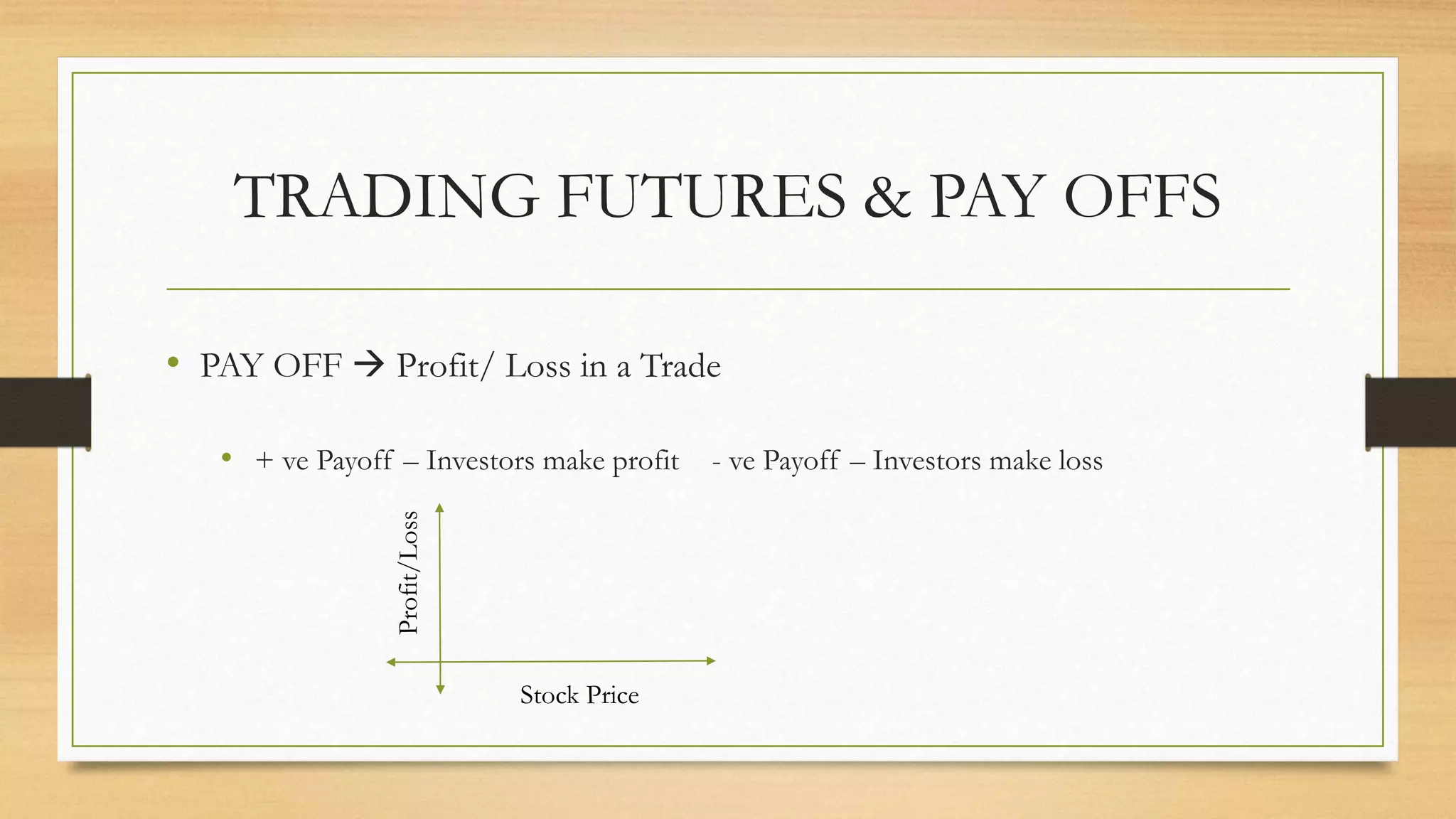
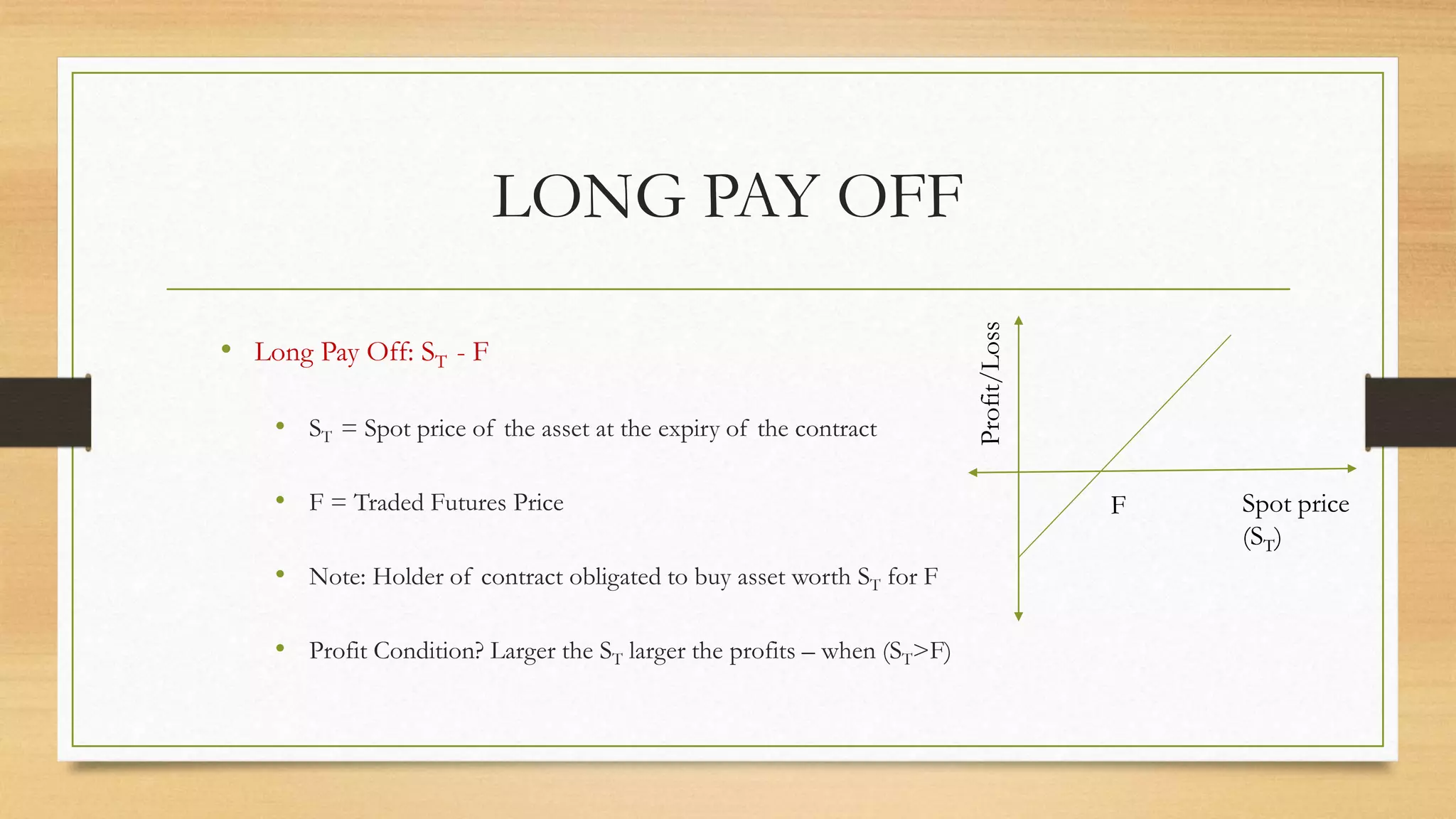
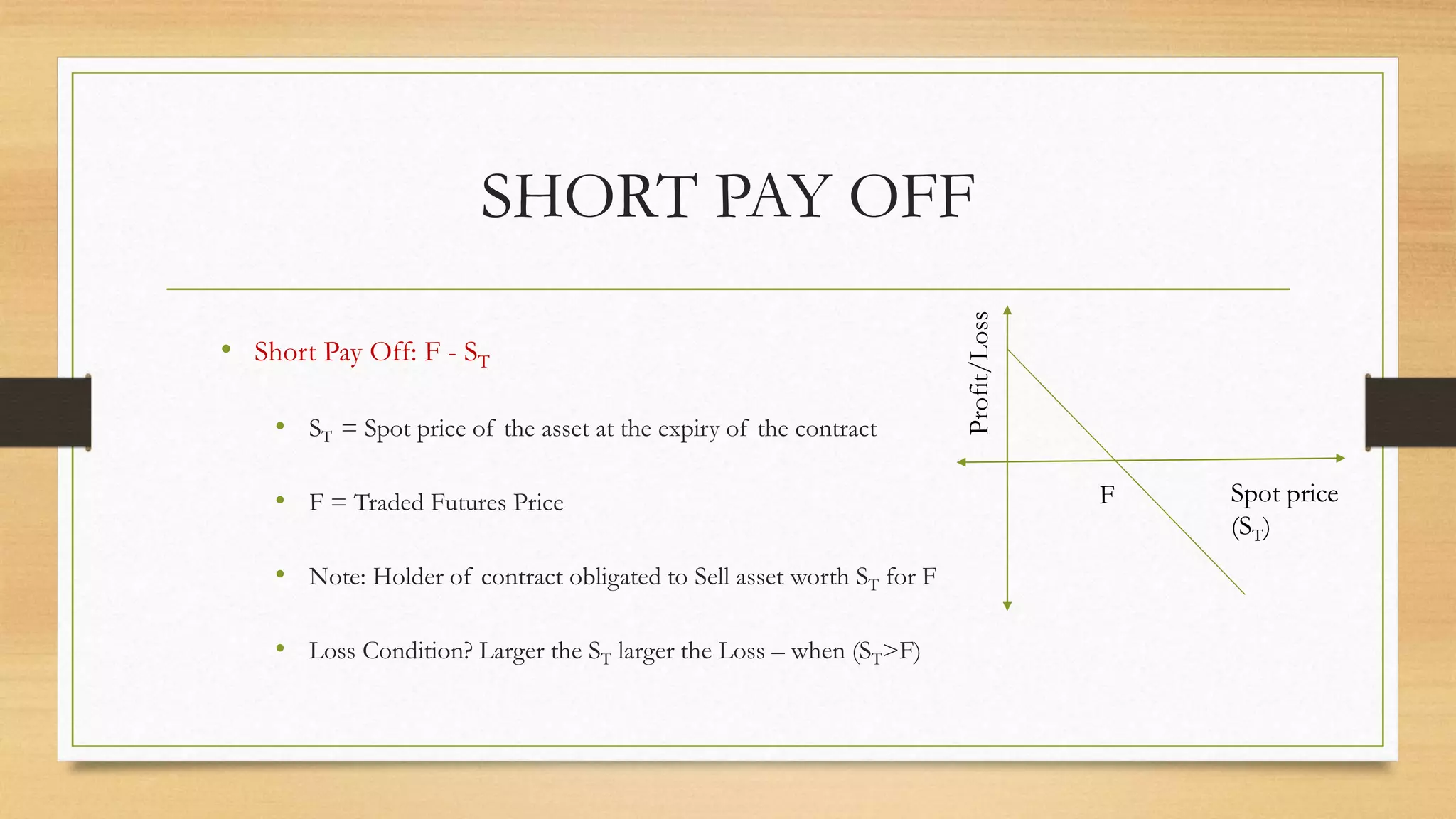
The document provides an overview of key terminologies and concepts related to derivatives in finance, including spot prices, forward/future prices, strike prices, and expiration dates. It discusses the types of options, such as American and European, along with profit/loss scenarios associated with trading futures and options. Additionally, it outlines the roles of option buyers and sellers, and the implications of market opinions on trading strategies.