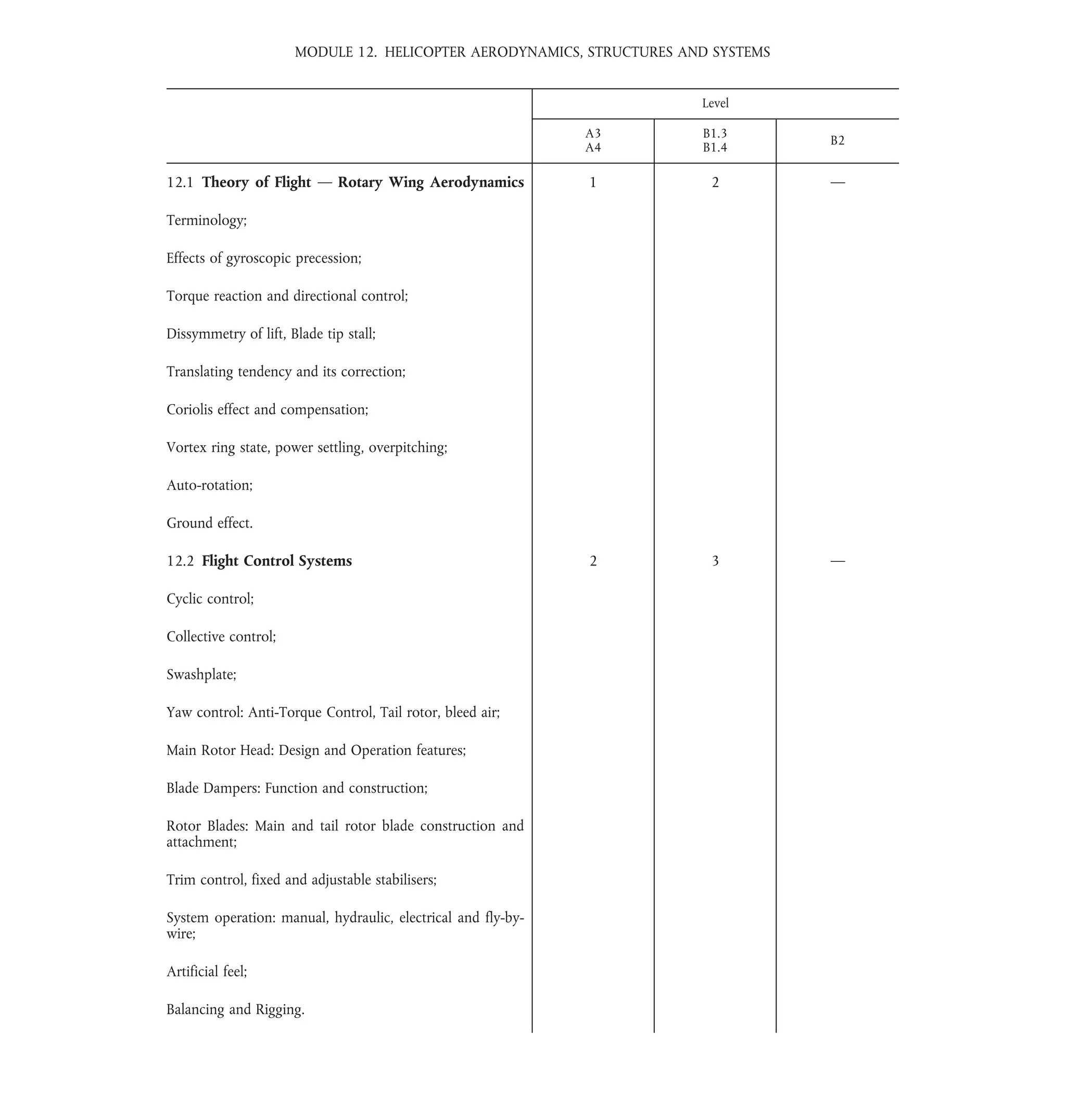
The document outlines various technical aspects of helicopter aerodynamics, structures, and systems, including modules on flight theory, flight control systems, blade tracking, and vibration analysis. It also covers details about airframe structures, air conditioning, electrical systems, equipment, fire protection, fuel systems, hydraulic power, and landing gear. Each section provides information essential for understanding the operational and safety requirements for aircraft systems.