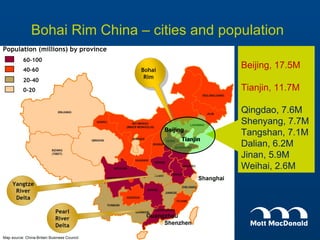
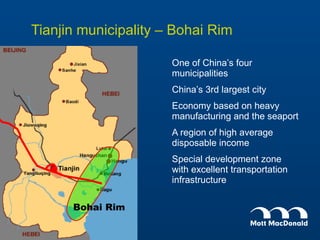
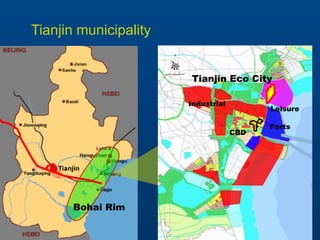
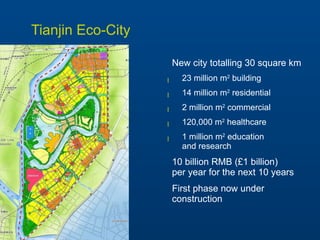
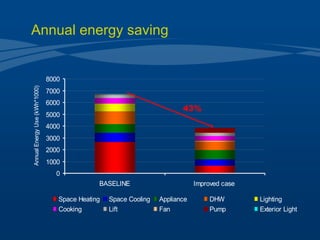
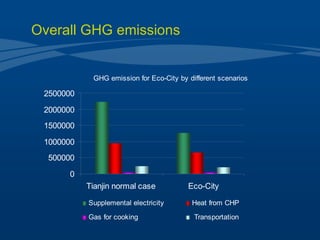
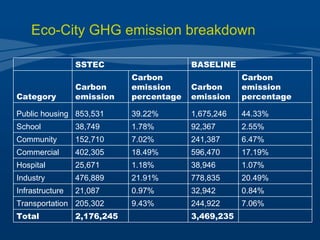
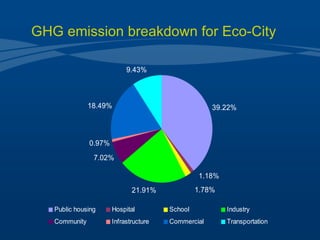
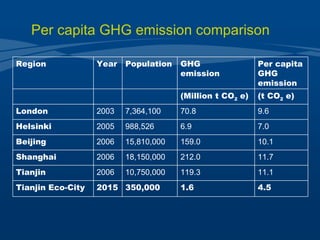
Tianjin Eco-City is a new city being developed in Tianjin, China as a model of sustainable development. It is a joint project between China and Singapore to apply concepts of green building, transportation, and planning. The goals are to reduce carbon emissions, encourage non-motorized transportation, and create a livable community on reclaimed former salt lands. Specific plans include developing mass transit systems, requiring green building standards that reduce energy use by 43%, and limiting per capita carbon emissions to less than half that of other Chinese cities. The hope is that Tianjin Eco-City can demonstrate how to plan new communities in China and around the world in a more environmentally friendly manner.