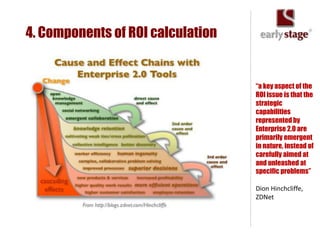
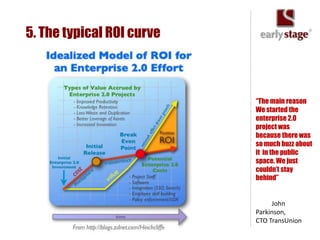
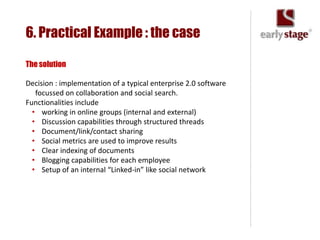
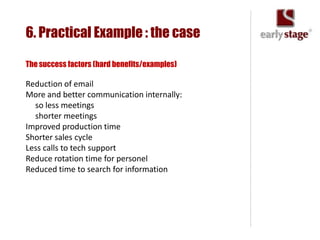
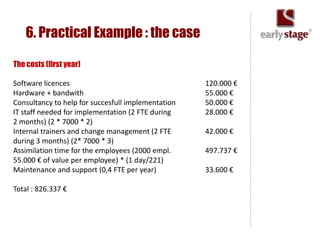
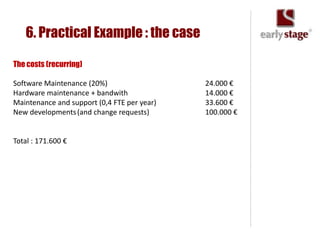
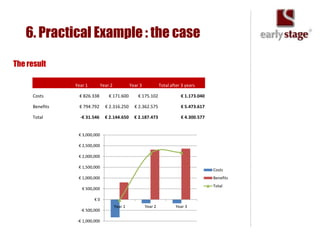
The document discusses the calculation of ROI for collaboration tools in enterprise settings, outlining the importance of understanding benefits and challenges associated with Enterprise 2.0 projects. It includes specific components for ROI calculation, provides a practical example of an enterprise implementation, and highlights both hard and soft benefits derived from improved collaboration. Additionally, it touches on the value of professional contacts, estimating that an average email contact is worth $948 in revenue.