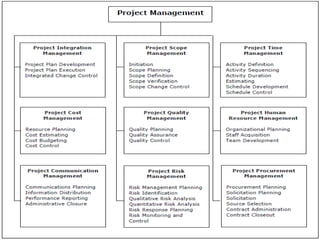
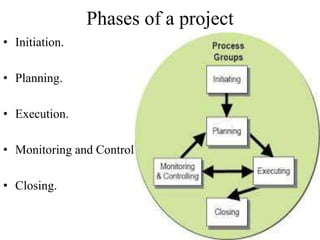
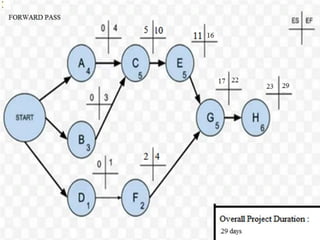
Project management involves planning, executing, monitoring, and closing a project to achieve objectives on schedule and within budget. It utilizes techniques like work breakdown structure, critical path method, Gantt charts, and PERT charts to define tasks, durations, dependencies, and calculate schedules. The triple constraints of scope, time, and cost must be balanced throughout the project phases of initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closing.