The olfactory nerve is responsible for smell detection. It contains bipolar sensory neurons whose receptors are located in the nasal cavity. The nerve fibers penetrate the cribriform plate and synapse in the olfactory bulb. Secondary fibers from the bulb project to areas involved in smell perception and integration like the piriform cortex and amygdala. Common causes of smell disorders include upper respiratory infections, head injuries, nasal/sinus diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. Lesions in different areas can cause unilateral or bilateral smell loss or distortions.










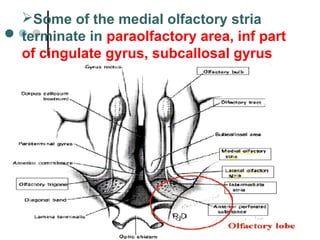







![• This in turn project to the thalamus,
cingulate gyrus,striatum and
mesencephalic reticular formation]
• Olfaction is the only sensation not
directly processed in the thalamus
• Connection with the superior and
inferior salivatory nucleus is important
in reflex salivation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1olf-150522055351-lva1-app6892/85/olfactory-nerve-19-320.jpg)




















