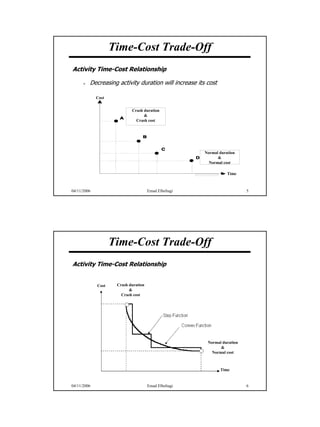
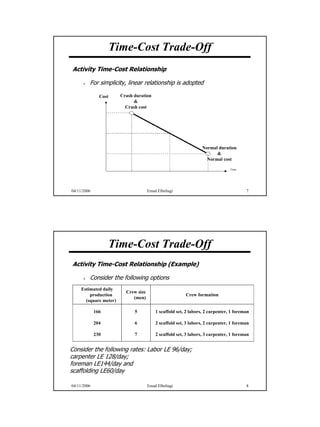
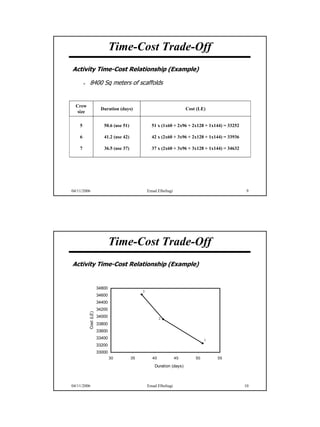
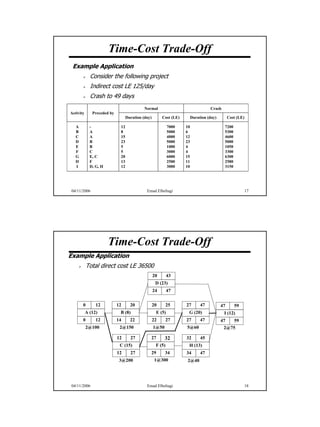
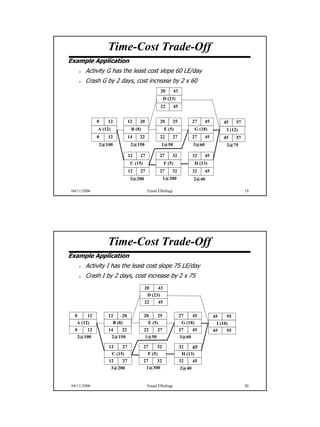
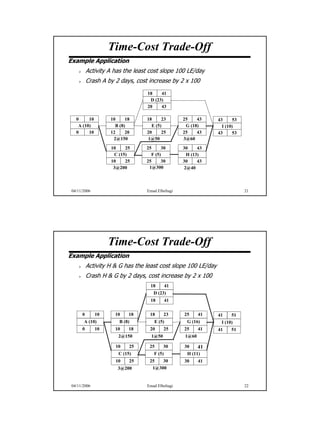
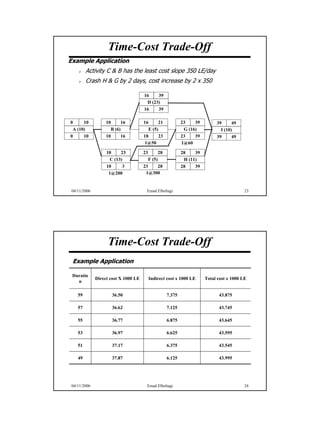
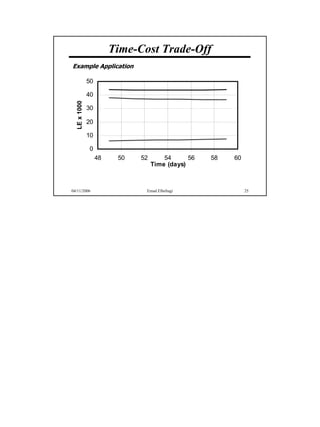
The document discusses the relationship between time and cost for activities and projects. It explains that reducing the duration of an activity typically increases its cost in a linear relationship. For projects, reducing the overall duration lowers indirect costs but raises direct costs due to crashing activities. An example demonstrates calculating optimal project duration that results in lowest total cost by shortening critical path activities based on their cost slopes.