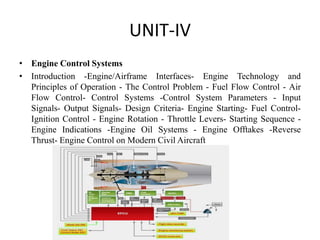
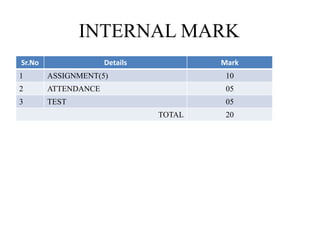
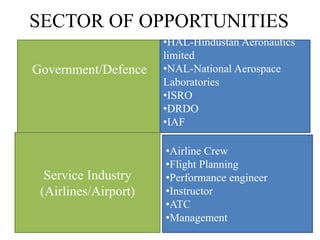
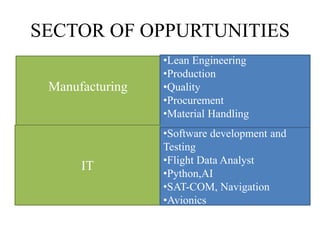
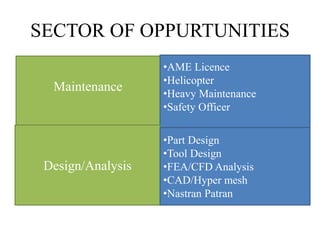
This document provides an overview of an aircraft hydraulic systems course, including prerequisites, outcomes, unit topics, internal marking, and career opportunities. The 6 units cover introduction to aircraft systems and hydraulic principles, flight control systems, electrical systems, engine control systems, fuel systems, and emergency systems. Assessment includes assignments, attendance, and tests. Career paths mentioned include roles in government, manufacturing, airlines, IT, maintenance, design, and entrepreneurship such as UAV development.