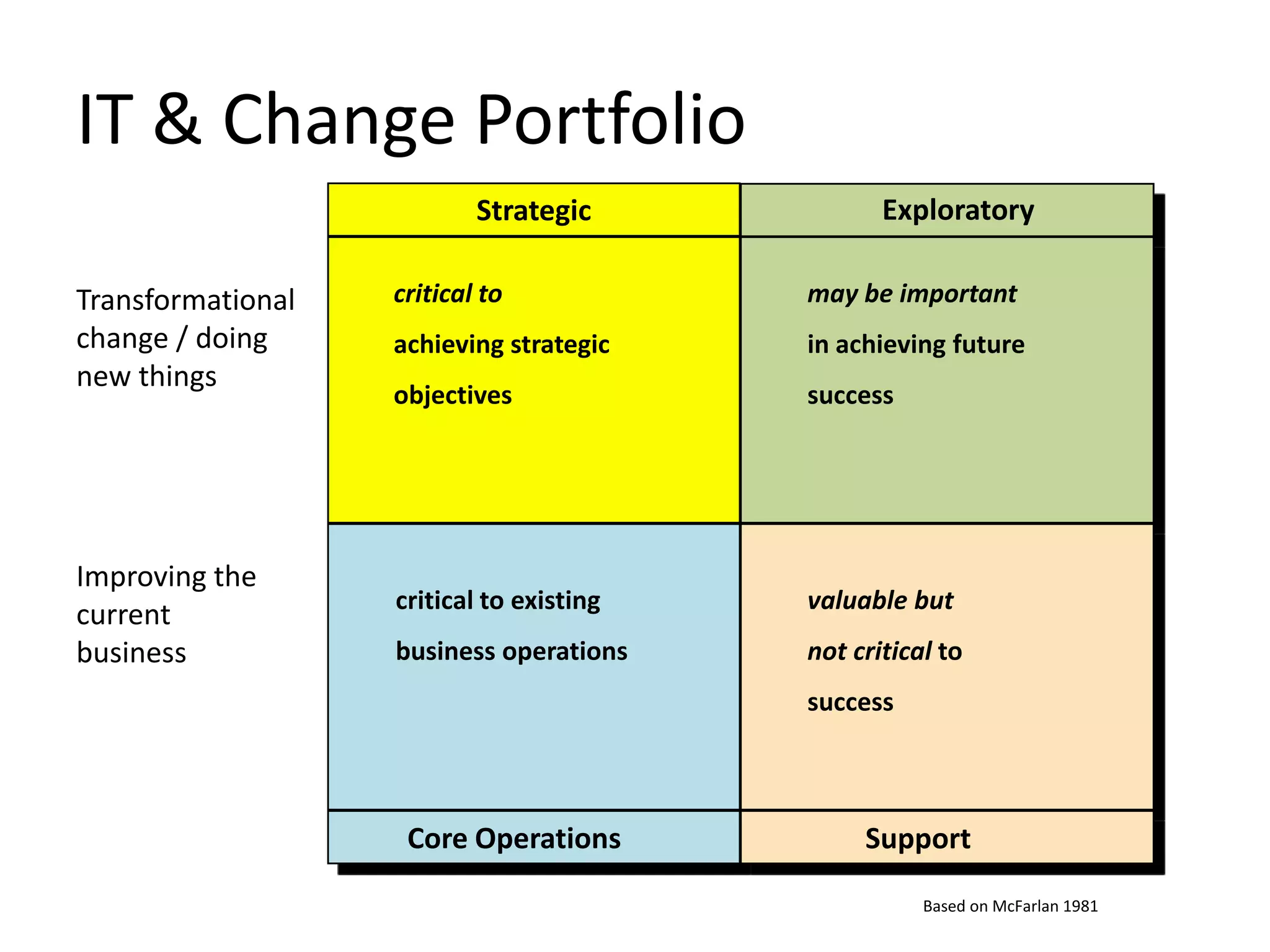
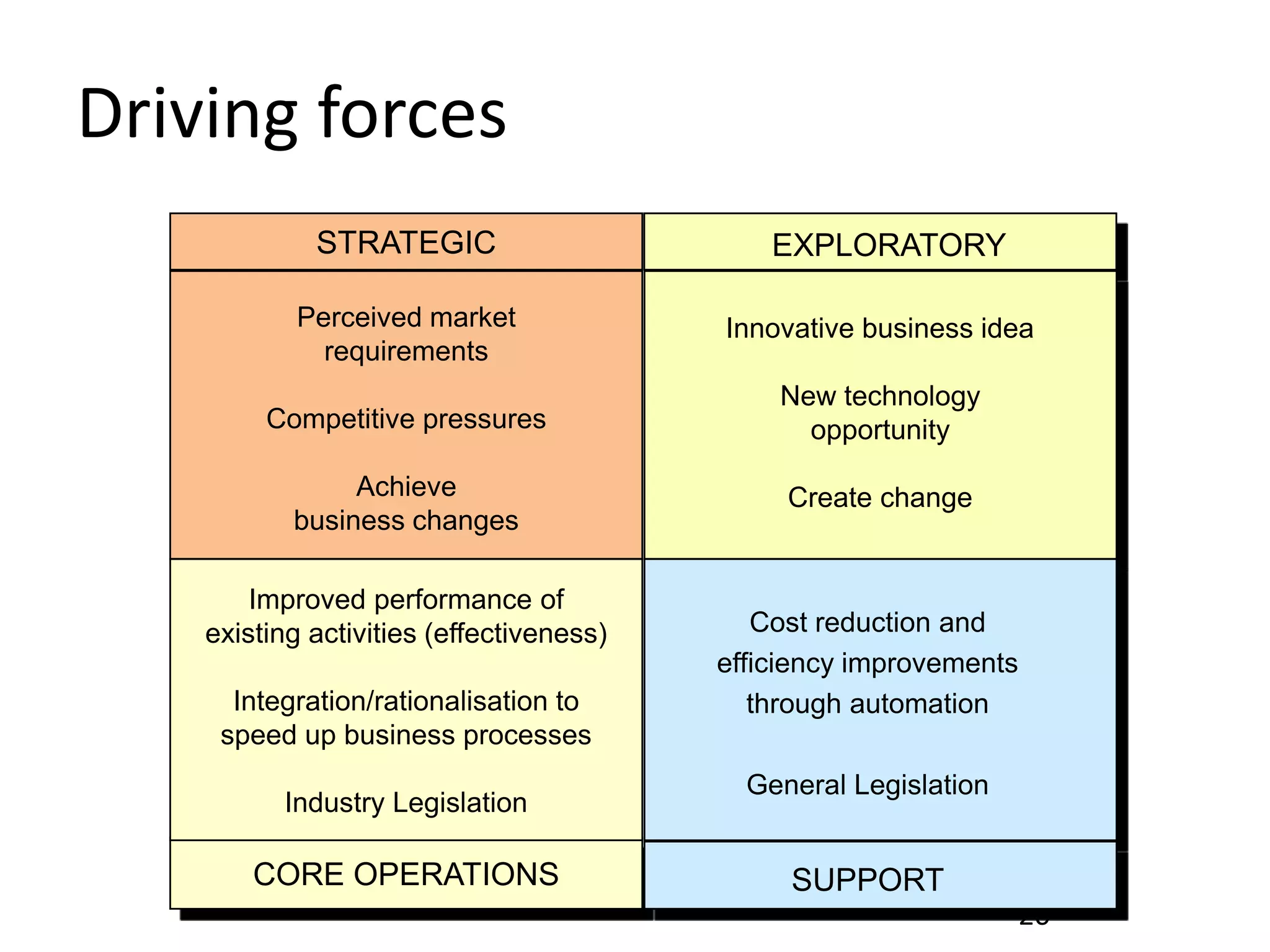
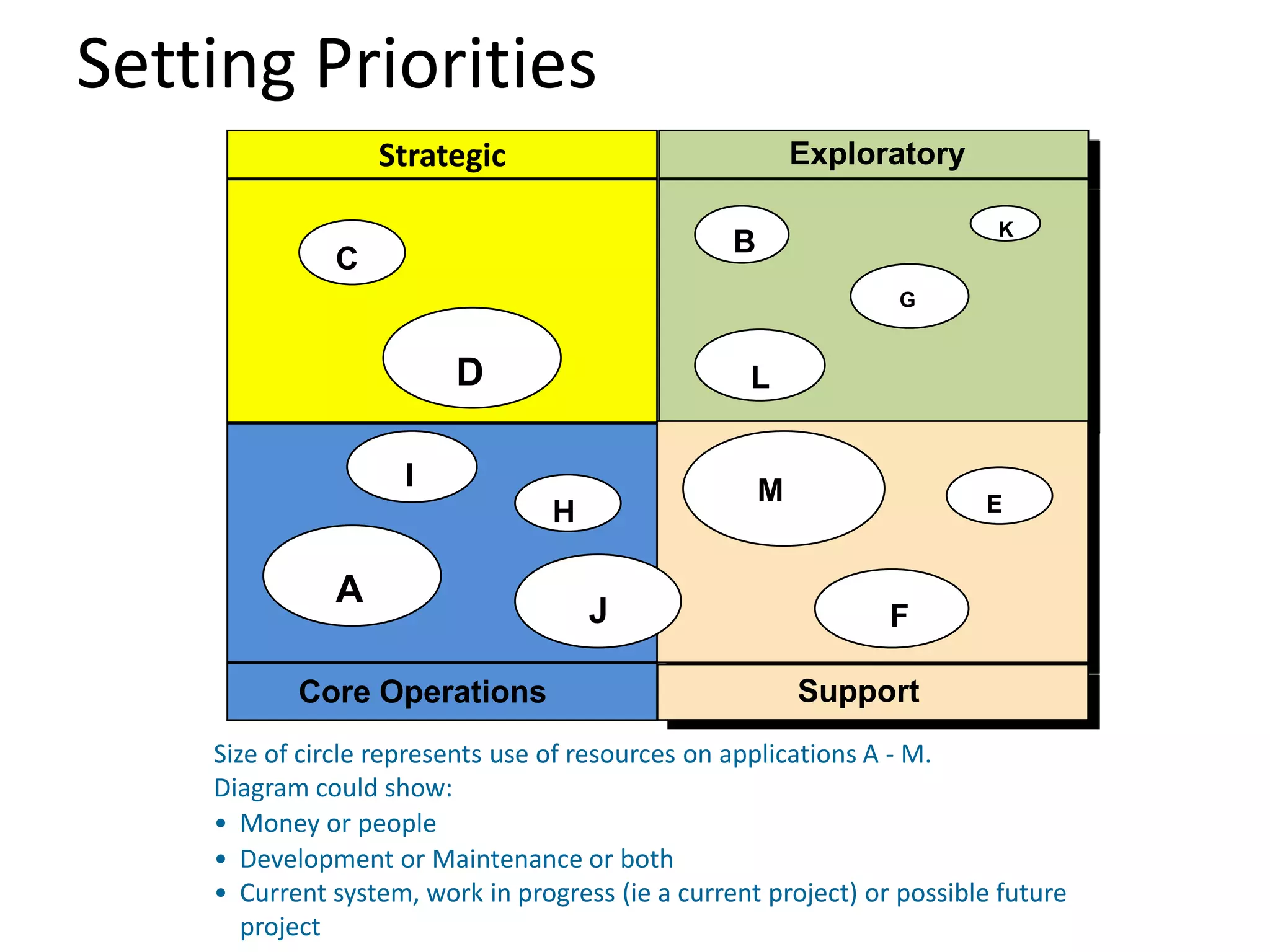
