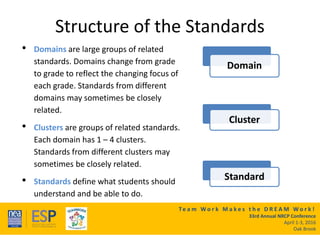
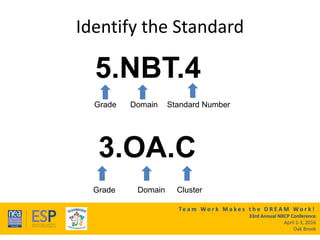
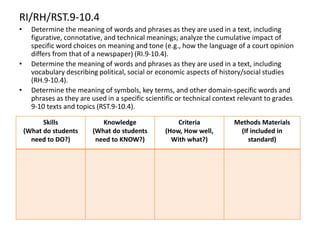
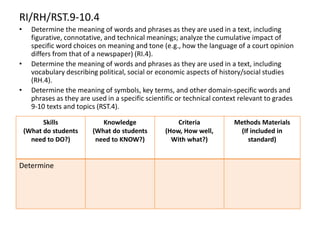
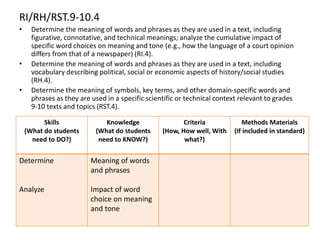
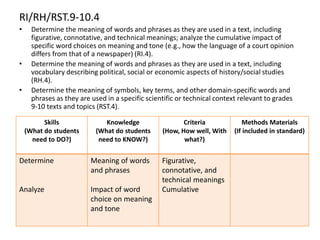
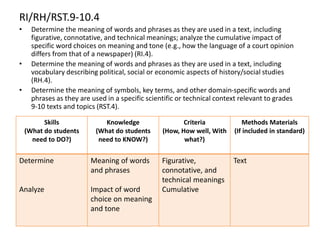
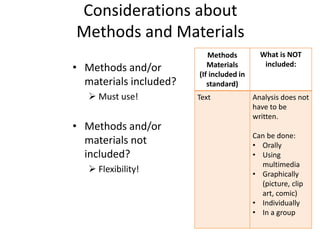
This document outlines a presentation on the Common Core State Standards given at the 33rd Annual NRCP Conference on April 1-3, 2016 in Oak Brook. The presentation provides an overview of the CCSS, including what they are and are not, how they are organized, instructional shifts, and how to unwrap standards. It encourages attendees to select a standard and consider different methods for teaching it to reach all learners. Contact information is provided for follow up questions.