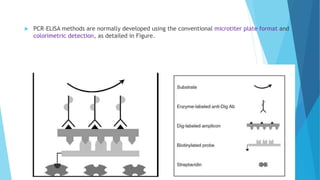
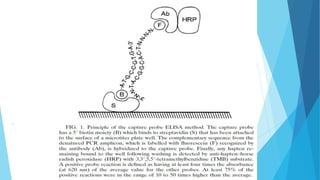
This document discusses PCR-ELISA (polymerase chain reaction - enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), a sensitive and specific method for detecting nucleic acids present in low concentrations that combines PCR amplification with ELISA detection. PCR-ELISA involves labeling PCR amplicons, hybridizing them with target-specific probes, capturing the labeled hybrids on microtiter plates, and detecting them by immunoassay. While real-time PCR provides similar sensitivity and advantages like rapid detection, PCR-ELISA does not require expensive equipment and can detect different genotypes of infectious agents more easily than real-time PCR.