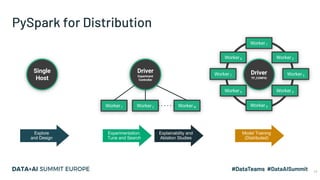
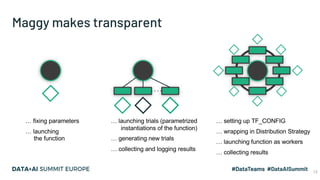
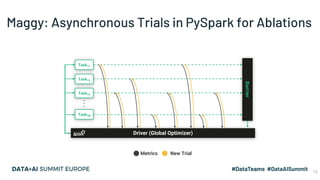
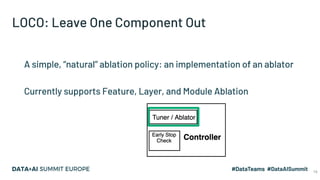
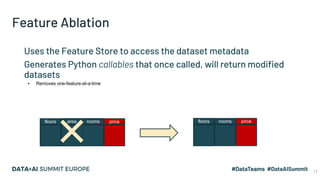
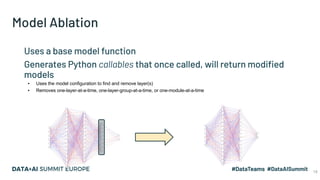
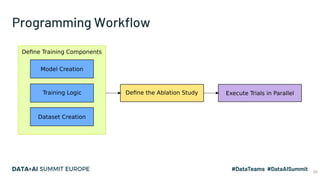
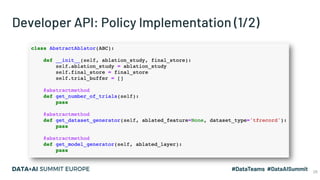
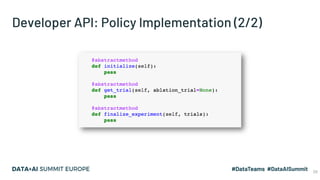
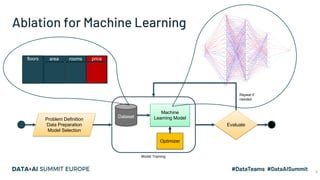
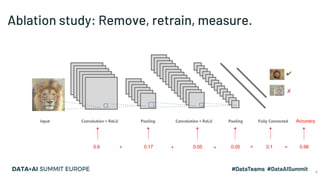
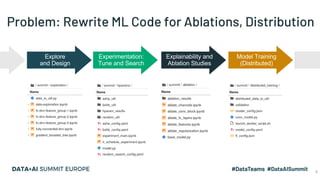
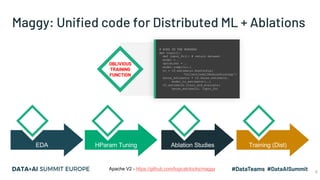
The document discusses the application of parallel ablation studies in machine learning using the Maggy framework on Apache Spark. It highlights the significance of ablation studies for deep learning model optimization and presents methodologies for distributed training and hyperparameter tuning. Additionally, it includes a programming model for Maggy, examples of model and feature ablation, and acknowledges contributions from various collaborators.



![Maggy: Distribution and Tracking in One Function*
# RUNS ON THE WORKERS
def train(depth, lr):
from hops import model as mr
def build_data():
..
model = generate_model()
optimizer = …
model.compile(…)
print(…)
mr.export_model(model)
return { ‘accuracy’: acc }
# RUNS ON THE DRIVER
from maggy import experiment
sp=Searchspace(depth=('INTEGER',[2,8]), lr=(..))
experiment.set_context('optimization', 'random’,
sp, direction='max’, num_trials=15)
experiment.lagom(train)
training function & Hparams
save model to Hopsworks Model Registry
track this dict with Experiment results
print to notebook & store in experiment log
define HParams
launch 15 ‘train’ functions on workers
define Trials
https://youtu.be/xora_4iDcQ8
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/138sheikholeslamidowling-201129185109/85/Parallel-Ablation-Studies-for-Machine-Learning-with-Maggy-on-Apache-Spark-8-320.jpg)
![Maggy vs
*https://www.logicalclocks.com/blog/hopsworks-ml-experiments
def train(depth, weight):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = build_data(..)
...
model.fit(X_train, y_train) # auto-logging
...
hops.export_model(model, "tensorflow",..,model_name)
...
# import matplotlib,create diagram.png
plt.savefig(diagram.png')
return {'accuracy': accuracy, 'diagram': 'diagram.png’}
from maggy import experiment
sp=Searchspace(depth=('INTEGER',[2,8]), weight=('INTEGER’,[2,8]))
experiment.set_context('optimization', 'random’, sp,
direction='max’, num_trials=15)
experiment.lagom(train)
def train(depth, weight):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = build_data(..)
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("jdbc:mysql://uname:pwd@host:3306/db")
mlflow.set_experiment("My Experiment")
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
...
mlflow.log_param("depth", depth)
mlflow.log_param("weight", weight)
with open("test.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("hello world!")
mlflow.log_artifacts("/full/path/to/test.txt")
...
model.fit(X_train, y_train) # auto-logging
...
mlflow.tensorflow.log_model(model, "tensorflow-model",
registered_model_name=model_name)
Maggy Tracking, Model Registry & HParam Tuning MLFlow Tracking & Model Registry (No Hparam Tuning)
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/138sheikholeslamidowling-201129185109/85/Parallel-Ablation-Studies-for-Machine-Learning-with-Maggy-on-Apache-Spark-9-320.jpg)