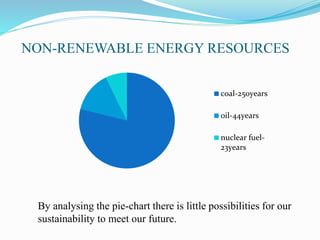
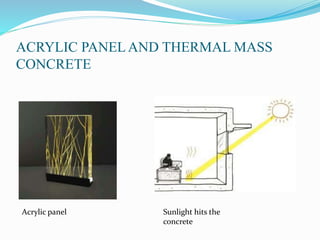
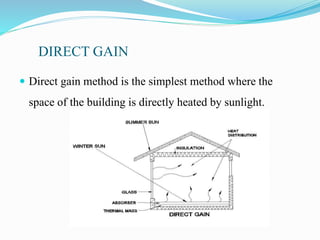
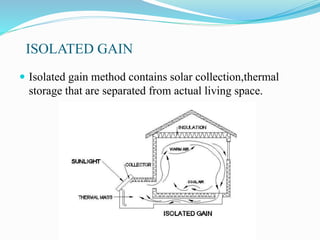
The document discusses passive solar energy as a sustainable method for heating, cooling, and lighting in buildings, emphasizing its cost-effectiveness and reduced reliance on non-renewable resources. It details various methods of passive solar energy collection and the materials required, highlighting advantages such as lower installation costs and eco-friendliness. The conclusion notes the growing importance of passive solar systems for future sustainability and energy efficiency.