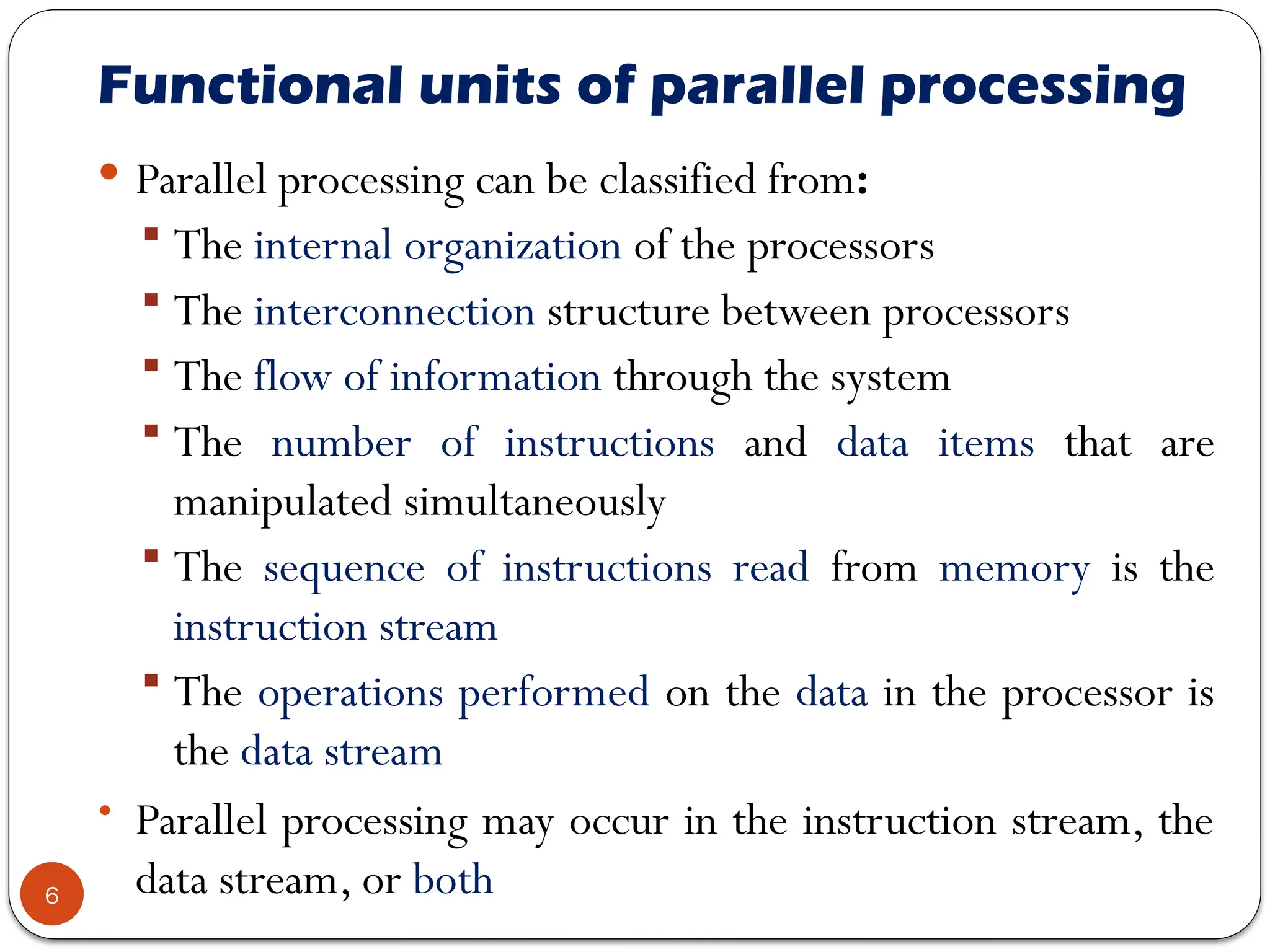
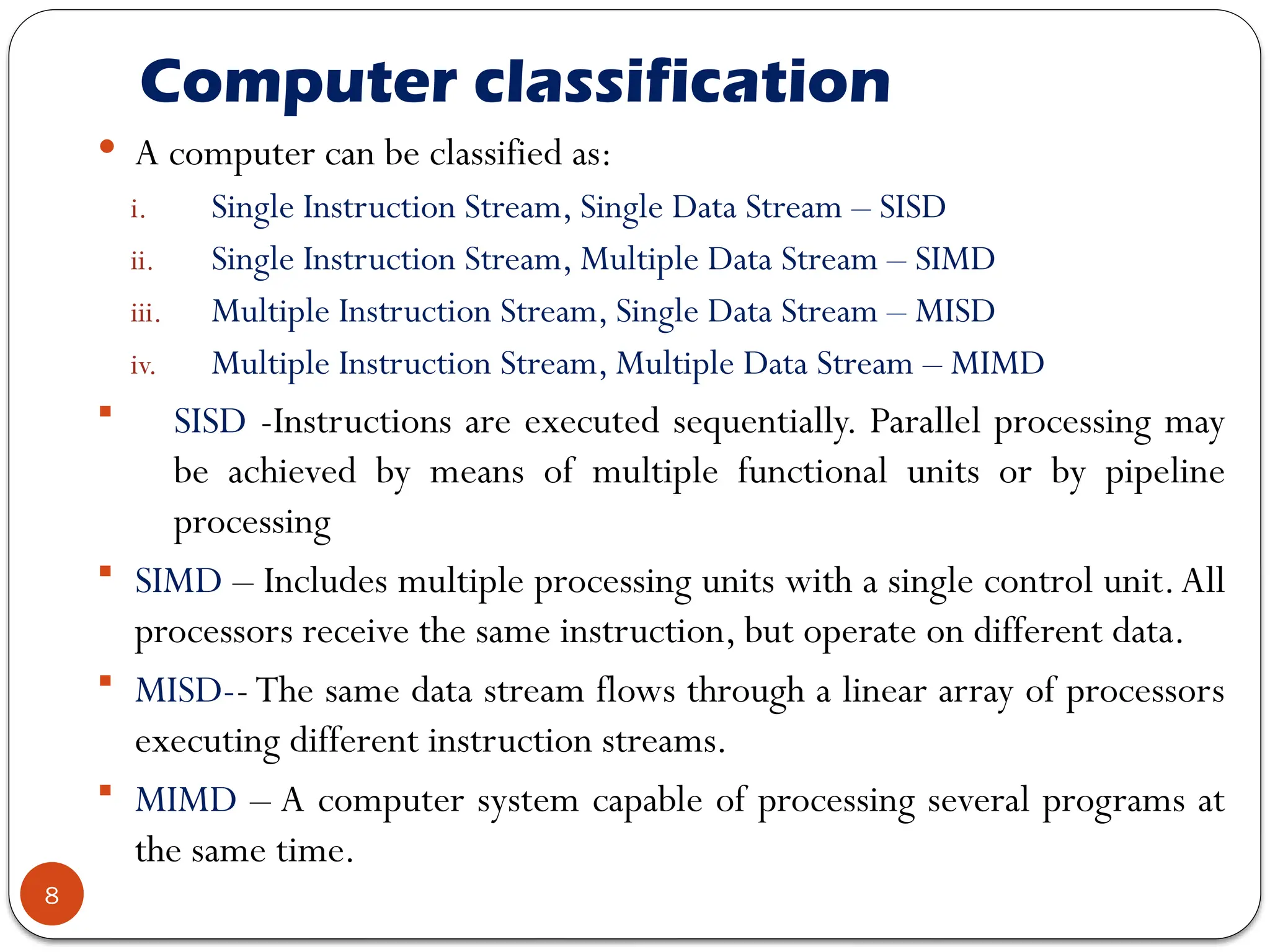
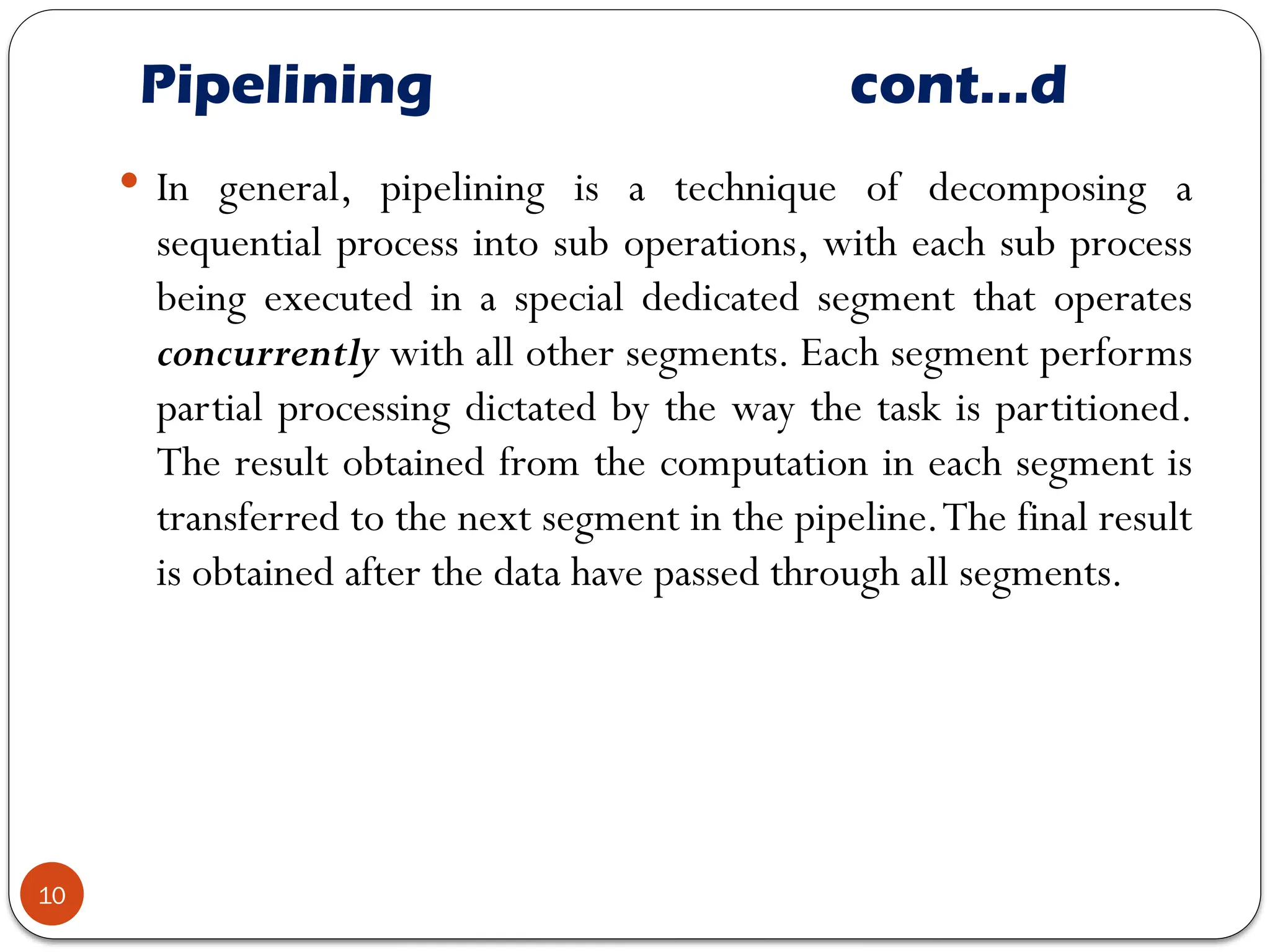
