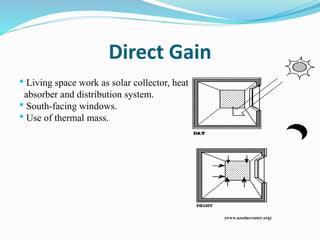
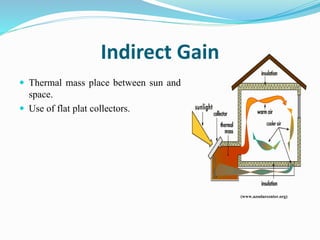
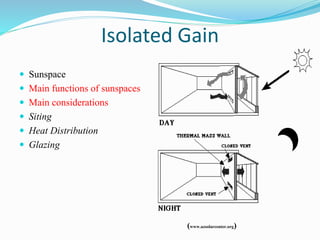
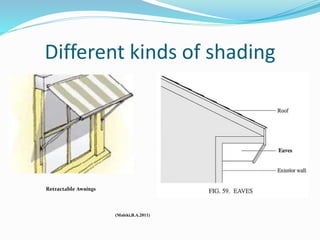
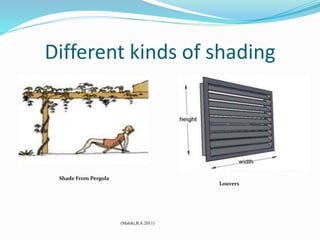
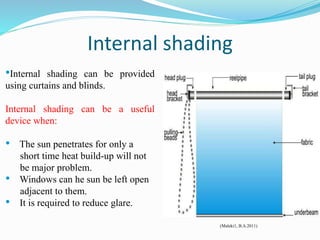
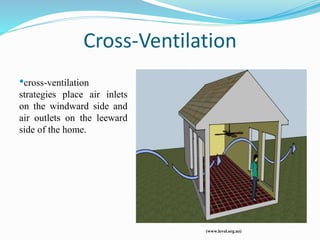
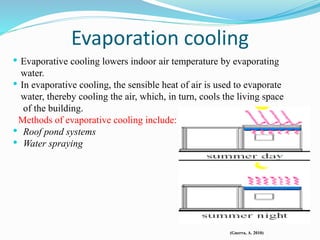
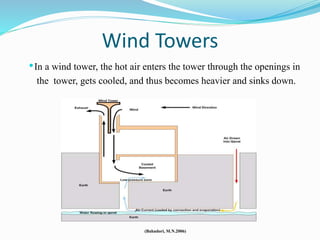
The document discusses passive solar design and its various principles and techniques. It defines passive solar design as using elements like a building's orientation, windows, walls, roof and floors to collect, store and distribute solar energy for heating or cooling without active mechanical systems. It describes different passive solar heating and cooling techniques like direct gain, indirect gain, isolated gain, shading, ventilation, thermal mass, solar chimneys and wind towers. It also provides examples and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of passive solar design.