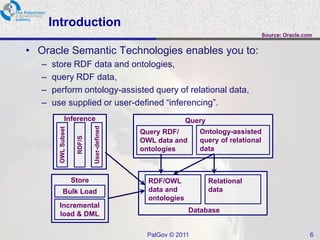
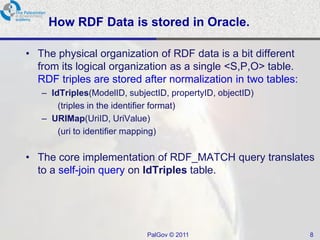
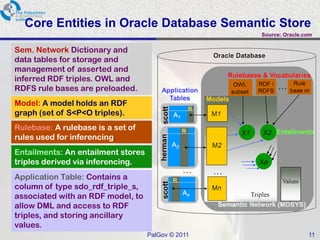
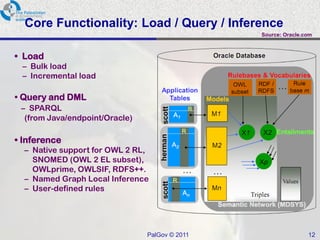
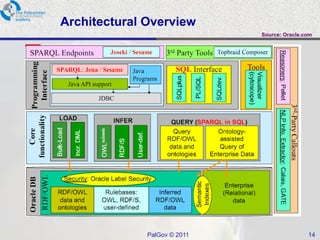
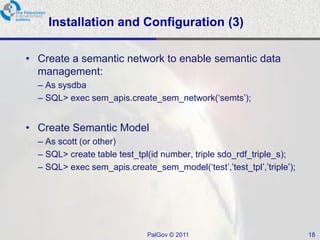
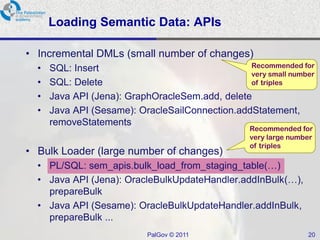
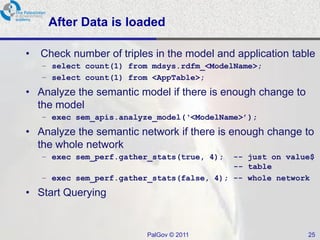
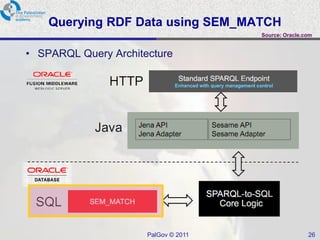
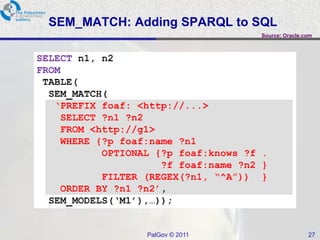
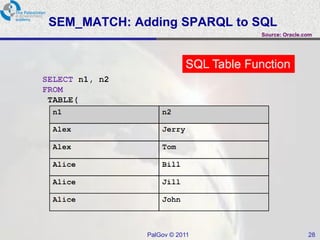
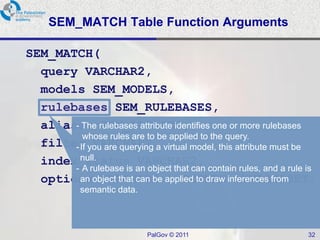
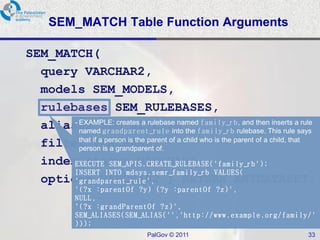
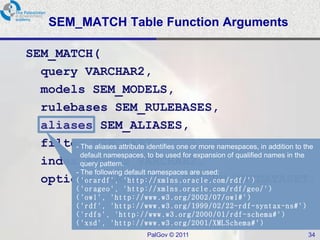
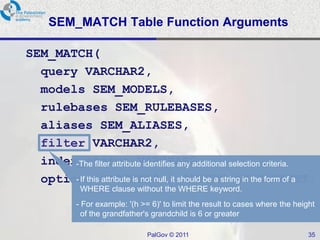
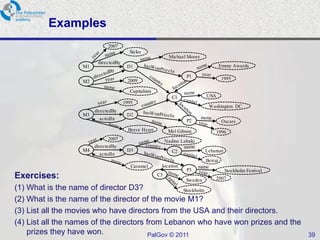
The document discusses Oracle Semantic Technologies for storing and querying RDF data. It provides an overview of how RDF data is stored and organized in Oracle databases using ID triples and URI mapping tables. It describes how the SEM_MATCH SQL function allows querying RDF data using a SPARQL-like syntax. Optimization techniques for SEM_MATCH queries include indexes and materialized views. The core entities in the Oracle Semantic Store include semantic networks, models, rulebases, and entailments. Functionality includes bulk loading, incremental loading, SPARQL querying, and built-in or user-defined inference rules.