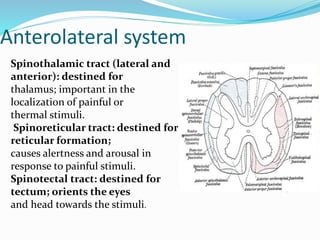
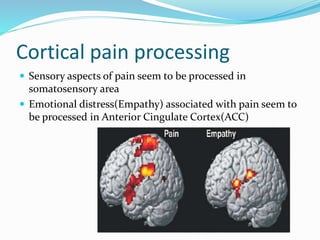
The document provides an overview of pain pathways and physiology. It discusses:
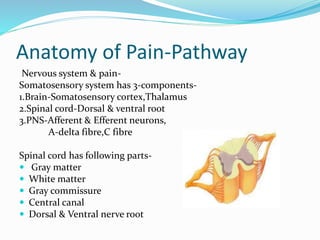
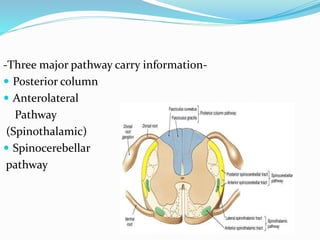
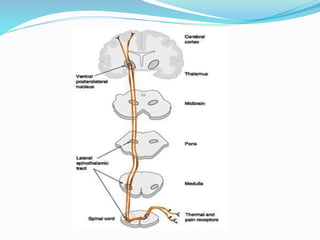
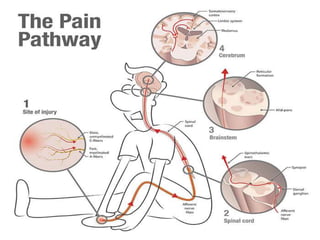
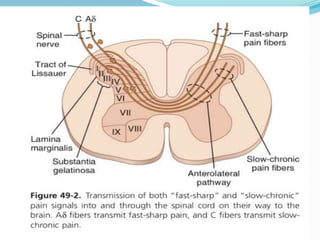
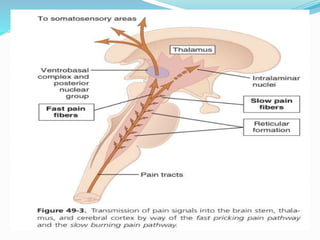
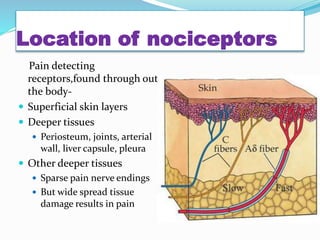
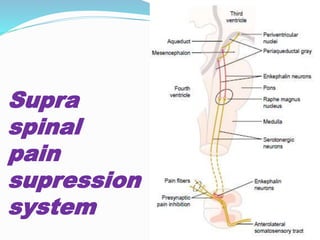
- The anatomy of pain pathways in the nervous system and spinal cord.
- The types of nerve fibers (A-delta and C fibers) that transmit pain signals and their characteristics.
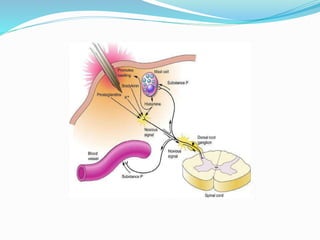
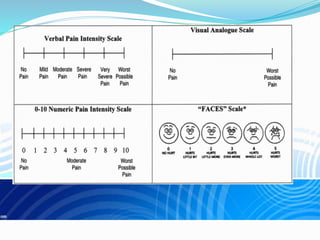
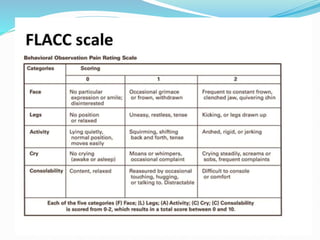
- The process of pain perception, transmission, and modulation within the nervous system.
- Different types of pain (nociceptive, neuropathic, acute, chronic) and clinical pain syndromes.
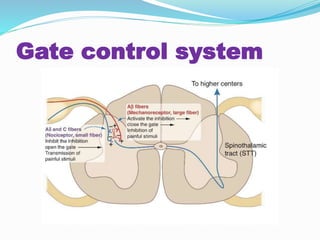
- The gate control theory of pain modulation in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.
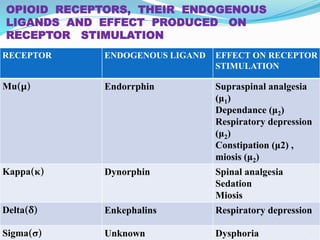
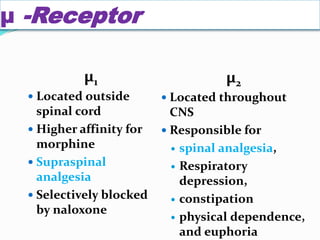
- The roles of various opioid receptors (mu, kappa, delta) in mediating analgesia and side effects.