products in business. It involves planning, doing, checking, and acting, establishing objectives, executing plans, analyzing results, and implementing changes. Developed by Walter Shewhart in the 1930s and later revised by W. Edwards Deming, PDCA is foundational in quality management and applicable across various industries.
Introduction of the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle by Rahul Laxman Iyer, ASQ Certified Quality Engineer.
Exploration of PDCA, its history, applications, and examples.
PDCA is a four-step iterative management method crucial for continuous process and product improvement.
Details the four phases: Plan, Do, Check, and Act, highlighting their roles in the iterative process.
History traces back to W. Edwards Deming and Walter Shewhart, rooted in scientific methods from the 1930s.
Highlights key contributors: W. Edwards Deming, Walter Shewhart, and Francis Bacon in PDCA's evolution.
PDCA is applicable to process improvement and product improvement in various fields.
Examples of PDCA demonstrated through the evolution of mobile phones and automobiles.
Recap of what PDCA is, its historical background, applications, and examples discussed.
Concluding thoughts on the definition, history, applications, and examples of the PDCA cycle.









