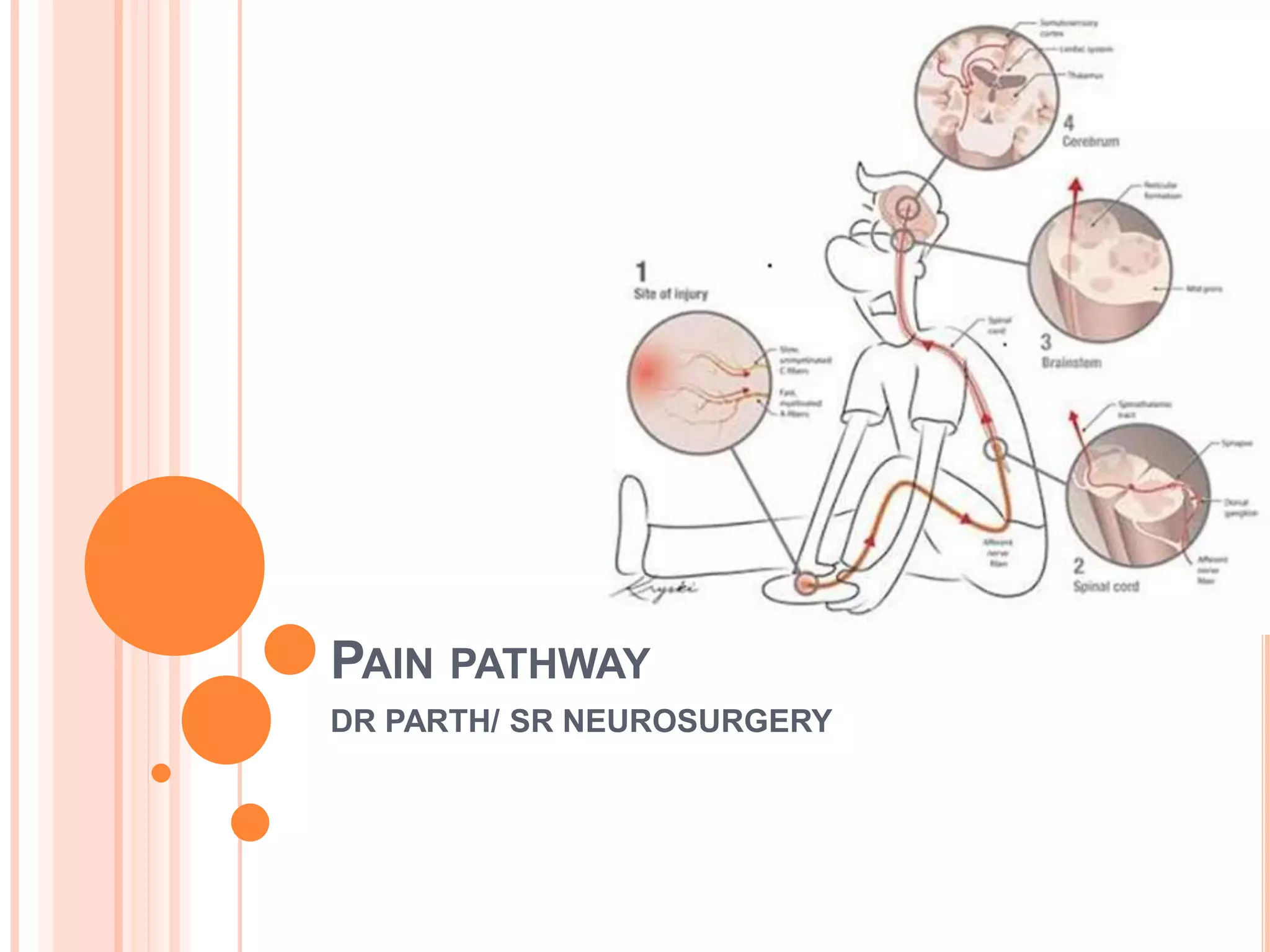
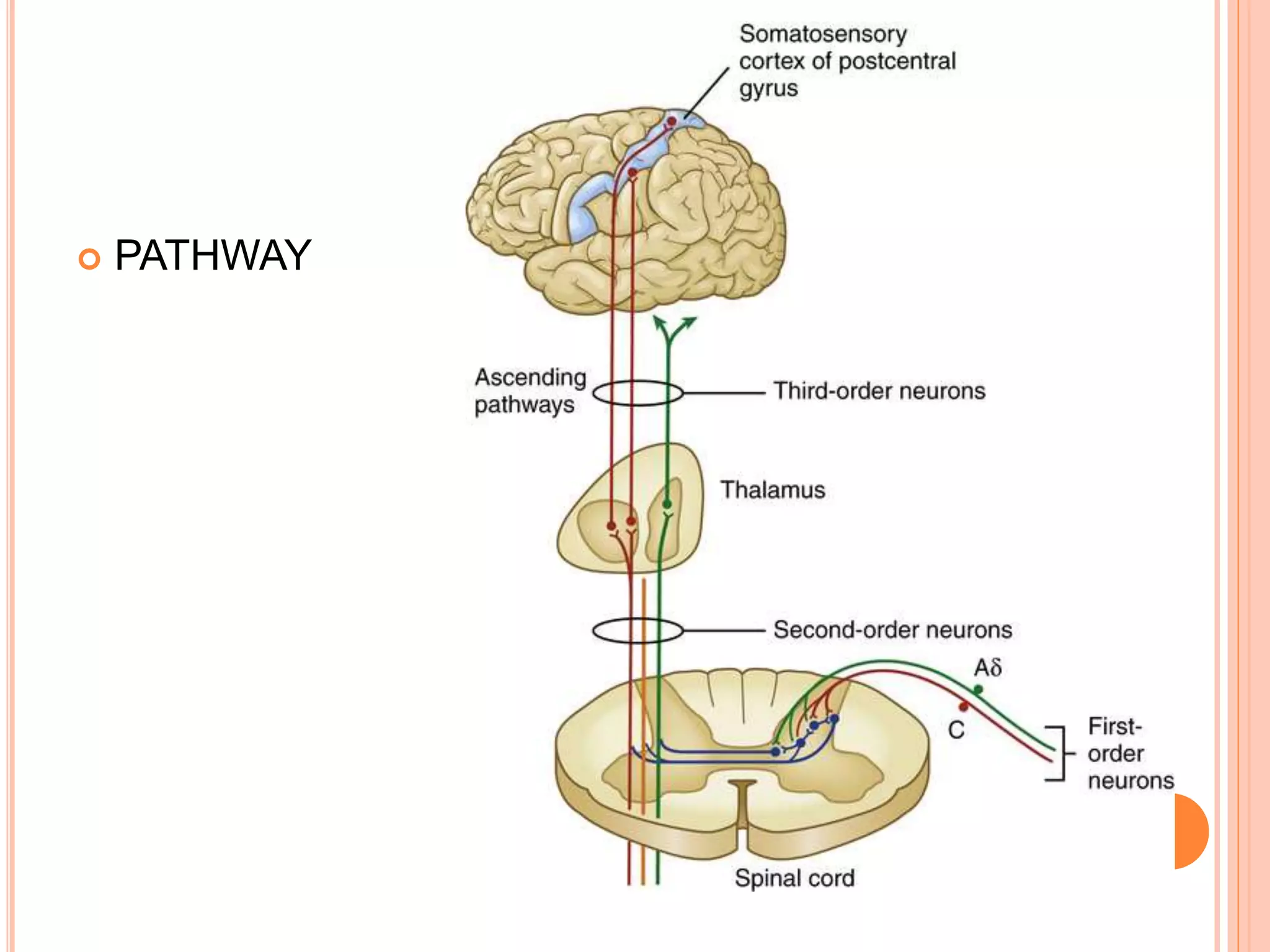
The document provides an overview of pain pathways and mechanisms, categorizing pain into nociceptive, inflammatory, and neuropathic types. It describes the roles of various neurons and pathways in processing pain, including first, second, and third-order neurons, as well as different central structures involved in the pain matrix. Additionally, it addresses the clinical implications of these pathways and highlights craniofacial pain syndromes.