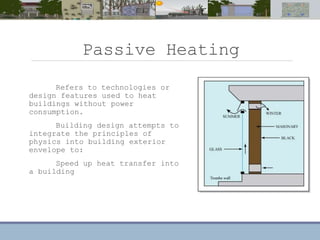
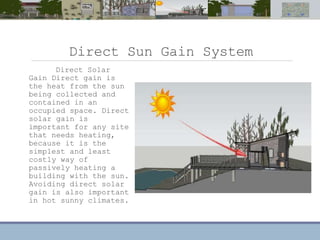
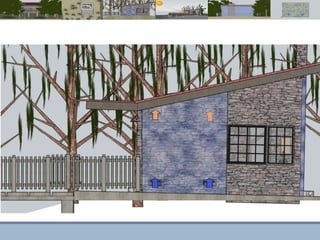
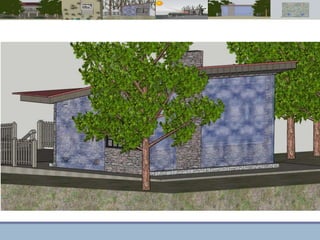
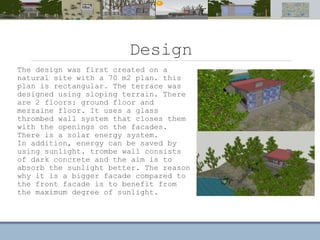
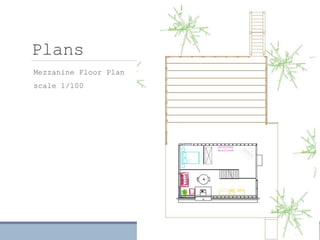
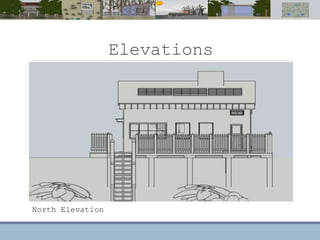
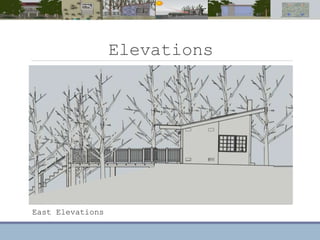
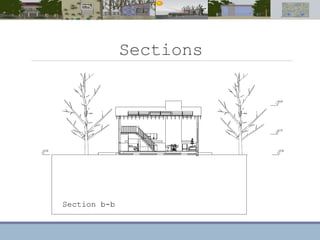
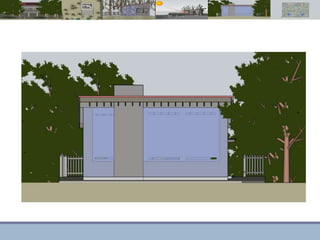
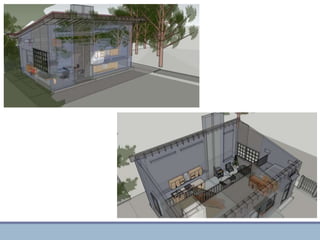
This document discusses passive heating systems for buildings. It describes how 35-40% of energy is used for building heating and 85% of that is for space heating alone. Passive heating technologies are introduced that can heat buildings without energy usage through building design. Direct solar gain and Trombe walls are passive solar systems explained in detail. Trombe walls consist of a dark wall with glazing in front to capture solar heat. Design plans, elevations, sections and details of a sample building project using a Trombe wall system are presented, showing how passive heating is integrated into the design. The conclusion states that passive heating can significantly reduce heating bills and improve comfort through simple techniques.