The document discusses pain pathways and pain receptors. It can be summarized as:
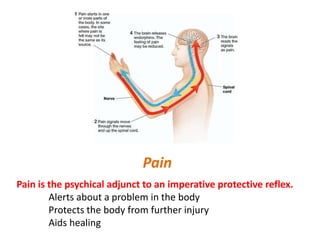
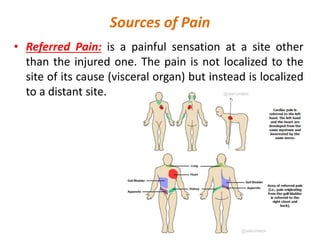
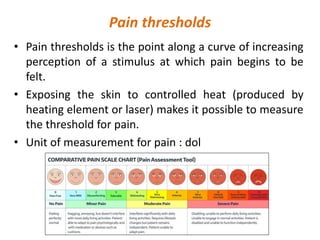
Pain serves an important protective function and alerts the body to potential damage. Pain is transmitted through three main pathways - neospinothalamic, paleospinothalamic, and archispinothalamic - to different regions of the brain. Nociceptors, the sensory receptors that detect pain, contain various receptors that respond to tissue damage or threat of damage. Nociceptor activation initiates action potentials that signal pain.