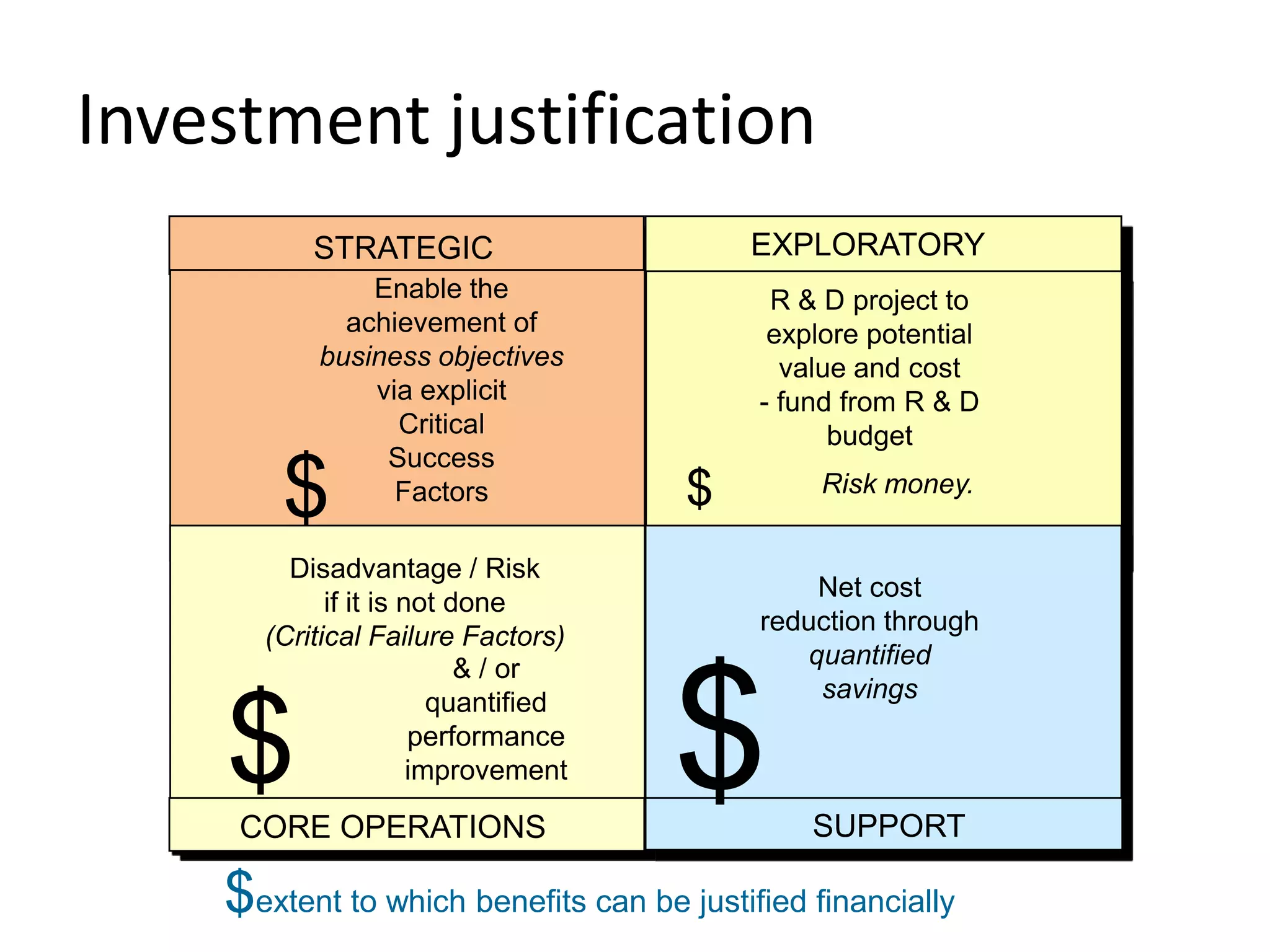
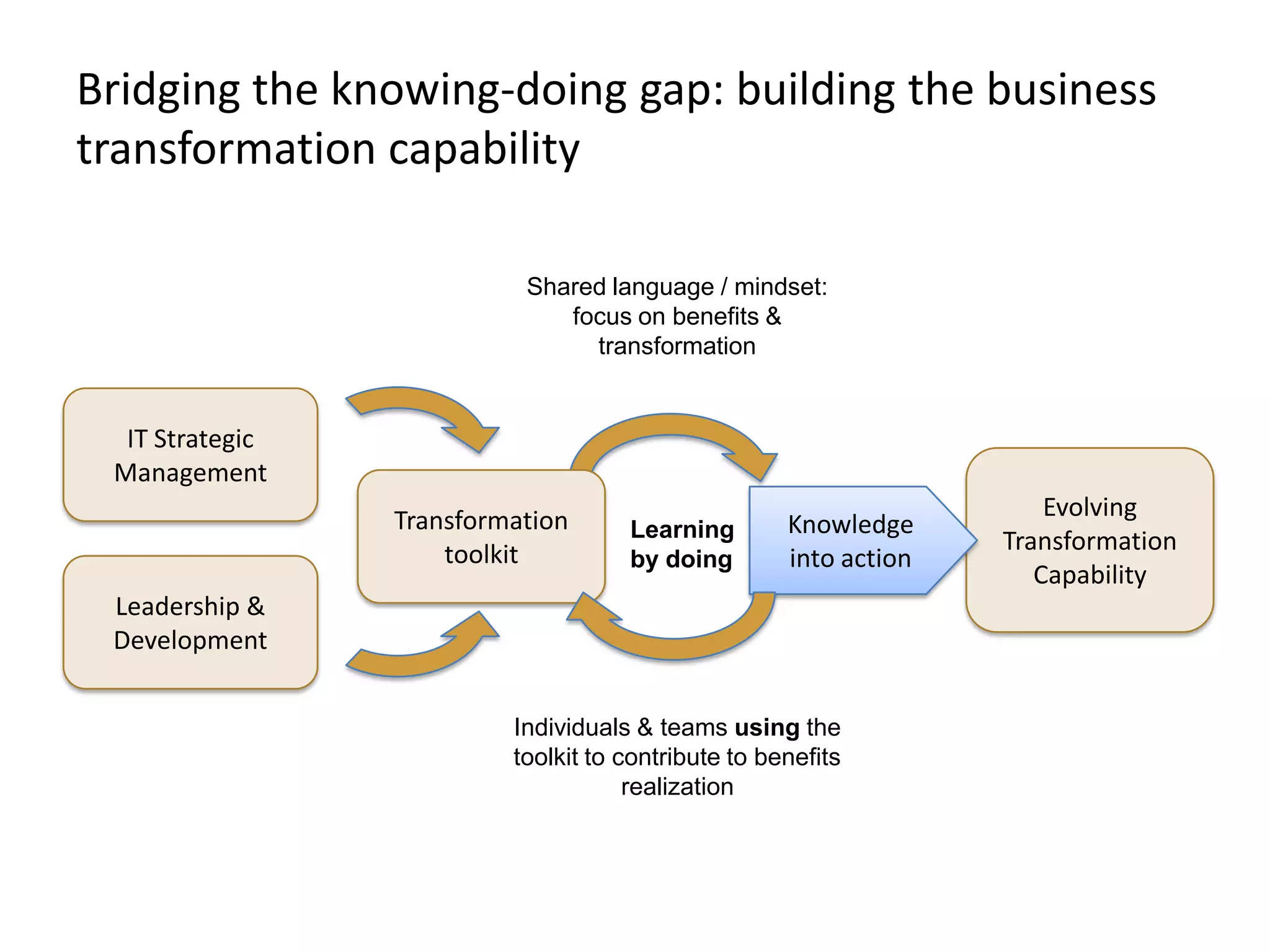
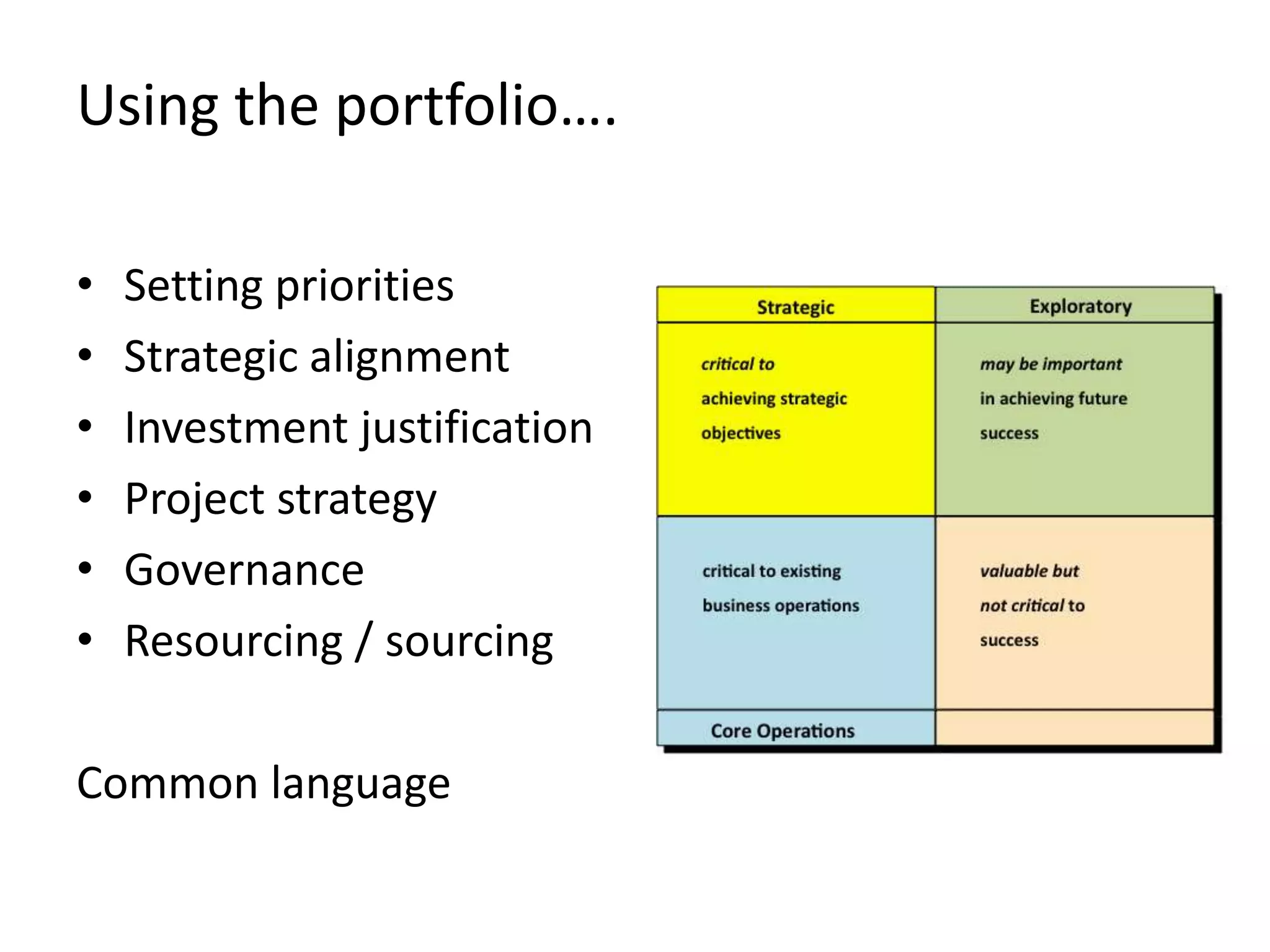
The document discusses challenges and opportunities for successful innovation through the use of information systems and technology, providing examples of how organizations have maximized their innovation investments, expertise, and data through various initiatives. It also examines factors that contribute to successful innovation, such as clear sponsorship, diversity, engagement, and alignment of IT and business strategies. The document advocates using a portfolio approach to assess opportunities and prioritize initiatives to improve realization of benefits from innovation investments.