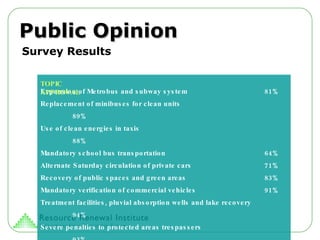
The document outlines Mexico City's ambitious sustainability plan aimed at addressing key environmental challenges such as water management, air quality, waste management, and urban mobility. It includes specific goals and strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote renewable energy, and enhance public spaces while ensuring civic participation and regulatory compliance. The plan is comprehensive, targeting a balance of economic growth and ecological preservation through various initiatives and the involvement of multiple government agencies.