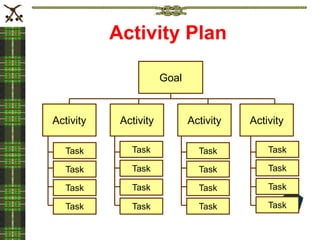
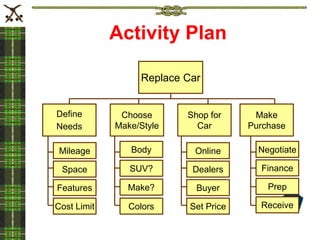
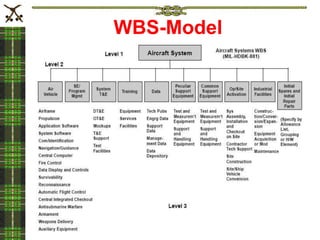
The document discusses the importance of project planning and describes the five stages of project planning: 1) Develop a project overview to define goals, objectives, approach and risks. 2) Plan the work by creating an activity plan that organizes and prioritizes tasks. 3) Make activity assignments by allocating tasks to team members. 4) Put the plan into action and track progress. 5) Prepare a closeout report to review lessons learned. Effective project planning is critical to project success by clarifying the scope and ensuring all necessary tasks are completed on schedule.