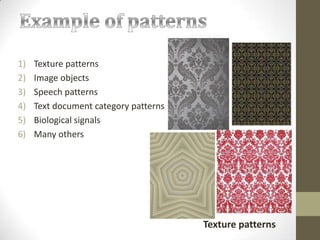
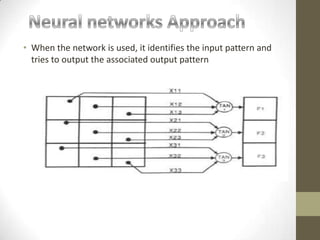
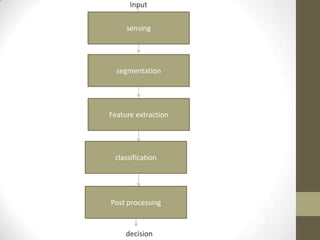
This document defines and describes pattern recognition. It discusses what patterns are, pattern recognition systems, the pattern recognition procedure, approaches to pattern recognition including statistical, syntactic/structural, and neural network approaches. It also covers the components of a pattern recognition system including sensing, segmentation/grouping, feature extraction, classification, and post-processing. Finally, it discusses the design cycle for pattern recognition systems including data collection, feature/model choice, training, evaluation, and computational complexity.