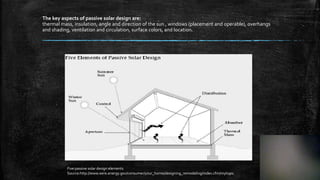
The document discusses key concepts of passive solar design including using thermal mass, insulation, window placement and orientation to maximize solar gain. Passive solar design utilizes natural heating and cooling principles to reduce energy consumption by strategically placing windows on the south side of a building and incorporating materials like concrete or stone with high heat capacity to absorb and store solar heat. Common passive solar design techniques include direct gain, indirect gain and isolated gain systems.








![Thermal Mass and Materials
*The best materials used for
thermalmass will have high heat
capacity and high material density.
Build Green Canada. (August 28, 2015). An explanation of thermal mass [Online].
Available: http://www.buildgreen.ca/2008/09/an-explanation-of-thermal-mass/
Thermal mass is in reference
to material inside a building that can help
reduce the temperature change throughout
the day; reducing the heating and cooling
demand of the building itself.
Materials:
Gypsum
Air
Concrete
Brick
Limestone
Basalt
Dry Sand
Soil
Granite
Wood](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/archtpresentationfinalpresentation-210524044636/85/Passive-Solar-10-320.jpg)





![Citation:
▪ Five passive solar design elements Source:http://www.eere.energy.gov/consumer/ your_home/designing_remodeling/index.cfm/mytopic
▪ Build Green Canada. (August 28, 2015). An explanation of thermal mass [Online]. Available: http://www.buildgreen.ca/2008/09/an-explanation-of-
thermal-mass/
▪ “Southern Facing Windows in Passive Solar Houses: Green Passive Solar Magazine.” Green Passive Solar Magazine | Highlighting the Sustainable,
Renewable and Green Building Technologies of Passive (and Active!) Solar Design, 31 July 2014, greenpassivesolar.com/passive-solar/building-
characteristics/orientation-south-facing-windows.
▪ Five Elements of Passive Solar Home Design, Your Home, Energy Savers. Last updated March 24, 2009. Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy, US
Department of Energy. Accessed October 22, 2009. http://www.energysavers.gov/your_home/designing_remodeling/index.cfm/mytopic=10270
▪ Passive Solar Design. Choices for the Home Construction, Consumer Energy Center, California Energy Commission. Accessed October 22, 2009.
http://www.consumerenergycenter.org/home/construction/solardesign/index.html
▪ Passive Solar Design. Sustainable Sources. (Provides a great introduction to solar design, including "rules of thumb," and many diagrams that illustrate
thermal storage, ventilation and other techniques) Accessed October 22, 2009. http://www.greenbuilder.com/sourcebook/PassiveSol.html
▪ Passive Solar Design – Thermal Mass. Consumer Energy Center, California Energy Commission. Accessed October 22, 2009.
http://www.consumerenergycenter.org/home/construction/solardesign/thermal.html
▪ SolarWall – Specializing in solar heating (solar air heating and ventilation), solar agriculture. Conserval Engineering Inc. Accessed October 22, 2009.
http://www.solarwall.com
▪ “Passive Solar Design.” Sustainable Sources LLC, sustainablesources.com/energy/passive-solar-design/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/archtpresentationfinalpresentation-210524044636/85/Passive-Solar-16-320.jpg)