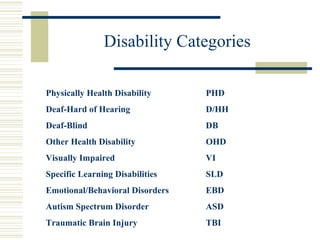
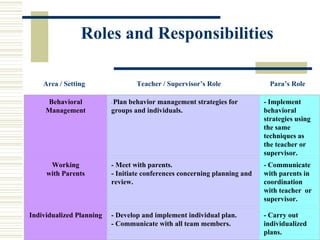
The document serves as an orientation guide for paraprofessionals in public schools, outlining their roles, responsibilities, legal and ethical duties, and the importance of maintaining confidentiality regarding students. It emphasizes the need for proper training, effective communication, and collaboration with educators to support students with disabilities effectively. Additionally, it provides information about mandated reporting laws concerning abuse and neglect as well as strategies for effective teamwork.