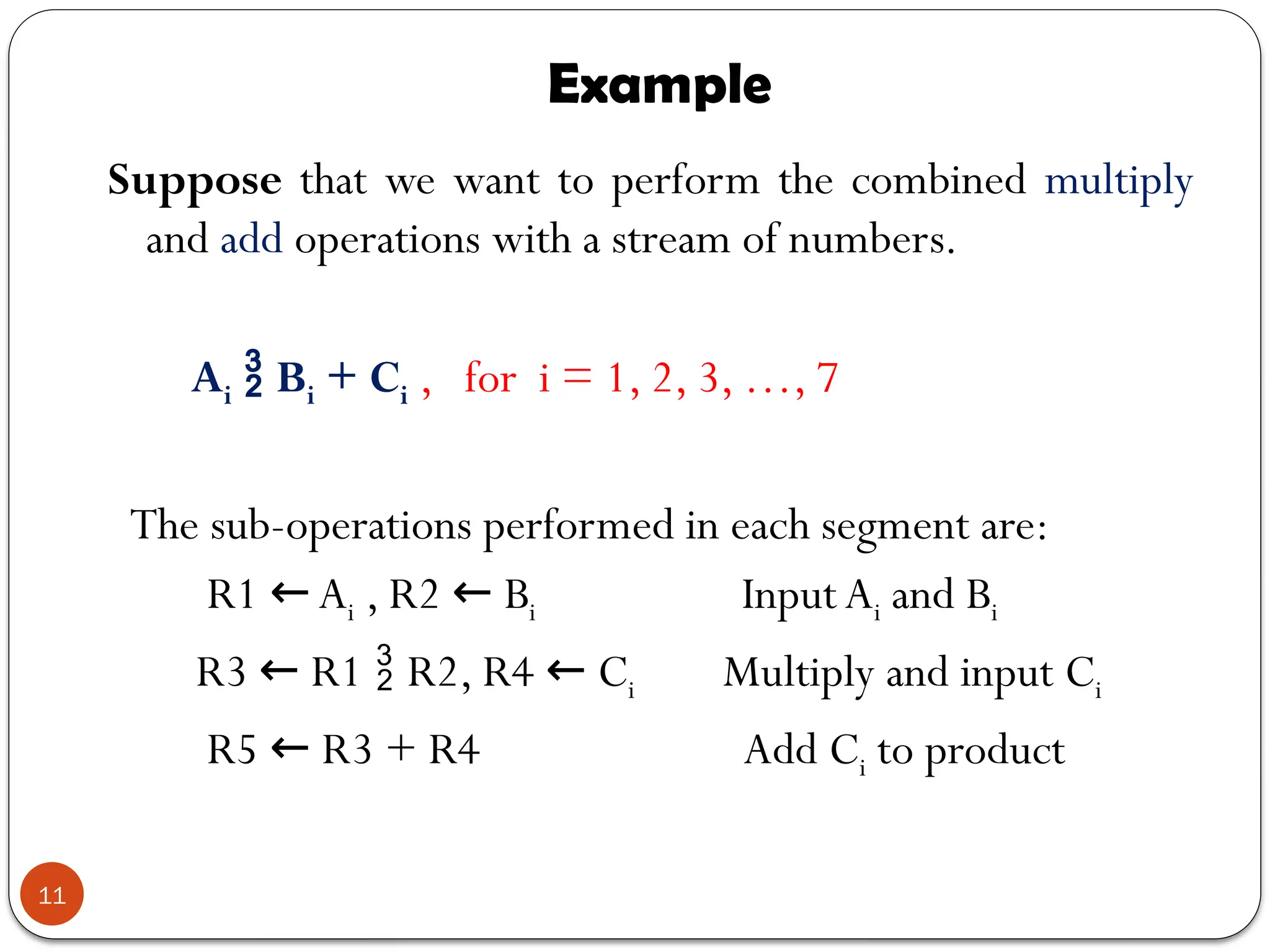
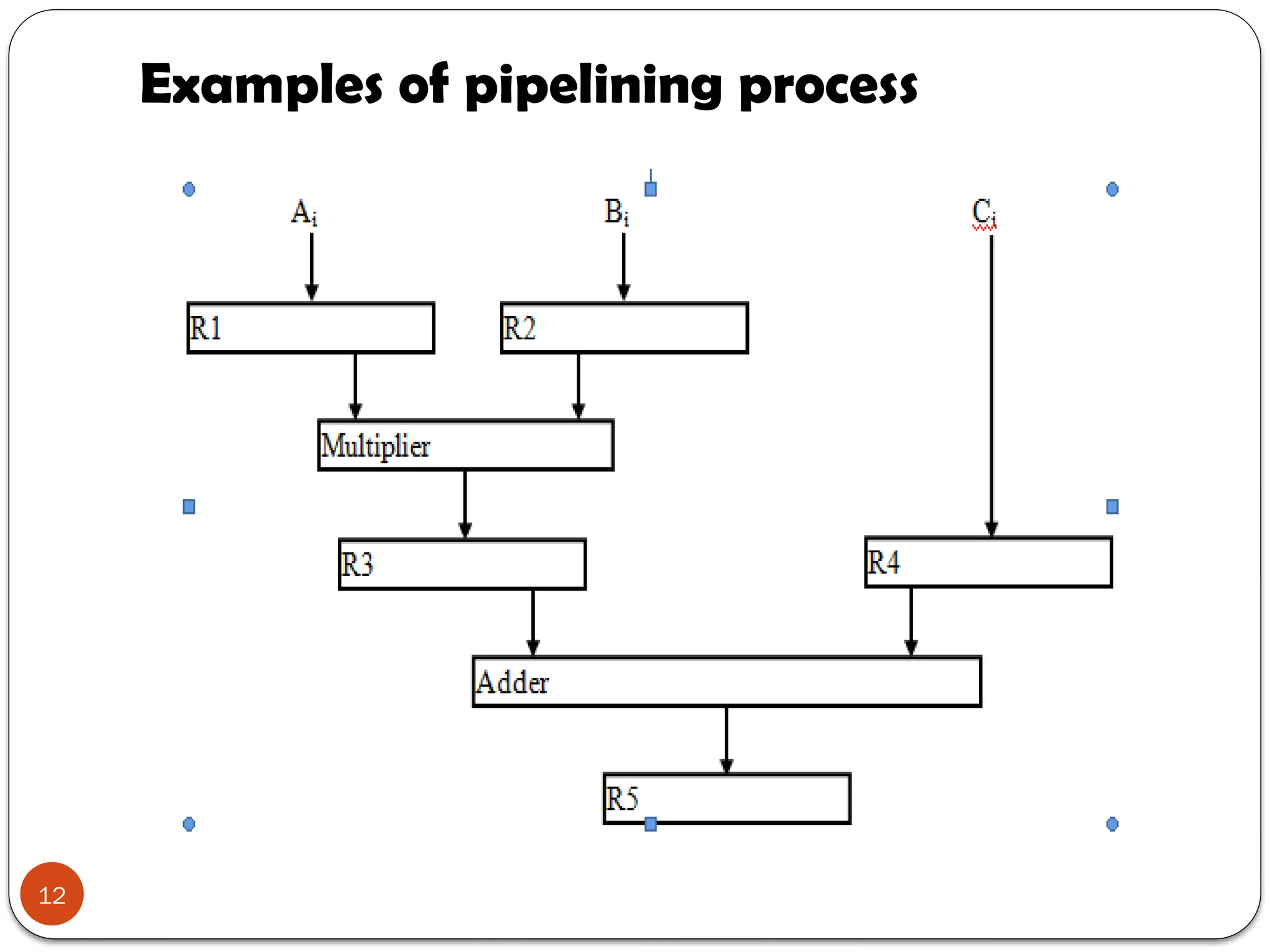
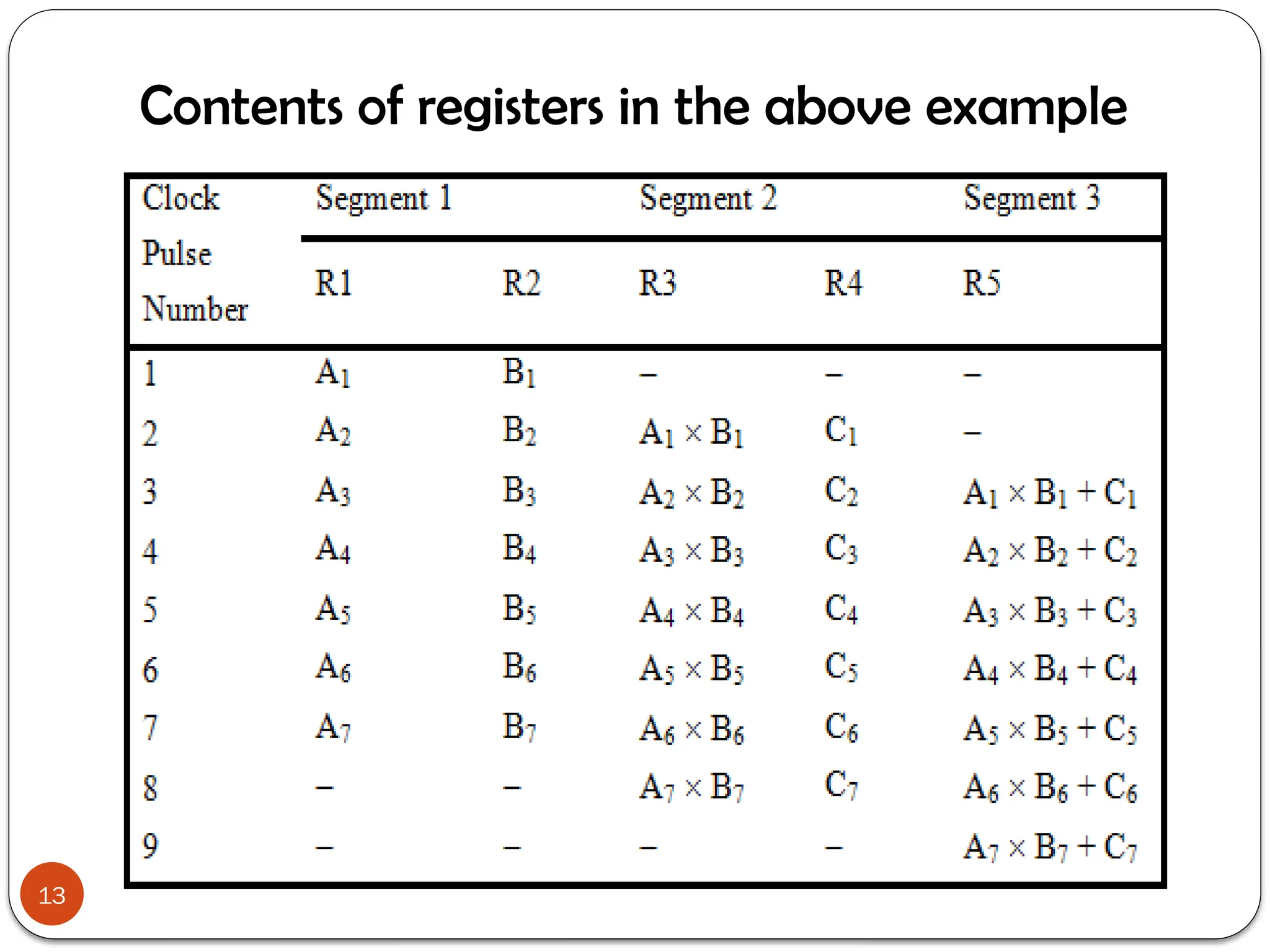
Chapter 7 discusses parallel processing as a method to enhance computer performance by utilizing multiple processors to handle tasks simultaneously. It explains various configurations, including symmetric multiprocessors (SMP) and different instruction/data stream classifications (SISD, SIMD, MISD, MIMD), along with the pipelining technique that overlaps instruction execution to improve efficiency. The chapter emphasizes the importance of dividing large problems into smaller, independent parts that can be processed concurrently.