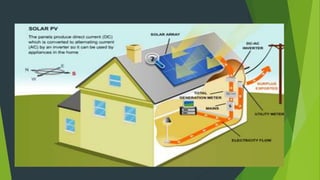
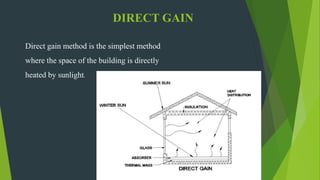
This document discusses passive solar buildings. Passive solar buildings are designed to collect, store, and distribute solar energy for heating and cooling. They use elements like south-facing windows, thermal mass materials, and shading to regulate temperatures. Passive solar design works by allowing sunlight to provide heat in winter while blocking excess heat in summer. It can reduce heating bills by 40% annually and includes different techniques like direct gain, indirect gain, and isolated gain. Examples of successful passive solar buildings are provided from the US and Germany.