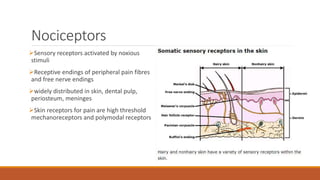
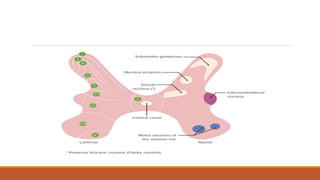
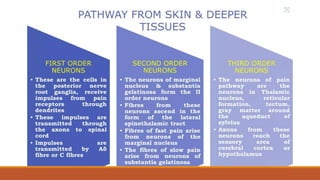
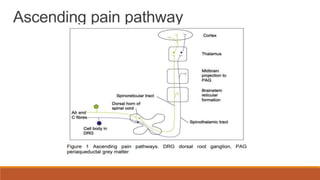
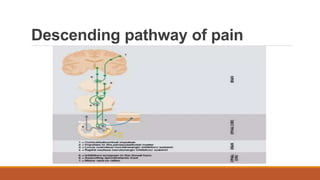
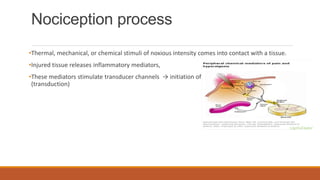
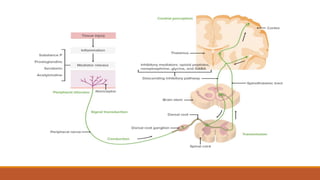
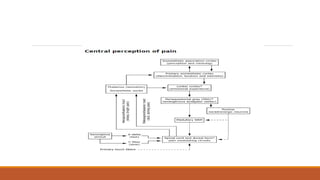
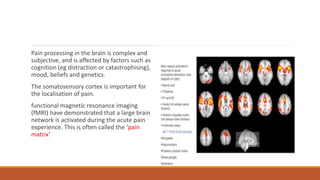
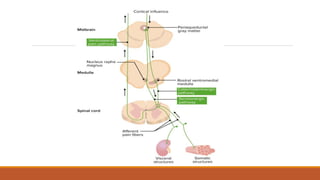
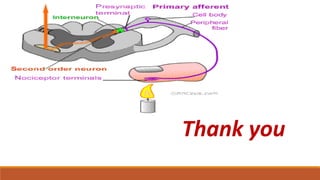
I. Pain pathways involve nociceptors detecting damaging stimuli and transmitting signals along primary afferent neurons to the dorsal horn. Signals then project up the spinal cord and through ascending tracts to various brain regions for processing. Descending pathways from the brain modulate pain transmission.
II. The document outlines the history of pain theories, definitions of pain terminology, embryological development of pain pathways, types of pain, and components of the pain pathway including nociceptors, neurons, and brain regions involved in perception.
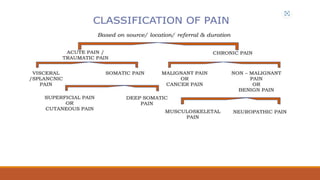
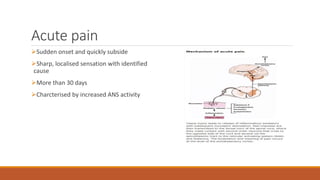
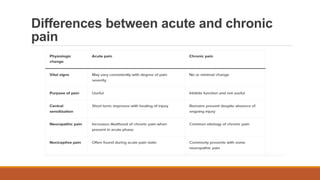
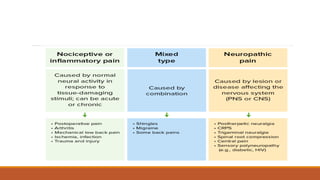
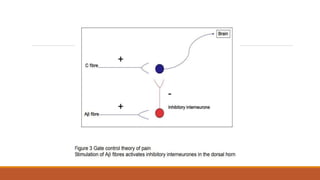
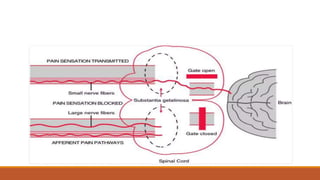
III. Key aspects of acute and chronic pain are distinguished. The gate control theory proposes that non-painful stimuli can inhibit pain transmission at the dorsal horn. Overall the document provides a comprehensive overview of